Identification of shared risk loci and pathways for bipolar disorder and schizophrenia
- PMID: 28166306
- PMCID: PMC5293228
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171595
Identification of shared risk loci and pathways for bipolar disorder and schizophrenia
Abstract
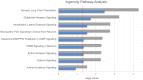
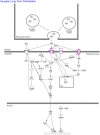
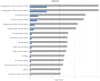
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a highly heritable neuropsychiatric disease characterized by recurrent episodes of mania and depression. BD shows substantial clinical and genetic overlap with other psychiatric disorders, in particular schizophrenia (SCZ). The genes underlying this etiological overlap remain largely unknown. A recent SCZ genome wide association study (GWAS) by the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium identified 128 independent genome-wide significant single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The present study investigated whether these SCZ-associated SNPs also contribute to BD development through the performance of association testing in a large BD GWAS dataset (9747 patients, 14278 controls). After re-imputation and correction for sample overlap, 22 of 107 investigated SCZ SNPs showed nominal association with BD. The number of shared SCZ-BD SNPs was significantly higher than expected (p = 1.46x10-8). This provides further evidence that SCZ-associated loci contribute to the development of BD. Two SNPs remained significant after Bonferroni correction. The most strongly associated SNP was located near TRANK1, which is a reported genome-wide significant risk gene for BD. Pathway analyses for all shared SCZ-BD SNPs revealed 25 nominally enriched gene-sets, which showed partial overlap in terms of the underlying genes. The enriched gene-sets included calcium- and glutamate signaling, neuropathic pain signaling in dorsal horn neurons, and calmodulin binding. The present data provide further insights into shared risk loci and disease-associated pathways for BD and SCZ. This may suggest new research directions for the treatment and prevention of these two major psychiatric disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

