Draft genome sequence of type strain HBR26T and description of Rhizobium aethiopicum sp. nov
- PMID: 28163823
- PMCID: PMC5278577
- DOI: 10.1186/s40793-017-0220-z
Draft genome sequence of type strain HBR26T and description of Rhizobium aethiopicum sp. nov
Abstract
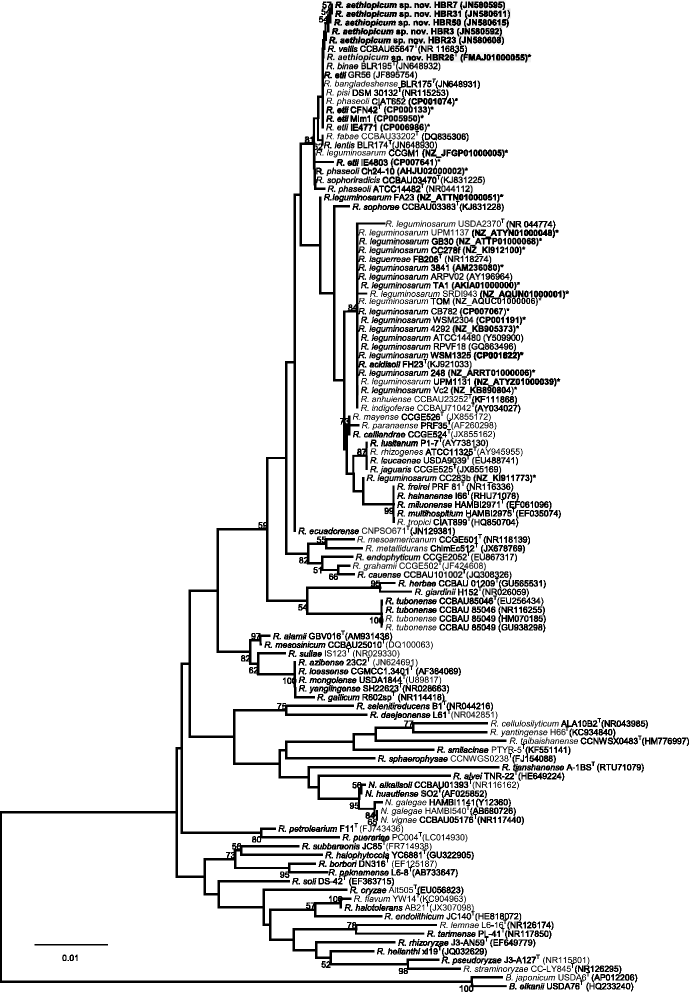
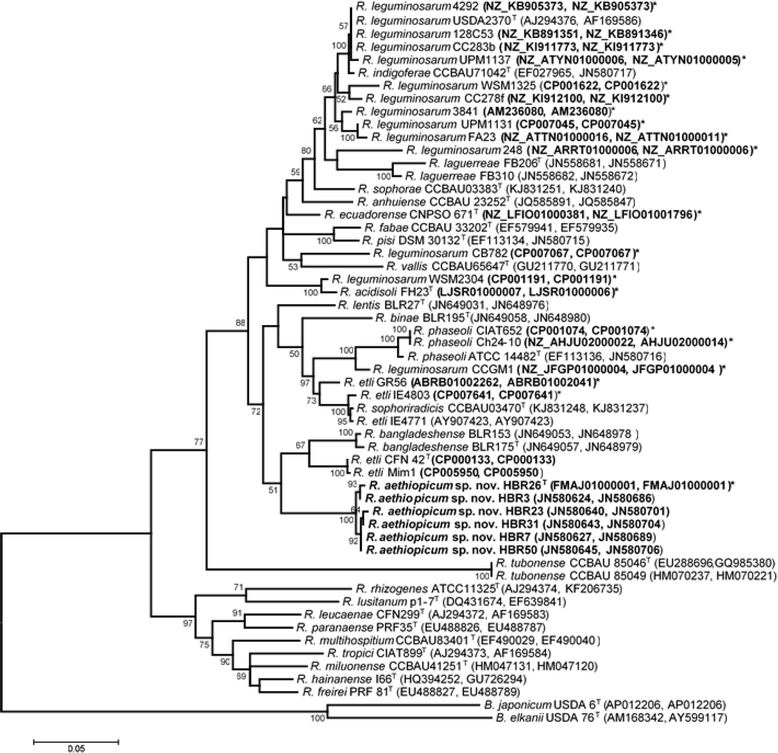
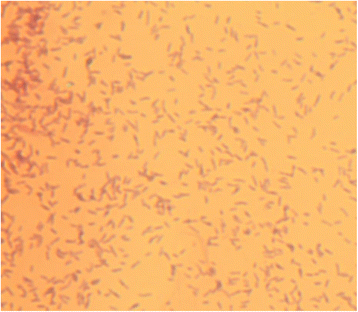
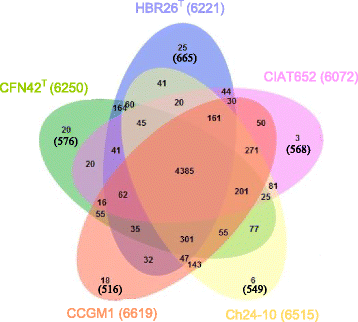
Rhizobium aethiopicum sp. nov. is a newly proposed species within the genus Rhizobium. This species includes six rhizobial strains; which were isolated from root nodules of the legume plant Phaseolus vulgaris growing in soils of Ethiopia. The species fixes nitrogen effectively in symbiosis with the host plant P. vulgaris, and is composed of aerobic, Gram-negative staining, rod-shaped bacteria. The genome of type strain HBR26T of R. aethiopicum sp. nov. was one of the rhizobial genomes sequenced as a part of the DOE JGI 2014 Genomic Encyclopedia project designed for soil and plant-associated and newly described type strains. The genome sequence is arranged in 62 scaffolds and consists of 6,557,588 bp length, with a 61% G + C content and 6221 protein-coding and 86 RNAs genes. The genome of HBR26T contains repABC genes (plasmid replication genes) homologous to the genes found in five different Rhizobium etli CFN42T plasmids, suggesting that HBR26T may have five additional replicons other than the chromosome. In the genome of HBR26T, the nodulation genes nodB, nodC, nodS, nodI, nodJ and nodD are located in the same module, and organized in a similar way as nod genes found in the genome of other known common bean-nodulating rhizobial species. nodA gene is found in a different scaffold, but it is also very similar to nodA genes of other bean-nodulating rhizobial strains. Though HBR26T is distinct on the phylogenetic tree and based on ANI analysis (the highest value 90.2% ANI with CFN42T) from other bean-nodulating species, these nod genes and most nitrogen-fixing genes found in the genome of HBR26T share high identity with the corresponding genes of known bean-nodulating rhizobial species (96-100% identity). This suggests that symbiotic genes might be shared between bean-nodulating rhizobia through horizontal gene transfer. R. aethiopicum sp. nov. was grouped into the genus Rhizobium but was distinct from all recognized species of that genus by phylogenetic analyses of combined sequences of the housekeeping genes recA and glnII. The closest reference type strains for HBR26T were R. etli CFN42T (94% similarity of the combined recA and glnII sequences) and Rhizobium bangladeshense BLR175T (93%). Genomic ANI calculation based on protein-coding genes also revealed that the closest reference strains were R. bangladeshense BLR175T and R. etli CFN42T with ANI values 91.8 and 90.2%, respectively. Nevertheless, the ANI values between HBR26T and BLR175T or CFN42T are far lower than the cutoff value of ANI (> = 96%) between strains in the same species, confirming that HBR26T belongs to a novel species. Thus, on the basis of phylogenetic, comparative genomic analyses and ANI results, we formally propose the creation of R. aethiopicum sp. nov. with strain HBR26T (=HAMBI 3550T=LMG 29711T) as the type strain. The genome assembly and annotation data is deposited in the DOE JGI portal and also available at European Nucleotide Archive under accession numbers FMAJ01000001-FMAJ01000062.
Keywords: Average Nucleotide Identity; Common bean; Ethiopia; Genome; Rhizobium aethiopicum; Symbiotic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The promiscuity of Phaseolus vulgaris L. (common bean) for nodulation with rhizobia: a review.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Apr 20;36(5):63. doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02839-w. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32314065 Review.
-
