Effect of Nigella sativa (black seeds) against methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in mice
- PMID: 28163954
- PMCID: PMC5289094
- DOI: 10.5455/jice.20161208013809
Effect of Nigella sativa (black seeds) against methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in mice
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the protective effect of Nigella sativa (NS) against nephrotoxicity of methotrexate (MTX) in mice.
Materials and methods: Four groups of Swiss albino male mice, eight in each group were used. The study was carried on between October 2014 and April 2015. Group 1 (control) were administered 0.3 ml distilled water orally daily for 21 days and injected with normal saline (0.25 ml) IP weekly. Group 2 (MTX group) were treated with MTX, 10 mg/kg IP weekly, while Group 3 were treated with 0.125 ml of NS oil by mouth daily and injected with normal saline (0.25 ml) IP weekly. Group 4 received 0.125 ml of NS oil by mouth daily and injected with 10 mg/kg MTX IP weekly. Oral treatments were administered using a special curved smooth tip nontraumatic metal needle and IP injections were given for 3 weeks at days 7, 14 and 21. Animals were sacrificed at day 23. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH) measurements were performed on kidney homogenate. Histopathology of the kidneys were prepared and examined.
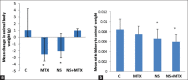
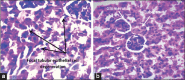
Results: MTX has resulted in a small elevation in MDA and reduction in GSH levels in kidney homogenate which was returned back to control values when NS and MTX were administered in combination. Statistical significance was achieved with elevation of GSH by MTX and NS compared to MTX alone. MTX caused histopathological changes suggesting nephrotoxicity in 6 animals out of 8, while no changes were found in all animals treated with MTX and NS.
Conclusion: NS is protective against MTX-induced nephrotoxicity.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Nigella sativa; kidney toxicity; methotrexate.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of virgin coconut oil supplementation abrogate acute chemotherapy oxidative nephrotoxicity induced by anticancer drug methotrexate in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Dec;96:905-911. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.008. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 29224791
-
A study of the effect of Nigella sativa (Black seeds) in isoniazid (INH)-induced hepatotoxicity in rabbits.Indian J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov-Dec;44(6):678-82. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.103239. Indian J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23248393 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin alleviates methotrexate-induced liver and kidney injury in mice.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021 Oct;40(10):1721-1731. doi: 10.1177/09603271211009964. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33845614
-
Paracetamol-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats: the protective role of Nigella sativa.Pharm Biol. 2016 Oct;54(10):2082-91. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2016.1145701. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Pharm Biol. 2016. PMID: 26956915
-
Study of the protective effects of cyanocobalamin on methotrexate induced nephrotoxicity in rats.F1000Res. 2022 Sep 7;11:1012. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.124081.2. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2022. PMID: 36405556 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Protective Effects of Nutraceutical Components in Methotrexate-Induced Toxicity Models-An Overview.Microorganisms. 2022 Oct 18;10(10):2053. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10102053. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa) and Its Bioactive Constituent, Thymoquinone against Kidney Injury: An Aspect on Pharmacological Insights.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 23;22(16):9078. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169078. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review on Phytochemistry, Health Benefits, Molecular Pharmacology, and Safety.Nutrients. 2021 May 24;13(6):1784. doi: 10.3390/nu13061784. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34073784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Nigella sativa and Its Constituent Thymoquinone on Chemotherapy-Induced Nephrotoxicity: Evidences from Experimental Animal Studies.Nutrients. 2017 Jun 17;9(6):625. doi: 10.3390/nu9060625. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28629150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hazlewood GS, Barnabe C, Tomlinson G, Marshall D, Devoe D, Bombardier C. Methotrexate monotherapy and methotrexate combination therapy with traditional and biologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis: Abridged Cochrane systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2016;353:i1777. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carrascosa JM, de la Cueva P, Ara M, Puig L, Bordas X, Carretero G, et al. Methotrexate in moderate to severe psoriasis: Review of the literature and expert recommendations. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016;107:194–206. - PubMed
-
- Cecchino GN, Araujo Júnior E, Elito Júnior J. Methotrexate for ectopic pregnancy: when and how. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;290:417–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
