DNA Vaccine Encoding HPV16 Oncogenes E6 and E7 Induces Potent Cell-mediated and Humoral Immunity Which Protects in Tumor Challenge and Drives E7-expressing Skin Graft Rejection
- PMID: 28166181
- PMCID: PMC5293162
- DOI: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000156
DNA Vaccine Encoding HPV16 Oncogenes E6 and E7 Induces Potent Cell-mediated and Humoral Immunity Which Protects in Tumor Challenge and Drives E7-expressing Skin Graft Rejection
Abstract
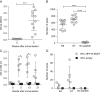
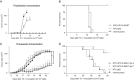
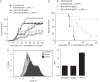
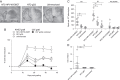
We have previously shown that a novel DNA vaccine technology of codon optimization and the addition of ubiquitin sequences enhanced immunogenicity of a herpes simplex virus 2 polynucleotide vaccine in mice, and induced cell-mediated immunity when administered in humans at relatively low doses of naked DNA. We here show that a new polynucleotide vaccine using the same technology and encoding a fusion protein of the E6 and E7 oncogenes of high-risk human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) is immunogenic in mice. This vaccine induces long-lasting humoral and cell-mediated immunity and protects mice from establishment of HPV16-E7-expressing tumors. In addition, it suppresses growth of readily established tumors and shows enhanced efficacy when combined with immune checkpoint blockade targeted at PD-L1. This vaccine also facilitates rejection of HPV16-E7-expressing skin grafts that demonstrate epidermal hyperplasia with characteristics of cervical and vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Clinical studies evaluating the efficacy of this vaccine in patients with HPV16 premalignancies are planned.
Figures
References
-
- Liu WJ, Zhao KN, Gao FG, et al. Polynucleotide viral vaccines: codon optimisation and ubiquitin conjugation enhances prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy. Vaccine. 2001;20:862–869. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

