Expression of CD200R1 and its Ligand CD200 on T-helper Lymphocytes of Pediatric Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 28164626
- PMCID: PMC6423534
- DOI: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2016.151231
Expression of CD200R1 and its Ligand CD200 on T-helper Lymphocytes of Pediatric Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Background: CD200 and its receptor CD200R are both type I membrane glycoproteins that modulate the activity of myeloid and lymphoid cells, and their interaction is functionally important in the suppression of effector T-cell responses by regulatory T-cells. We aimed to investigate the extent of expression of CD200 and CD200R1 on CD4+ T-cells in blood of children with ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) and to explore their correlations with effector T cell subsets, regulatory T cells (Treg), and routine clinical and serological markers.
Methods: The frequencies of blood CD4+ expressing CD200 and CD200R1 as well as T-helper CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg, CD4+ IL-17+ (Th17), CD4+ IFN-γ + (Th1), and CD4+IL-4+ (Th2) were estimated by flow cytometry in 23 patients with CD, 14 with UC, and 14 healthy volunteers (HCs). The clinical and inflammatory markers were also investigated.
Results: IBD patients showed decreased CD4+CD200R1+ T-cells, whereas, CD4+CD200+ T-cells were significantly higher in patient groups compared with healthy controls. Treg cells were found significantly decreased in the patients with UC and CD compared with healthy controls (both at p < 0.01). The percentage of Th17 was found significantly increased in CD (p < 0.05) compared with UC patients and healthy subjects (p = 0.014). CD200+CD4+ T-cells showed significant positive correlations with ESR, Th1, and Th17 (r = 0.438, p < 0.05; r = 0.411, p < 0.05; r = 0.492, p < 0.01, respectively). CD200R1+CD4+ T-cells correlated positively with Th2 and Treg (r = 0.482, p < 0.01, and r = 0.457, p < 0.01, respectively) and negatively with ESR (r = -0.387, p < 0.01).
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates an aberrant expression of CD200/CD200R1 on CD4+ T-cells in IBD patients and these data may have potent pathological significance in IBD pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest:
None of the authors has any potential financial conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Figures
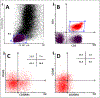
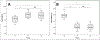

Similar articles
-
Reduced Dendritic Cells Expressing CD200R1 in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Correlation with Th17 and Regulatory T Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Dec 4;16(12):28998-9010. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226143. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26690123 Free PMC article.
-
Crossover Subsets of CD4+ T Lymphocytes in the Intestinal Lamina Propria of Patients with Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Sep;62(9):2357-2368. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4596-9. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28573508
-
Role of CD200/CD200R Signaling Pathway in Regulation of CD4+T Cell Subsets During Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Mar 6;25:1718-1728. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913094. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30838977 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased CD200R expression on monocyte-derived macrophages correlates with Th17/Treg imbalance and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Inflamm Res. 2014 Jun;63(6):441-50. doi: 10.1007/s00011-014-0716-6. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Inflamm Res. 2014. PMID: 24496593
-
The role of IL-13 and NK T cells in experimental and human ulcerative colitis.Mucosal Immunol. 2008 Nov;1 Suppl 1(0 1):S31-3. doi: 10.1038/mi.2008.40. Mucosal Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19079225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Genes Involved in Ulcerative Colitis Activity and Tumorigenesis Through Systematic Mining of Gene Co-expression Networks.Front Physiol. 2019 May 31;10:662. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00662. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31214045 Free PMC article.
-
The CD200 Regulates Inflammation in Mice Independently of TNF-α Production.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 19;22(10):5358. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105358. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34069671 Free PMC article.
-
CD200/CD200 receptor axis in psoriasis vulgaris.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 23;15(3):e0230621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230621. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32203537 Free PMC article.
-
CD200 and CD200R Expression on Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes and Serum CD200 Concentration as a New Marker of Endometriosis.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 21;9(9):3035. doi: 10.3390/jcm9093035. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32967175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Persson P, Bernell O, Leijonmarck CE, Farahmand BY, Hellers G, Ahlbom A. Survival and cause-specific mortality in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 1996;110(5):1339–45. - PubMed
-
- El Mouzan MI, Abdullah AM, Al Habbal MT. Epidemiology of juvenile-onset inflammatory bowel disease in central Saudi Arabia. J Trop Pediatr 2006;52(1):69–71. - PubMed
-
- Benchimol EI, Manuel DG, Guttmann A, et al. Changing age demographics of inflammatory bowel disease in Ontario, Canada: a population-based cohort study of epidemiology trends. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014;20(10):1761–9. - PubMed
-
- Martin-de-Carpi J, Rodriguez A, Ramos E, et al. Increasing incidence of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Spain (1996–2009): the SPIRIT Registry. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2013;19(1):73–80. - PubMed
-
- El Mouzan MI, Saadah O, Al-Saleem K, et al. Incidence of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Saudi Arabia: A Multicenter National Study. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014;20(6):1085–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

