The interaction of perceptual biases in bistable perception
- PMID: 28165061
- PMCID: PMC5292733
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42018
The interaction of perceptual biases in bistable perception
Abstract
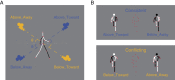
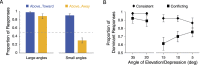
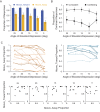
When viewing ambiguous stimuli, people tend to perceive some interpretations more frequently than others. Such perceptual biases impose various types of constraints on visual perception, and accordingly, have been assumed to serve distinct adaptive functions. Here we demonstrated the interaction of two functionally distinct biases in bistable biological motion perception, one regulating perception based on the statistics of the environment - the viewing-from-above (VFA) bias, and the other with the potential to reduce costly errors resulting from perceptual inference - the facing-the-viewer (FTV) bias. When compatible, the two biases reinforced each other to enhance the bias strength and induced less perceptual reversals relative to when they were in conflict. Whereas in the conflicting condition, the biases competed with each other, with the dominant percept varying with visual cues that modulate the two biases separately in opposite directions. Crucially, the way the two biases interact does not depend on the dominant bias at the individual level, and cannot be accounted for by a single bias alone. These findings provide compelling evidence that humans robustly integrate biases with different adaptive functions in visual perception. It may be evolutionarily advantageous to dynamically reweight diverse biases in the sensory context to resolve perceptual ambiguity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
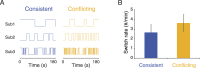
Similar articles
-
The relationship between social anxiety and the perception of depth-ambiguous biological motion stimuli is mediated by inhibitory ability.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2015 May;157:93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2015.02.012. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25747575
-
Emotional cues and social anxiety resolve ambiguous perception of biological motion.Exp Brain Res. 2018 May;236(5):1409-1420. doi: 10.1007/s00221-018-5233-3. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Exp Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29536149
-
Does anxiety induced by social interaction influence the perception of bistable biological motion?Acta Psychol (Amst). 2021 Apr;215:103277. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2021.103277. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2021. PMID: 33640594
-
United we sense, divided we fail: context-driven perception of ambiguous visual stimuli.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Apr 5;367(1591):932-41. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0358. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22371615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smelling x as y? On (the impossibility of) multistable perception in the chemical senses.Conscious Cogn. 2025 Jul;132:103875. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2025.103875. Epub 2025 May 7. Conscious Cogn. 2025. PMID: 40339447 Review.
Cited by
-
Circular inference in bistable perception.J Vis. 2020 Apr 9;20(4):12. doi: 10.1167/jov.20.4.12. J Vis. 2020. PMID: 32315404 Free PMC article.
-
Psychotic Experiences in Schizophrenia and Sensitivity to Sensory Evidence.Schizophr Bull. 2020 Jul 8;46(4):927-936. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbaa003. Schizophr Bull. 2020. PMID: 32090246 Free PMC article.
-
Cueing the Necker cube: Pupil dilation reflects the viewing-from-above constraint in bistable perception.J Vis. 2020 Apr 9;20(4):7. doi: 10.1167/jov.20.4.7. J Vis. 2020. PMID: 32293651 Free PMC article.
-
Flying enhances viewing from above bias on ambiguous visual stimuli.J Vis. 2023 Jun 1;23(6):11. doi: 10.1167/jov.23.6.11. J Vis. 2023. PMID: 37335570 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of visual reversals from ambiguous spinning biological-motion and rigid structure-from-motion.Iperception. 2025 May 21;16(3):20416695251342410. doi: 10.1177/20416695251342410. eCollection 2025 May-Jun. Iperception. 2025. PMID: 40443534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Long G. M. & Toppino T. C. Enduring interest in perceptual ambiguity: alternating views of reversible figures. Psychol. Bull. 130, 748–768 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Sterzer P., Kleinschmidt A. & Rees G. The neural bases of multistable perception. Trends Cogn. Sci. 13, 310–318 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Haselton M. G. et al.. Adaptive Rationality: An Evolutionary Perspective on Cognitive Bias. Soc. Cognition 27, 733–763 (2009).
-
- Haselton M. G., Daniel N. & Murray D. The Evolution of Cognitive Bias In The Handbook of Evolutionary Psychology (ed. Buss D. M.) 968–987 (John Wiley & Sons, 2015).
-
- Mamassian P., Landy M. S. & Maloney L. T. Bayesian Modelling of Visual Perception In Probabilistic models of the brain: Perception and neural function (eds Rao Rajesh, P. N., Olshausen Bruno A. & Lewicki Michael S.) 13–35 (MIT press, 2002).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

