Emollients and moisturisers for eczema
- PMID: 28166390
- PMCID: PMC6464068
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012119.pub2
Emollients and moisturisers for eczema
Abstract
Background: Eczema is a chronic skin disease characterised by dry skin, intense itching, inflammatory skin lesions, and a considerable impact on quality of life. Moisturisation is an integral part of treatment, but it is unclear if moisturisers are effective.
Objectives: To assess the effects of moisturisers for eczema.
Search methods: We searched the following databases to December 2015: Cochrane Skin Specialised Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, LILACS, the GREAT database. We searched five trials registers and checked references of included and excluded studies for further relevant trials.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials in people with eczema.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard Cochrane methodological procedures.
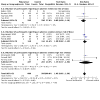
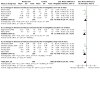
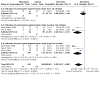
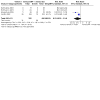
Main results: We included 77 studies (6603 participants, mean age: 18.6 years, mean duration: 6.7 weeks). We assessed 36 studies as at a high risk of bias, 34 at unclear risk, and seven at low risk. Twenty-four studies assessed our primary outcome 'participant-assessed disease severity', 13 assessed 'satisfaction', and 41 assessed 'adverse events'. Secondary outcomes included investigator-assessed disease severity (addressed in 65 studies), skin barrier function (29), flare prevention (16), quality of life (10), and corticosteroid use (eight). Adverse events reporting was limited (smarting, stinging, pruritus, erythema, folliculitis).Six studies evaluated moisturiser versus no moisturiser. 'Participant-assessed disease severity' and 'satisfaction' were not assessed. Moisturiser use yielded lower SCORAD than no moisturiser (three studies, 276 participants, mean difference (MD) -2.42, 95% confidence interval (CI) -4.55 to -0.28), but the minimal important difference (MID) (8.7) was unmet. There were fewer flares with moisturisers (two studies, 87 participants, RR 0.40, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.70), time to flare was prolonged (median: 180 versus 30 days), and less topical corticosteroids were needed (two studies, 222 participants, MD -9.30 g, 95% CI -15.3 to -3.27). There was no statistically significant difference in adverse events (one study, 173 participants, risk ratio (RR) 15.34, 95% CI 0.90 to 261.64). Evidence for these outcomes was low quality.With Atopiclair (three studies), 174/232 participants experienced improvement in participant-assessed disease severity versus 27/158 allocated to vehicle (RR 4.51, 95% CI 2.19 to 9.29). Atopiclair decreased itching (four studies, 396 participants, MD -2.65, 95% CI -4.21 to -1.09) and achieved more frequent satisfaction (two studies, 248 participants, RR 2.14, 95% CI 1.58 to 2.89), fewer flares (three studies, 397 participants, RR 0.18, 95% CI 0.11 to 0.31), and lower EASI (four studies, 426 participants, MD -4.0, 95% CI -5.42 to -2.57), but MID (6.6) was unmet. The number of participants reporting adverse events was not statistically different (four studies, 430 participants, RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.79 to 1.33). Evidence for these outcomes was moderate quality.Participants reported skin improvement more frequently with urea-containing cream than placebo (one study, 129 participants, RR 1.28, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.53; low-quality evidence), with equal satisfaction between the two groups (one study, 38 participants, low-quality evidence). Urea-containing cream improved dryness (investigator-assessed) more frequently (one study, 128 participants, RR 1.40, 95% CI 1.14 to 1.71; moderate-quality evidence) with fewer flares (one study, 44 participants, RR 0.47, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.92; low-quality evidence), but more participants in this group reported adverse events (one study, 129 participants, RR 1.65, 95% CI 1.16 to 2.34; moderate-quality evidence).Three studies assessed glycerol-containing moisturiser versus vehicle or placebo. More participants in the glycerol group noticed skin improvement (one study, 134 participants, RR 1.22, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.48; moderate-quality evidence), and this group saw improved investigator-assessed SCORAD (one study, 249 participants, MD -2.20, 95% CI -3.44 to -0.96; high-quality evidence), but MID was unmet. Participant satisfaction was not addressed. The number of participants reporting adverse events was not statistically significant (two studies, 385 participants, RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.19; moderate-quality evidence).Four studies investigated oat-containing moisturisers versus no treatment or vehicle. No significant differences between groups were reported for participant-assessed disease severity (one study, 50 participants, RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.84 to 1.46; low-quality evidence), satisfaction (one study, 50 participants, RR 1.06, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.52; very low-quality evidence), and investigator-assessed disease severity (three studies, 272 participants, standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.23, 95% CI -0.66 to 0.21; low-quality evidence). In the oat group, there were fewer flares (one study, 43 participants, RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.7; low-quality evidence) and less topical corticosteroids needed (two studies, 222 participants, MD -9.30g, 95% CI 15.3 to -3.27; low-quality evidence), but more adverse events were reported (one study, 173 participants; Peto odds ratio (OR) 7.26, 95% CI 1.76 to 29.92; low-quality evidence).All moisturisers above were compared to placebo, vehicle, or no moisturiser. Participants considered moisturisers more effective in reducing eczema (five studies, 572 participants, RR 2.46, 95% CI 1.16 to 5.23; low-quality evidence) and itch (seven studies, 749 participants, SMD -1.10, 95% CI -1.83 to -0.38) than control. Participants in both treatment arms reported comparable satisfaction (three studies, 296 participants, RR 1.35, 95% CI 0.77 to 2.26; low-quality evidence). Moisturisers led to lower investigator-assessed disease severity (12 studies, 1281 participants, SMD -1.04, 95% CI -1.57 to -0.51; high-quality evidence) and fewer flares (six studies, 607 participants, RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.17 to 0.62; moderate-quality evidence), but there was no difference in adverse events (10 studies, 1275 participants, RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.30; moderate-quality evidence).Topical active treatment combined with moisturiser was more effective than active treatment alone in reducing investigator-assessed disease severity (three studies, 192 participants, SMD -0.87, 95% CI -1.17 to -0.57; moderate-quality evidence) and flares (one study, 105 participants, RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.20 to 0.93), and was preferred by participants (both low-quality evidence). There was no statistically significant difference in number of adverse events (one study, 125 participants, RR 0.39, 95% CI 0.13 to 1.19; very low-quality evidence). Participant-assessed disease severity was not addressed.
