Effect of Entonox on reducing the need for Pethidine and the Relevant Fetal and Maternal Complications for Painless Labor
- PMID: 28163844
- PMCID: PMC5279962
- DOI: 10.19082/3325
Effect of Entonox on reducing the need for Pethidine and the Relevant Fetal and Maternal Complications for Painless Labor
Abstract
Background: Pain relief during labour is one of the major concerns in obstetrics; severe labor pain causes fear of the next pregnancy, and interferes with the mother's family relationship.
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the analgesic effects of Entonox during labor on reducing the need for pethidine (Meperidine) and fetal-maternal complications.
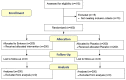
Methods: This double-blind randomized clinical trial was conducted on pregnant women who were candidates for vaginal delivery in Educational Hospitals of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Iran between January 2014 and November 2015. After entering into the inactive phase of labor, participants were randomly allocated to receive inhaled Entonox gas (n=200) or inhale Oxygen (n=200) as a control group. Mothers inhaled the gas at commencement of pain, and ceased as soon as the pain diminished, up to the end of the second stage of labor which was the neonate's birth. Main outcomes were pain score based on NRS (numerical rating scale), duration of delivery, required pethidine, maternal complications and satisfaction during labour. Chi-square and Independent T-test were used via SPSS for data analysis and P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Four-hundred pregnant women with a mean age of 26.4±5.9 years were studied. Complications such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and drowsiness were reported in 25% of the Entonox group and 23% in the control group (p=0.640). Mean of pain severity score during labor in the Entonox and control groups was 4.5±1.2 and 5.2±1.4, respectively (p<0.001). Pethidine requirement, significantly was lower in the Entonox group (31.6±11.8 versus 35.7±12.4; p<0.001).
Conclusion: In our study, Entonox significantly reduced pain during delivery without significant increase in maternal and neonatal complications.
Trial registration: The trial is registered at the Iranian Clinical Trial Registry (IRCT.ir) with the IRCT identification number IRCT2015102713159N6.
Funding: This research has been financially supported by Research Council of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Keywords: Analgesia; Entonox; Inhalation; Narcotics; Obstetrical; Pethidine.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to be declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Entonox® versus Pethidine in Labor Pain Relief: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 29;18(23):12571. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182312571. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34886299 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Use of Enthonox With Pethidine for Pain Relief in Primigravid Women During the Active Phase of Labor.Anesth Pain Med. 2016 Jul 24;6(4):e37420. doi: 10.5812/aapm.37420. eCollection 2016 Aug. Anesth Pain Med. 2016. PMID: 27843776 Free PMC article.
-
The IDvIP trial: a two-centre randomised double-blind controlled trial comparing intramuscular diamorphine and intramuscular pethidine for labour analgesia.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2011 Jul 8;11:51. doi: 10.1186/1471-2393-11-51. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2011. PMID: 21740578 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Maternal expectations and experiences of labor analgesia with nitrous oxide.Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2012 Dec;14(12):792-7. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.3470. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2012. PMID: 23483128 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), entonox, pethidine + promazine and lumbar epidural for pain relief in labor.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1987;66(1):9-14. doi: 10.3109/00016348709092945. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1987. PMID: 3300138 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Oliceridine- Opioid of the 21st Century.Saudi J Anaesth. 2022 Jan-Mar;16(1):69-75. doi: 10.4103/sja.sja_510_21. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Saudi J Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 35261592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficiency and safety: comparison between preoperative analgesia and postoperative analgesia using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in patients receiving arthroscopic knee surgery in a multicenter, randomized, controlled study.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Jun;29(3):651-659. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00792-0. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33797658 Clinical Trial.
-
Relationship between COMT Gene Polymorphism, Anxiety, and Pain Perception during Labour.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 29;12(19):6298. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196298. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37834942 Free PMC article.
-
Entonox® versus Pethidine in Labor Pain Relief: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 29;18(23):12571. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182312571. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34886299 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of the effects of ENTONOX inhalation and spinal anesthesia on labor pain reduction and apgar score in vaginal delivery: a clinical trial study.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2018 Sep;8(3):17. doi: 10.1051/bmdcn/2018080317. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2018. PMID: 30141404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khadem N, Zirak N, Soltani G, Sahebdelfar N, Sepehri Shamloo A, Ebrahimzadeh S. Comparison of Epidural versus Entonox for Labor Analgesia in Nulliparous Women. Journal of Surgery and Trauma. 2013;1(1):1–5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources