No benefits of statins for sudden cardiac death prevention in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 28166237
- PMCID: PMC5293250
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171168
No benefits of statins for sudden cardiac death prevention in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background and objectives: Statins showed mixed results in heart failure (HF) patients. The benefits in major HF outcomes, including all-cause mortality and sudden cardiac death (SCD), have always been discordant across systematic reviews and meta-analyses. We intended to systematically identify and appraise the available evidence that evaluated the effectiveness of statins in clinical outcomes for HF patients.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data sources: We searched, until April 28, 2016: Medline, Embase, ISI Web of Science and EBM reviews (Cochrane DSR, ACP journal club, DARE, CCTR, CMR, HTA, and NHSEED), checked clinicaltrials.gov for ongoing trials and manually searched references of included studies.
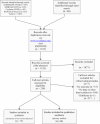
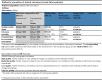
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: We identified 24 randomized clinical trials that evaluated the efficacy of statins for HF patients. All randomized clinical trials were assessed for risk of bias and pooled together in a meta-analysis. Pre-specified outcomes were sudden cardiac death, all-cause mortality, and hospitalization for worsening heart failure.
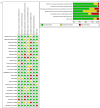
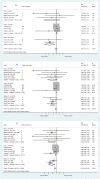
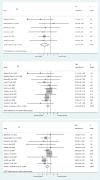
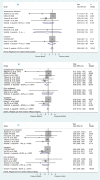
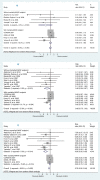
Results: Statins did not reduce sudden cardiac death (SCD) events in HF patients [relative risk (RR) 0.92, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.70 to 1.21], all-cause mortality [RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.02] but significantly reduced hospitalization for worsening heart failure (HWHF) although modestly [RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.66 to 0.94]. Nevertheless, estimated predictive intervals were insignificant in SCD, all-cause mortality and HWHF [RR, 0.54 to 1.63, 0.64 to 1.19, and 0.54 to 1.15], respectively. An important finding was the possible presence of publication bias, small-study effects and heterogeneity of the trials conducted in HF patients.
Conclusions: Statins do not reduce sudden cardiac death, all-cause mortality, but may slightly decrease hospitalization for worsening heart failure in HF patients. The evaluation of the risk of biases suggested moderate quality of the published results. Until new evidence is available, this study supports the 2013 ACCF/AHA guidelines to not systematically prescribe statins in "only" HF patients, which should help avoid unnecessary polypharmacy.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Lopez-Sendon J, Swedberg K, McMurray J, Tamargo J, Maggioni AP, Dargie H, et al. Expert consensus document on angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in cardiovascular disease. The Task Force on ACE-inhibitors of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2004;25(16):1454–70. Epub 2004/08/11. 10.1016/j.ehj.2004.06.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Le HH, El-Khatib C, Mombled M, Guitarian F, Al-Gobari M, Fall M, et al. Impact of Aldosterone Antagonists on Sudden Cardiac Death Prevention in Heart Failure and Post-Myocardial Infarction Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0145958 Epub 2016/02/20. PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPmc4758660. 10.1371/journal.pone.0145958 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

