Kv4.2 knockout mice display learning and memory deficits in the Lashley maze
- PMID: 28163893
- PMCID: PMC5247778
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.9664.2
Kv4.2 knockout mice display learning and memory deficits in the Lashley maze
Abstract
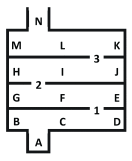
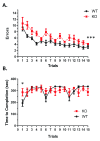
Background: Potassium channels have been shown to be involved in neural plasticity and learning. Kv4.2 is a subunit of the A-type potassium channel. Kv4.2 channels modulate excitability in the dendrites of pyramidal neurons in the cortex and hippocampus. Deletion of Kv4.2 results in spatial learning and conditioned fear deficits; however, previous studies have only examined deletion of Kv4.2 in aversive learning tests. Methods: For the current study, we used the Lashley maze as an appetitive learning test. We examined Kv4.2 wildtype (WT) and knockout (KO) mice in the Lashley maze over 4 days during adulthood. The first day consisted of habituating the mice to the maze. The mice then received five trials per day for the next 3 days. The number of errors and the time to the goal box was recorded for each trial. The goal box contained a weigh boat with an appetitive reward (gelatin with sugar). There was an intertrial interval of 15 minutes. Results: We found that Kv4.2 KO mice committed more errors across the trials compared to the WT mice p<0.001. There was no difference in the latency to find the goal box over the period. Discussion: Our finding that deletion of Kv4.2 resulted in more errors in the Lashley maze across 15 trials contribute to a growing body of evidence that Kv4.2 channels are significantly involved in learning and memory.
Keywords: A type current; Kv4.2; hippocampus; lashley maze; learning; potassium ion channel.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

