β1- and β2-adrenergic stimulation-induced electrogenic transport by human endolymphatic sac epithelium and its clinical implications
- PMID: 28165045
- PMCID: PMC5292703
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42217
β1- and β2-adrenergic stimulation-induced electrogenic transport by human endolymphatic sac epithelium and its clinical implications
Abstract
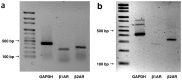
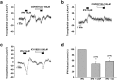
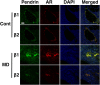
The endolymphatic sac (ES) is a cystic structure of the inner ear connected to the cochlea and vestibule, which plays a role in regulating ion homeostasis in inner ear fluid. Disruption of ion homeostasis can cause inner ear disorders with hearing loss and dizziness, such as Meniere's disease. Herein, we found, for the first time, functional evidence for the involvement of β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors in apical electrogenic ion transport by human ES epithelium by using electrophysiological/pharmacological and molecular biological methods, which were dependent on K+ and Cl- ion transport. The apical electrogenic transport was absent or very weak in ES epithelia of patients with Meniere's disease. These results suggested that adrenergic stimulation via β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors in the human ES was involved in regulation of inner ear fluid ion homeostasis and impairment of this response could be a pathological mechanism of Meniere's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

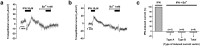
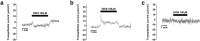
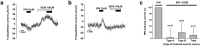
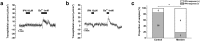
Similar articles
-
Electrogenic transport and K(+) ion channel expression by the human endolymphatic sac epithelium.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 14;5:18110. doi: 10.1038/srep18110. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26655723 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of locally applied drugs on the endolymphatic sac potential.Laryngoscope. 1998 Apr;108(4 Pt 1):592-8. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199804000-00024. Laryngoscope. 1998. PMID: 9546276
-
Claudin expression in the rat endolymphatic duct and sac - first insights into regulation of the paracellular barrier by vasopressin.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 4;7:45482. doi: 10.1038/srep45482. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28374851 Free PMC article.
-
Re-evaluation of the role of the human endolymphatic sac in Menière's disease.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990 Jun;102(6):732-44. doi: 10.1177/019459989010200618. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990. PMID: 2115662 Review.
-
Histopathologic findings in Menière's disease.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995 Jan;112(1):90-100. doi: 10.1016/S0194-59989570307-1. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995. PMID: 7816463 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognosis of asymptomatic endolymphatic hydrops in healthy volunteers: A five-year cohort study.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024 Nov 7;9(6):e70026. doi: 10.1002/lio2.70026. eCollection 2024 Dec. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39525523 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and localization of α2A-adrenergic receptor in the rat post-natal developing cochlea.Eur J Histochem. 2023 Aug 7;67(3):3748. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2023.3748. Eur J Histochem. 2023. PMID: 37548252 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenaline Modulates the Membrane Potential and Holding Current of Medial Prefrontal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons via β1-Adrenergic Receptors and HCN Channels.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Nov 2;11:341. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00341. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29209170 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between the Onset of Ménière's Disease and Sympathetic Hyperactivity.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 17;13:804777. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.804777. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35370896 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I Clinical Trial of Combination Propranolol and Pembrolizumab in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Melanoma: Safety, Tolerability, and Preliminary Evidence of Antitumor Activity.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;27(1):87-95. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2381. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33127652 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Meredith F. L. & Rennie K. J. Channeling your inner ear potassium: K+ channels in vestibular hair cells. Hear Res 338, 40–51 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Moller M. N. et al.. Gene expression in the human endolymphatic sac: the solute carrier molecules in endolymphatic fluid homeostasis. Otol Neurotol 36, 915–922 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Kim C. H. et al.. Dopamine increases Na+ absorption in the Reissner’s membrane of the gerbil cochlea. Auris Nasus Larynx 40, 266–272 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