Average nucleotide identity of genome sequences supports the description of Rhizobium lentis sp. nov., Rhizobium bangladeshense sp. nov. and Rhizobium binae sp. nov. from lentil (Lens culinaris) nodules.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2015 Sep;65(9):3037-3045. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.000373. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26060217
-
Draft genome sequences of Bradyrhizobium shewense sp. nov. ERR11T and Bradyrhizobium yuanmingense CCBAU 10071T.Stand Genomic Sci. 2017 Dec 5;12:74. doi: 10.1186/s40793-017-0283-x. eCollection 2017. Stand Genomic Sci. 2017. PMID: 29225730 Free PMC article.
-
Rhizobium esperanzae sp. nov., a N2-fixing root symbiont of Phaseolus vulgaris from Mexican soils.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017 Oct;67(10):3937-3945. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002225. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28895521
-
Horizontal Transfer of Symbiosis Genes within and Between Rhizobial Genera: Occurrence and Importance.Genes (Basel). 2018 Jun 27;9(7):321. doi: 10.3390/genes9070321. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29954096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phylogeographic distribution of rhizobia nodulating common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Ethiopia.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2021 Apr 1;97(4):fiab046. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiab046. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2021. PMID: 33724341 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Interaction Studies Reveal Superior Performance of Rhizobium tropici CIAT899 on a Range of Diverse East African Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Genotypes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Nov 27;85(24):e01763-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01763-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31562174 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization at the species and symbiovar level of indigenous rhizobial isolates nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris in Greece.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 21;11(1):8674. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88051-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33883620 Free PMC article.
-
The promiscuity of Phaseolus vulgaris L. (common bean) for nodulation with rhizobia: a review.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Apr 20;36(5):63. doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02839-w. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32314065 Review.
-
Phylogenetic diversity of Rhizobium species recovered from nodules of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in fields in Uganda: R. phaseoli, R. etli, and R. hidalgonense.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2024 Oct 25;100(11):fiae120. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiae120. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2024. PMID: 39270668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franche C, Lindström K, Elmerich C. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with leguminous and non-leguminous plants. Plant Soil. 2009;321:35–59. doi: 10.1007/s11104-008-9833-8. - DOI
-
- Gepts P, Debouck D. Origin, domestication and evolution of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) In: van Schoonhoven A, Voysest O, editors. Common beans, research for crop improvement. Wallingford, UK, Cali-Colombia: CAB; 1991. pp. 7–53.
-
- Kaplan L. Archeology and domestication in American Phaseolus (Beans) Econ Bot. 1965;19:558–68. doi: 10.1007/BF02904806. - DOI
-
- Singh SP. Production and utilization. In: Singh SP, editor. Common bean improvement in the twenty-first century. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1999. pp. 1–24.
-
- Ribeiro MC, Metzger JP, Martensen AC, Ponzoni FJ, Hirota MM. The Brazilian Atlantic Forest: how much is left, and how is the remaining forest distributed? Implications for conservation. Biol Conserv. 2009;142:1141–53. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2009.02.021. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

