Solving the puzzle: What is behind our forefathers' anti-inflammatory remedies?
- PMID: 28163971
- PMCID: PMC5289082
- DOI: 10.5455/jice.20161204021732
Solving the puzzle: What is behind our forefathers' anti-inflammatory remedies?
Abstract
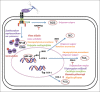
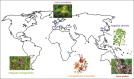
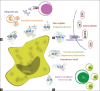
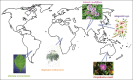
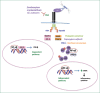
Inflammation is a ubiquitous host response in charge of restoring normal tissue structure and function but is a double-edged sword, as the uncontrolled or excessive process can lead to the injury of host cells, chronic inflammation, chronic diseases, and also neoplastic transformation. Throughout history, a wide range of species has been claimed to have anti-inflammatory effects worldwide. Among them, Angelica sinensis, Tropaeolum majus, Castilleja tenuiflora, Biophytum umbraculum, to name just a few, have attracted the scientific and general public attention in the last years. Efforts have been made to assess their relevance through a scientific method. However, inflammation is a complex interdependent process, and phytomedicines are complex mixtures of compounds with multiple mechanisms of biological actions, which restricts systematic explanation. For this purpose, the omics techniques could prove extremely useful. They provide tools for interpreting and integrating results from both the classical medical tradition and modern science. As a result, the concept of network pharmacology applied to phytomedicines emerged. All of this is a step toward personalized therapy.
Keywords: Inflammation; omics applied to phytomedicine; rational phytotherapy; traditional medicinal system.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiplasmodial, anti-complement and anti-inflammatory in vitro effects of Biophytum umbraculum Welw. traditionally used against cerebral malaria in Mali.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 22;190:159-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.058. Epub 2016 May 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27260410
-
In vivo anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcerogenic activities of extracts from wild growing and in vitro plants of Castilleja tenuiflora Benth. (Orobanchaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):1032-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24145005
-
Redefining Chronic Disease Care: Unleashing the Potential of Phytomedicines.Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2024 Oct 28. doi: 10.2174/012772574X324849240912071511. Online ahead of print. Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2024. PMID: 39473243
-
Angelica sinensis in China-A review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 22;190:116-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.023. Epub 2016 May 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27211015 Review.
-
Medicinal plants in Brazil: Pharmacological studies, drug discovery, challenges and perspectives.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Oct;112:4-29. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.01.021. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 26812486 Review.
Cited by
-
A Reassessment of the Marrubium Vulgare L. Herb's Potential Role in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: First Results Guide the Investigation toward New Horizons.Medicines (Basel). 2017 Aug 2;4(3):57. doi: 10.3390/medicines4030057. Medicines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28930271 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Characterization of Flowers and Leaf Extracts Obtained from Turnera subulata and Their Immunomodulatory Effect on LPS-Activated RAW 264.7 Macrophages.Molecules. 2022 Feb 6;27(3):1084. doi: 10.3390/molecules27031084. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu W, Wu L, Qiang Q, Ji L, Wang X, Luo H, et al. The dichloromethane fraction from Mahonia bealei (Fort.). Carr. leaves exerts an anti-inflammatory effect both in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;188:134–43. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence T, Willoughby DA, Gilroy DW. Anti-inflammatory lipid mediators and insights into the resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:787–95. - PubMed
-
- Borges FR, Silva MD, Córdova MM, Schambach TR, Pizzolatti MG, Santos AR. Anti-inflammatory action of hydroalcoholic extract, dichloromethane fraction and steroid a-spinasterol from Polygala sabulosa in LPS-induced peritonitis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151:144–50. - PubMed
-
- la Torre Fabiola VD, Ralf K, Gabriel B, Victor Ermilo AA, Martha MG, Mirbella CF, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of Critonia aromatisans leaves: Downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;190:174–82. - PubMed
-
- Fangkrathok N, Junlatat J, Sripanidkulchai B. In vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of Lentinus polychrous extract. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;147:631–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
