Role of E-type prostaglandin receptor EP3 in the vasoconstrictor activity evoked by prostacyclin in thromboxane-prostanoid receptor deficient mice
- PMID: 28165064
- PMCID: PMC5292700
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42167
Role of E-type prostaglandin receptor EP3 in the vasoconstrictor activity evoked by prostacyclin in thromboxane-prostanoid receptor deficient mice
Abstract
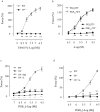
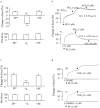
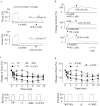
Prostacyclin, also termed as prostaglandin I2 (PGI2), evokes contraction in vessels with limited expression of the prostacyclin receptor. Although the thromboxane-prostanoid receptor (TP) is proposed to mediate such a response of PGI2, other unknown receptor(s) might also be involved. TP knockout (TP-/-) mice were thus designed and used to test the hypothesis. Vessels, which normally show contraction to PGI2, were isolated for functional and biochemical analyses. Here, we showed that the contractile response evoked by PGI2 was indeed only partially abolished in the abdominal aorta of TP-/- mice. Interestingly, further antagonizing the E-type prostaglandin receptor EP3 removed the remaining contractile activity, resulting in relaxation evoked by PGI2 in such vessels of TP-/- mice. These results suggest that EP3 along with TP contributes to vasoconstrictor responses evoked by PGI2, and hence imply a novel mechanism for endothelial cyclooxygenase metabolites (which consist mainly of PGI2) in regulating vascular functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
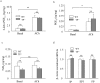
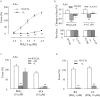
References
-
- Bunting S., Gryglewski R., Moncada S. & Vane J. R. Arterial walls generate from prostaglandin endoperoxides a substance (prostaglandin X) which relaxes strips of mesenteric and coeliac ateries and inhibits platelet aggregation. Prostaglandins 12, 897–913 (1976). - PubMed
-
- Davidge S. T. Prostaglandin H synthase and vascular function. Circ Res 89, 650–660 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Needleman P. et al. Identification of an enzyme in platelet microsomes which generates thromboxane A2 from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Nature 261, 558–560 (1976). - PubMed
-
- Smith W. L., DeWitt D. L. & Garavito R. M. Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem 69, 145–182 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

