Use of hormones and nutritional supplements among gyms' attendees in Riyadh
- PMID: 28163569
- PMCID: PMC5248439
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8229.197175
Use of hormones and nutritional supplements among gyms' attendees in Riyadh
Abstract
Background: Worldwide, studies have shown a high prevalence of hormones and nutritional supplement use by athletes and gym members. Many athletes consume unproven, potentially harmful or even banned supplements.
Objectives: To assess the prevalence of the use of hormones and nutritional supplements by people who exercise in gyms in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, and the types of supplements they most commonly use and to obtain a general view of the main reasons for using these enhancements.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study using a self-administered questionnaire was conducted at gyms in Riyadh that were selected randomly from different sectors of the city. The sample size was estimated at 289, but the actual number of randomly selected participants in the study was 457.
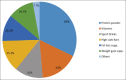
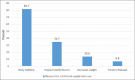
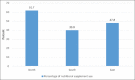
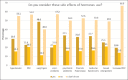
Results: The number of gym members who participated in this study was 457. Approximately 47.9% of the sample reported an intake of nutritional supplements and 7.9% reported that they took hormones. Protein powder was consumed by 83.1% of the participants. Approximately 16.8% of supplement users had noticed some side effects, and 25.7% of those who took hormones had stopped taking them because of adverse effects. Only half of the hormone users (54.2%) reported that they had had medical checkups. The major source of information on supplement and hormone use was non-health professionals; friends being major source (40%) of information on the use of hormones. The use of nutritional supplements was significantly associated with BMI (OR = 1.89, CI = 1.06-3.39), duration of daily exercise (OR = 4.23, CI = 2.06-8.68), and following a special diet (OR = 8.42, CI = 5.37-13.2). There was a very strong association between nutritional supplement consumption and hormone use (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Approximately half of the participants who regularly exercised in gyms took nutritional supplements, and most had received their information from nonhealth professionals. There was an association between the duration of exercise and the use of hormones and supplements. Fewer than half of hormone users had obtained a health-care provider's advice before taking it. The atmosphere in the gym can play an important role in members' decisions. Educating gym employees and members may have a positive influence on the use of supplements and hormones.
Keywords: Gyms; Saudi Arabia; hormones; nutritional supplements.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Prevalence and Awareness of Dietary Supplement Use Among Saudi Women Visiting Fitness Centers in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2023 Jun 27;15(6):e41031. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41031. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37519554 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of dietary supplement use by gym members in Portugal and associated factors.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020 Feb 24;17(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-00342-z. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32093724 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Supplement Intake and Associated Factors Among Gym Users in a University Community.J Diet Suppl. 2018 Jan 2;15(1):88-97. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2017.1326430. Epub 2017 May 30. J Diet Suppl. 2018. PMID: 28557663
-
A systematic review of outdoor gym use: Current evidence and future directions.J Sci Med Sport. 2019 Dec;22(12):1335-1343. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2019.08.003. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Sci Med Sport. 2019. PMID: 31444034
-
Dietary supplements in sport.Sports Med. 1993 Jan;15(1):43-65. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199315010-00005. Sports Med. 1993. PMID: 8426943 Review.
Cited by
-
Androgenic-anabolic steroid abuse trend and management: A prospective, cross-sectional, questionnaire-based survey.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 9;6(1):e1032. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1032. eCollection 2023 Jan. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36628108 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence and Awareness of Dietary Supplement Use Among Saudi Women Visiting Fitness Centers in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2023 Jun 27;15(6):e41031. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41031. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37519554 Free PMC article.
-
Illegal Use of Testosterone and Other Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids in the Population of Amateur Athletes in Wrocław, Poland-An Unfavorable Lifestyle Trend in the Population of Men of Reproductive Age.J Clin Med. 2024 Jun 26;13(13):3719. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133719. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999285 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of knowledge and beliefs on consumption of performance enhancing agents in north-western Saudi Arabia.Ann Saudi Med. 2017 Jul-Aug;37(4):317-325. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2017.317. Ann Saudi Med. 2017. PMID: 28761032 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of dietary supplement use by gym members in Portugal and associated factors.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020 Feb 24;17(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-00342-z. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32093724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tian HH, Ong WS, Tan CL. Nutritional supplement use among university athletes in Singapore. Singapore Med J. 2009;50:165–72. - PubMed
-
- Al-Falasi O, Al-Dahmani K, Al-Eisaei K, Al-Ameri S, Al-Maskari F, Nagelkerke N, et al. Knowledge, attitude and practice of anabolic steroids use among gym users in Al-Ain district, United Arab Emirates. Open Sports Med J. 2008;2:75–81.
-
- Froiland K, Koszewski W, Hingst J, Kopecky L. Nutritional supplement use among college athletes and their sources of information. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2004;14:104–20. - PubMed
-
- Morrison LJ, Gizis F, Shorter B. Prevalent use of dietary supplements among people who exercise at a commercial gym. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2004;14:481–92. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

