Geraniol attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced liver fatty acid alterations in male rats
- PMID: 28163957
- PMCID: PMC5289085
- DOI: 10.5455/jice.20160928012410
Geraniol attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced liver fatty acid alterations in male rats
Abstract
Background: Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an oxidant agent and this molecule naturally occurs in the body as a product of aerobic metabolism. Geraniol is a plant-derived natural antioxidant. The aim of this study was to determine the role of geraniol on hepatic fatty acids alterations following H2O2-induced oxidative stress in male rats.
Methods: After randomization, male Wistar rats were divided into four groups (n = 7 each group). Geraniol (50 mg/kg, dissolved in corn oil) and H2O2 (16 mg/kg, dissolved in distilled water) were administered by an intraperitoneal injection. Administrations were performed during 30 days with 1-day interval.
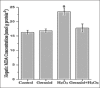
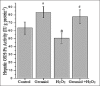
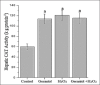
Results: Administration of H2O2 resulted with a significant increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) and a significant decrease in glutathione (GSH) peroxidase glutathione level; geraniol restored its effects on liver. However, hepatic catalase (CAT) activities were significantly higher in H2O2, geraniol, and geraniol+H2O2 groups than control group. The ratio of hepatic total saturated fatty acids increased in H2O2-treated animals compared with control. In addition, hepatic total unsaturated fatty acids reduced in H2O2 group compared with control. The percentages of both hepatic total saturated and unsaturated fatty acids were not different between geraniol+H2O2 and control groups.
Conclusions: H2O2-induced oxidative stress may affect fatty acid composition in liver and body. Geraniol can partly restore oxidative hepatic damage because it cannot completely reverse the H2O2-induced increase in hepatic CAT activities. Moreover, this natural compound can regulate hepatic total saturated and unsaturated fatty acids percentages against H2O2-induced alterations.
Keywords: Fatty acids; geraniol; hydrogen peroxide; liver; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Investigation of the role of α-lipoic acid on fatty acids profile, some minerals (zinc, copper, iron) and antioxidant activity against aluminum-induced oxidative stress in the liver of male rats.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2017 Jul 26;28(4):355-361. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2015-0160. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28306527
-
Protective effect of docosahexaenoic acid against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human lymphocytes.Biochem Pharmacol. 1999 May 1;57(9):1021-30. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00012-x. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10796072
-
The hepatoprotective effects of selenium against cadmium toxicity in rats.Toxicology. 2007 Dec 5;242(1-3):23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2007.09.001. Epub 2007 Sep 8. Toxicology. 2007. PMID: 17949884
-
Oxidative stress, histopathological alterations and anti-oxidant capacity in different tissues of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) exposed to a newly developed sodium carbonate peroxyhydrate granular algaecide formulated with hydrogen peroxide.Aquat Toxicol. 2020 Jan;218:105348. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105348. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Aquat Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31812647
-
Effects of intraperitoneally administered lipoic acid, vitamin E, and linalool on the level of total lipid and fatty acids in guinea pig brain with oxidative stress induced by H2O2.J Biochem Mol Biol. 2002 Nov 30;35(6):547-52. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2002.35.6.547. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12470587
Cited by
-
The Potential Role of Citrus limon Powder as a Natural Feed Supplement to Boost the Productive Performance, Antioxidant Status, and Blood Biochemistry of Growing Rabbits.Animals (Basel). 2019 Jul 7;9(7):426. doi: 10.3390/ani9070426. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31284654 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Geraniol and Its Metabolites in Mice After Oral Administration.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 9;13(1):e4653. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4653. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39803254 Free PMC article.
-
Catalase and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Dec;470(12):1721-1737. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2195-z. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 30120555 Review.
-
Geraniol activates Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway mediating protection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;393(10):1849-1858. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-01887-1. Epub 2020 May 16. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32417955
-
Geraniol Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Mediated Kidney Injury through Alteration of Antioxidant Status, Inflammation, and Apoptosis: Potential Roles of NF-κB and Nrf2/Ho-1.Nutrients. 2022 Apr 13;14(8):1620. doi: 10.3390/nu14081620. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35458182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halliwell B. Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: Curiosity, cause, or consequence? Lancet. 1994;344:721–4. - PubMed
-
- Poulsen HE, Prieme H, Loft S. Role of oxidative DNA damage in cancer initiation and promotion. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1998;7:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay U, Das D, Banerjee RK. Reactive oxygen species: Oxidative damage and pathogenesis. Curr Sci. 1999;77:658–66.
-
- Gilgun-Sherki Y, Melamed E, Offen D. Oxidative stress induced-neurodegenerative diseases: The need for antioxidants that penetrate the blood brain barrier. Neuropharmacology. 2001;40:959–75. - PubMed
-
- Pillai CK, Pillai KS. Antioxidants in health. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002;46:1–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
