Oral recombinant human or mouse lactoferrin reduces Mycobacterium tuberculosis TDM induced granulomatous lung pathology
- PMID: 28165282
- PMCID: PMC6006514
- DOI: 10.1139/bcb-2016-0061
Oral recombinant human or mouse lactoferrin reduces Mycobacterium tuberculosis TDM induced granulomatous lung pathology
Abstract
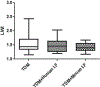
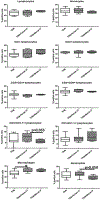
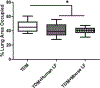
Trehalose 6'6-dimycolate (TDM) is the most abundant glycolipid on the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). TDM is capable of inducing granulomatous pathology in mouse models that resembles those induced by MTB infection. Using the acute TDM model, this work investigates the effect of recombinant human and mouse lactoferrin to reduce granulomatous pathology. C57BL/6 mice were injected intravenously with TDM at a dose of 25 μg·mouse-1. At day 4 and 6, recombinant human or mouse lactoferrin (1 mg·(100 μL)-1·mouse-1) were delivered by gavage. At day 7 after TDM injection, mice were evaluated for lung pathology, cytokine production, and leukocyte populations. Mice given human or mouse lactoferrin had reduced production of IL-12p40 in their lungs. Mouse lactoferrin increased IL-6 and KC (CXCL1) in lung tissue. Increased numbers of macrophages were observed in TDM-injected mice given human or mouse lactoferrin. Granulomatous pathology, composed of mainly migrated leukocytes, was visually reduced in mice that received human or mouse lactoferrin. Quantitation of granulomatous pathology demonstrated a significant decrease in mice given human or mouse lactoferrin compared with TDM control mice. This report is the first to directly compare the immune modulatory effects of both heterologous recombinant human and homologous mouse lactoferrin on the development of TDM-induced granulomas.
Le tréhalose 6’6 dimycolate (TDM) est le glycolipide le plus abondant de la paroi cellulaire de Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). Le TDM est capable d’induire des pathologies granulomateuses dans des modèles de souris qui ressemblent à celles qui sont induites par l’infection à MTB. Utilisant le modèle de TDM aigu, ce manuscrit examine l’effet de lactoferrine recombinante humaine et de souris pour réduire la pathologie granulomateuse. Des souris C57BL/6 ont reÇu par injection i.v. 25 µg souris−1 de TDM. Aux jours 4 et 6, de la lactoferrine recombinante humaine ou de souris (1 mg·(100 µL)−1·souris−1) a été administrée par gavage. Sept jours après l’injection de TDM, les souris ont été évaluées quant à la pathologie pulmonaire, à la production de cytokines et à la population de leucocytes. Les souris ayant reÇu de la lactoferrine humaine ou de souris présentaient une réduction de la production d’IL-12p40 dans le poumon. La lactoferrine de souris augmentait l’IL-6 et le KC (CXCL1) dans le tissu pulmonaire. Un accroissement de la population de macrophages était observé chez les souris injectées avec le TDM et ayant reÇu de la lactoferrine humaine ou de souris. La pathologie granulomateuse, composée principalement de leucocytes ayant migré, était visuellement réduite chez les souris ayant reÇu la lactoferrine humaine ou de souris. La quantification de la pathologie granulomateuse a démontré qu’elle était significativement diminuée chez les souris ayant reÇu de la lactoferrine humaine ou de souris comparativement aux souris contrôles ayant reÇu le TDM seul. Ce rapport est le premier qui compare directement les effets immuno-modulateurs tant de la lactoferrine humaine hétérologue que de la lactoferrine de souris homologue dans le développement des granulomes induits par le TDM. [Traduit par la Rédaction]
Keywords: human lactoferrin; lactoferrine de souris; lactoferrine humaine; mouse lactoferrin; trehalose dimycolate; tréhalose dimycolate.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lactoferrin modulation of mycobacterial cord factor trehalose 6-6'-dimycolate induced granulomatous response.Transl Res. 2010 Oct;156(4):207-15. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Transl Res. 2010. PMID: 20875896 Free PMC article.
-
Lactoferrin reduces mycobacterial M1-type inflammation induced with trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate and facilitates the entry of fluoroquinolone into granulomas.Biochem Cell Biol. 2021 Feb;99(1):73-80. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2020-0057. Epub 2020 May 15. Biochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 32402212
-
Modulation of TDM-induced granuloma pathology by human lactoferrin: a persistent effect in mice.Biometals. 2023 Jun;36(3):603-615. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00434-0. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Biometals. 2023. PMID: 35976499
-
Lactoferrin: A Modulator for Immunity against Tuberculosis Related Granulomatous Pathology.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:409596. doi: 10.1155/2015/409596. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26788020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple roles of cord factor in the pathogenesis of primary, secondary, and cavitary tuberculosis, including a revised description of the pathology of secondary disease.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2006 Autumn;36(4):371-86. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2006. PMID: 17127724 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibacterial and Anti-biofilm Activity of the Human Breast Milk Glycoprotein Lactoferrin against Group B Streptococcus.Chembiochem. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):2124-2133. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100016. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Chembiochem. 2021. PMID: 33755306 Free PMC article.
-
Host Antimicrobial Peptides: The Promise of New Treatment Strategies against Tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 7;8:1499. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01499. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29163551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Human Lactoferrin Reduces Inflammation and Increases Fluoroquinolone Penetration to Primary Granulomas During Mycobacterial Infection of C57Bl/6 Mice.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022 Feb 28;70(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s00005-022-00648-7. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022. PMID: 35226195 Free PMC article.
-
Time to Kill and Time to Heal: The Multifaceted Role of Lactoferrin and Lactoferricin in Host Defense.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 24;15(4):1056. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041056. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential for Lactoferrin to reduce SARS-CoV-2 induced cytokine storm.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jun;95:107571. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107571. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33765614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott AN, Guidry TV, Welsh KJ, Thomas AM, Kling MA, Hunter RL, and Actor JK. 200911β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases are regulated during the pulmonary granulomatous response to the mycobacterial glycolipid trehalose-6,6’-dimycolate. NeuroImmunoModulation, 16(3): 147-154. doi:10.1159/000204227. PMID:. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdi K, and Singh NJ. 2015. Makingmany from few: IL-12p40 as a model for the combinatorial assembly of heterodimeric cytokines. Cytokine, 76(1): 53-57. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2015.07.026. PMID:. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Actor JK. 2015. Lactoferrin: a modulator for immunity against tuberculosis related granulomatous pathology. Mediators Inflammation, 2015: 409596. doi:10.1155/2015/409596. PMID:. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Actor JK, Indrigo J, Beachdel CM, Olsen M, Wells A, Hunter RL, Jr., and Dasgupta A. 2002. Mycobacterial glycolipid cord factor trehalose 6,6’ - dimycolate causes a decrease in serum cortisol during the granulomatous response. NeuroImmunoModulation, 10(5): 270-282. doi:10.1159/000069971. PMID:. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahsan MJ. 2015. Recent advances in the development of vaccines for tuberculosis. Ther. Adv. Vaccines, 3(3): 66-75. doi:10.1177/2051013615593891. PMID: . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

