Minority stress, psychosocial resources, and psychological distress among sexual minority breast cancer survivors
- PMID: 28165265
- PMCID: PMC5444950
- DOI: 10.1037/hea0000465
Minority stress, psychosocial resources, and psychological distress among sexual minority breast cancer survivors
Abstract
Objective: Few studies have examined unique factors predicting psychological distress among sexual minority (i.e., lesbian and bisexual) women postbreast cancer diagnosis. The present study assessed the association of minority stress and psychosocial resource factors with depression and anxiety symptoms among sexual minority breast cancer survivors.
Method: Two hundred one sexual minority women who had ductal carcinoma in situ or Stage I-IV breast cancer participated in this study through the Love/Avon Army of Women. Self-report questionnaires were used to assess demographic and clinical factors, minority stress factors (discrimination, minority identity development, outness), psychosocial resources (resilience, social support), and psychological distress (anxiety and depression). These factors were included in a structural equation model, testing psychosocial resources as mediators between minority stress and psychological distress.
Results: There were no significant differences noted between lesbian and bisexual women. The final structural equation model demonstrated acceptable fit across all sexual minority women, χ2 = 27.83, p > .05; confirmatory fit index = 0.97, root-mean-square error of approximation = 0.04, Tucker-Lewis index = 0.93. The model accounted for significant variance in psychological distress (56%). Examination of indirect effects confirmed that exposure to discrimination was associated with distress via association with resilience.
Conclusions: Factors unique to sexual minority populations, such as minority stress, may be associated with higher rates of psychological distress among sexual minority breast cancer survivors. However, presence of psychosocial resources may mediate relationships with distress in this population; enhancement of resilience, in particular, could be an aim of psychological intervention. (PsycINFO Database Record
(c) 2017 APA, all rights reserved).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

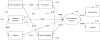
References
-
- Arena PL, Carver CS, Antoni MH, Weiss S, Ironson G, Duran RE. Psychosocial responses to treatment for breast cancer among lesbian and heterosexual women. Women Health. 2006;44(2):81–102. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17255060. - PubMed
-
- Boehmer U. Breast cancer in lesbian and bisexual women. In: Boehmer U, Elk R, editors. Cancer and the LGBT Community: Unique Perspectives from Risk to Survivorship. Cham: Springer; 2015. pp. 141–157.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

