Wnt7a Inhibits IL-1β Induced Catabolic Gene Expression and Prevents Articular Cartilage Damage in Experimental Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 28165497
- PMCID: PMC5292965
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41823
Wnt7a Inhibits IL-1β Induced Catabolic Gene Expression and Prevents Articular Cartilage Damage in Experimental Osteoarthritis
Abstract
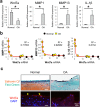
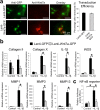
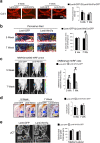
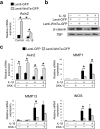
Wnt7a is a protein that plays a critical role in skeletal development. However, its effect on cartilage homeostasis under pathological conditions is not known. In this study, we found a unique inverse correlation between Wnt7a gene expression and that of MMP and IL-1β in individual human OA cartilage specimens. Upon ectopic expression in primary human articular chondrocytes, Wnt7a inhibited IL-1β-induced MMP and iNOS gene expression. Western blot analysis indicated that Wnt7a induced both canonical Wnt signaling and NFAT and Akt non-canonical signaling. Interestingly, inhibiting the canonical and Akt pathway did not affect Wnt7a activity. However, inhibiting the NFAT pathway impaired Wnt7a's ability to inhibit MMP expression, suggesting that Wnt7a requires NFAT signaling to exert this function. In vivo, intraarticular injection of lentiviral Wnt7a strongly attenuated articular cartilage damage induced by destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) OA-inducing surgery in mice. Consistently, Wnt7a also inhibited the progressive increase of joint MMP activity in DMM animals. These results indicate that Wnt7a signaling inhibits inflammatory stimuli-induced catabolic gene expression in human articular chondrocytes and is sufficient to attenuate MMP activities and promote joint cartilage integrity in mouse experimental OA, demonstrating a novel effect of Wnt7a on regulating OA pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insulin-Like Growth Factor II (IGF-II) Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Cartilage Matrix Loss and Promotes Cartilage Integrity in Experimental Osteoarthritis.J Cell Biochem. 2015 Dec;116(12):2858-69. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25232. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26015264 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 governs Wnt-mediated osteoarthritic cartilage destruction.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Jan 31;16(1):R37. doi: 10.1186/ar4466. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24479426 Free PMC article.
-
Anemonin attenuates osteoarthritis progression through inhibiting the activation of IL-1β/NF-κB pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Dec;21(12):3231-3243. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13227. Epub 2017 Jun 23. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28643466 Free PMC article.
-
Aucubin Protects Chondrocytes Against IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis In Vitro And Inhibits Osteoarthritis In Mice Model.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Oct 9;13:3529-3538. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S210220. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31631977 Free PMC article.
-
Articular cartilage vesicles and calcium crystal deposition diseases.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016 Mar;28(2):127-32. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000244. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26814404 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual protective role of velutin against articular cartilage degeneration and subchondral bone loss via the p38 signaling pathway in murine osteoarthritis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;13:926934. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.926934. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35937813 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signalling in the articular cartilage: A matter of balance.Int J Exp Pathol. 2023 Apr;104(2):56-63. doi: 10.1111/iep.12472. Epub 2023 Feb 26. Int J Exp Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36843204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Onset and Progression of Human Osteoarthritis-Can Growth Factors, Inflammatory Cytokines, or Differential miRNA Expression Concomitantly Induce Proliferation, ECM Degradation, and Inflammation in Articular Cartilage?Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 3;19(8):2282. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082282. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30081513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effects of microRNA-140 gene transfection with nucleus localization signal linked nucleic kinase substrate short peptide conjugated chitosan on rabbit articular chondrocytes].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Oct 15;31(10):1256-1261. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201705088. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29806331 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
RORβ modulates a gene program that is protective against articular cartilage damage.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 13;17(10):e0268663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268663. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36227956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Felson D. T. In Current Rheumatology Diagnosis & Treatment Vol. 104 (eds Imboden J., Hellman D., & Stone J.) (McGraw-Hill, 2007).
-
- Felson D. T. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine Vol. 13 (eds Longo D. L. et al..) (McGraw-Hill, 2012).
-
- Driban J. B., Barr A. E., Amin M., Sitler M. R. & Barbe M. F. Joint inflammation and early degeneration induced by high-force reaching are attenuated by ibuprofen in an animal model of work-related musculoskeletal disorder. Journal of biomedicine & biotechnology 2011, 691412, doi: 10.1155/2011/691412 (2011). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goldring M. B. & Goldring S. R. Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol 213, 626–634 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

