Intrinsic and Stable Conjugation of Thiolated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Radioarsenic
- PMID: 28165700
- PMCID: PMC5597940
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b14049
Intrinsic and Stable Conjugation of Thiolated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Radioarsenic
Abstract
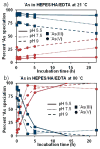
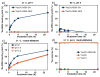
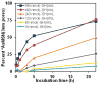
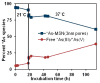
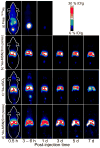
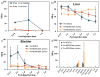
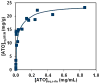
The development of new image-guided drug delivery tools to improve the therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapeutics remains an important goal in nanomedicine. Using labeling strategies that involve radioelements that have theranostic pairs of diagnostic positron-emitting isotopes and therapeutic electron-emitting isotopes has promise in achieving this goal and further enhancing drug performance through radiotherapeutic effects. The isotopes of radioarsenic offer such theranostic potential and would allow for the use of positron emission tomography (PET) for image-guided drug delivery studies of the arsenic-based chemotherapeutic arsenic trioxide (ATO). Thiolated mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) are shown to effectively and stably bind cyclotron-produced radioarsenic. Labeling studies elucidate that this affinity is a result of specific binding between trivalent arsenic and nanoparticle thiol surface modification. Serial PET imaging of the in vivo murine biodistribution of radiolabeled silica nanoparticles shows very good stability toward dearsenylation that is directly proportional to silica porosity. Thiolated MSNs are found to have a macroscopic arsenic loading capacity of 20 mg of ATO per gram of MSN, sufficient for delivery of chemotherapeutic quantities of the drug. These results show the great potential of radioarsenic-labeled thiolated MSN for the preparation of theranostic radiopharmaceuticals and image-guided drug delivery of ATO-based chemotherapeutics.
Keywords: As-72; As-76; As-77; arsenic trioxide; image-guided drug delivery; positron emission tomography; radioarsenic; radiolabeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiolabeling Silica-Based Nanoparticles via Coordination Chemistry: Basic Principles, Strategies, and Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Mar 20;51(3):778-788. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00635. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29489335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Yield Production and Radiochemical Isolation of Isotopically Pure Arsenic-72 and Novel Radioarsenic Labeling Strategies for the Development of Theranostic Radiopharmaceuticals.Bioconjug Chem. 2016 Jan 20;27(1):179-88. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00592. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Bioconjug Chem. 2016. PMID: 26646989 Free PMC article.
-
pH-triggered sustained release of arsenic trioxide by polyacrylic acid capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for solid tumor treatment in vitro and in vivo.J Biomater Appl. 2016 Jul;31(1):23-35. doi: 10.1177/0885328216637211. Epub 2016 Apr 7. J Biomater Appl. 2016. PMID: 27059495
-
Identification of pancreatic tumors in vivo with ligand-targeted, pH responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles by multispectral optoacoustic tomography.J Control Release. 2016 Jun 10;231:60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.055. Epub 2016 Jan 5. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26763377 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery and Theranostics.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(23):3367-3382. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161025153619. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 27784244 Review.
Cited by
-
Key Parameters for the Rational Design, Synthesis, and Functionalization of Biocompatible Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 2;14(12):2703. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122703. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A dual-modal approach to lung cancer treatment: in vitro and in silico. Evaluation of a hybrid nanocomposite for synergistic chemotherapy.Biometals. 2025 Aug;38(4):1109-1130. doi: 10.1007/s10534-025-00694-6. Epub 2025 May 14. Biometals. 2025. PMID: 40369325
-
Bioimaging predictors of rilpivirine biodistribution and antiretroviral activities.Biomaterials. 2018 Dec;185:174-193. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.09.018. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 30245386 Free PMC article.
-
Medical imaging modalities using nanoprobes for cancer diagnosis: A literature review on recent findings.J Res Med Sci. 2019 Apr 26;24:38. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_437_18. eCollection 2019. J Res Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31143239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiolabeling Silica-Based Nanoparticles via Coordination Chemistry: Basic Principles, Strategies, and Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Mar 20;51(3):778-788. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00635. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29489335 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De M, Ghosh PS, Rotello VM. Applications of Nanoparticles in Biology. Adv Mater. 2008;20:4225–4241.
-
- Peer D, Karp JM, Hong S, Farokhzad OC, Margalit R, Langer R. Nanocarriers as an Emerging Platform for Cancer Therapy. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:751–760. - PubMed
-
- Chow EKH, Ho D. Cancer Nanomedicine: From Drug Delivery to Imaging. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:216rv4. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm S, Tavares AJ, Dai Q, Ohta S, Audet J, Dvorak HF, Chan WCW. Analysis of Nanoparticle Delivery to Tumors. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;1:16014.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

