STAT5 and CD4 + T Cell Immunity
- PMID: 28163905
- PMCID: PMC5247784
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.9838.1
STAT5 and CD4 + T Cell Immunity
Abstract
STAT5 plays a critical role in the development and function of many cell types. Here, we review the role of STAT5 in the development of T lymphocytes in the thymus and its subsequent role in the differentiation of distinct CD4 + helper and regulatory T-cell subsets.
Keywords: STAT5; T-cell development; T-cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. No competing interests were disclosed. No competing interests were disclosed. No competing interests were disclosed. No competing interests were disclosed. No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
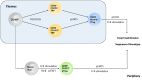
Similar articles
-
IL-6 activates STAT5 in T cells.Cytokine. 2012 Nov;60(2):575-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Cytokine. 2012. PMID: 22854263
-
Dynamic Roles for IL-2-STAT5 Signaling in Effector and Regulatory CD4+ T Cell Populations.J Immunol. 2020 Oct 1;205(7):1721-1730. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000612. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32958706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stat5-/- CD4+ T cells elicit anti-melanoma effect by CD4+ T cell remolding and Notch1 activation.Sci China Life Sci. 2022 Sep;65(9):1824-1839. doi: 10.1007/s11427-021-2078-6. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Sci China Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35508790
-
STAT5 programs a distinct subset of GM-CSF-producing T helper cells that is essential for autoimmune neuroinflammation.Cell Res. 2014 Dec;24(12):1387-402. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.154. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 25412660 Free PMC article.
-
Ikaros Zinc Finger Transcription Factors: Regulators of Cytokine Signaling Pathways and CD4+ T Helper Cell Differentiation.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 6;10:1299. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01299. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31244845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acriflavine, a HIF-1 inhibitor, preserves vision in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model of optic neuritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 23;14:1271118. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1271118. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37942317 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5A and STAT5B-Twins with Different Personalities in Hematopoiesis and Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 4;11(11):1726. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111726. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31690038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential impact of celiac disease genetic risk factors on T cell receptor signaling in gluten-specific CD4+ T cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 29;11(1):9252. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86612-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33927210 Free PMC article.
-
Ikaros antagonizes DNA binding by STAT5 in pre-B cells.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 12;15(11):e0242211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242211. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33180866 Free PMC article.
-
miR-10 and Its Negative Correlation with Serum IL-35 Concentration and Positive Correlation with STAT5a Expression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 18;23(14):7925. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147925. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wakao H, Schmitt-Ney M, Groner B: Mammary gland-specific nuclear factor is present in lactating rodent and bovine mammary tissue and composed of a single polypeptide of 89 kDa. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(23):16365–70. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