Authors' conclusions: Most moisturisers showed some beneficial effects, producing better results when used with active treatment, prolonging time to flare, and reducing the number of flares and amount of topical corticosteroids needed to achieve similar reductions in eczema severity. We did not find reliable evidence that one moisturiser is better than another.
Conflict of interest statement
Esther J van Zuuren: nothing to declare. Zbys Fedorowicz: nothing to declare. Adriana Lavrijsen: nothing to declare. Robin Christensen: nothing to declare. Bernd Arents: nothing to declare. Matthew Ridd (referee of the protocol): "I am chief investigator on a feasibility trial comparing four commonly used emollients in children with eczema (not yet published but likely to be included in this review). I have recently submitted an application for funding to take this study to a full trial." Sandra Lawton (referee of the protocol): "I have received an honorarium for speaking at meetings from Genus, Almirall, and Thornton & Ross Ltd, and for reviewing an educational programme for Bayer."
Figures






















Comment in
-
From the Cochrane Library: Emollients and Moisturizers for Eczema.Dermatology. 2022;238(3):594-596. doi: 10.1159/000518773. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Dermatology. 2022. PMID: 34511590 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abramovits 2008 {published data only}
-
- Abramovits W, Boguniewicz M, Adult Atopiclair Study Group. A multicenter, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical study to examine the efficacy and safety of MAS063DP (Atopiclair) in the management of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in adults. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2006;5(3):236-44. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Abramovits W, Hebert A, Boguniewicz M. A multicenter randomized, vehicle-controlled, double-blind clinical study to examine the safety and efficacy of MAS063DP in the management of AD. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2006;54(Suppl 3):AB84. - PubMed
-
- Abramovits W, Hebert AA, Boguniewicz M, Kempers SE, Tschen E, Jarratt MT, et al. Patient-reported outcomes from a multicenter, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical study of MAS063DP (Atopiclair) in the management of mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in adults. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2008;19(6):327-32. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Åkerström 2015 {published data only}
-
- Åkerström U, Reitamo S, Langeland T, Berg M, Rustad L, Korhonen L. Comparison of moisturizing creams for the prevention of atopic dermatitis relapse: a randomized double-blind controlled multicentre clinical trial. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2015;95(5):587-92. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Andersson 1999 {published data only}
-
- Andersson A-C, Lindberg M, Lodén M. The effect of two urea-containing creams on dry, eczematous skin in atopic patients. I. Expert, patient and instrumental evaluation. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 1999;10(3):165-9.
-
- Lodén M, Andersson AC, Lindberg M. The effect of two urea-containing creams on dry, eczematous skin in atopic patients. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 1999;10(3):171-5.
Angelova‐Fischer 2014 {published data only}
-
- Angelova-Fischer I, Neufang G, Jung K, Fischer TW, Zillikens D. A randomized, investigator-blinded efficacy assessment study of stand-alone emollient use in mild to moderately severe atopic dermatitis flares. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2014;28(Suppl 3):9-15. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Belloni 2005 {published data only}
-
- Belloni G, Pinelli S, Veraldi S. A randomised, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of MAS063D (Atopiclair) in the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. European Journal of Dermatology 2005;15(1):31-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Berents 2015 {published data only}
Berth‐Jones 2003 {published data only}
-
- Berth-Jones J, Damstra RJ, Golsch S, Livden JK, Van Hooteghem O, Allegra F, et al. Twice weekly fluticasone propionate added to emollient maintenance treatment to reduce risk of relapse in atopic dermatitis: randomised, double blind, parallel group study. BMJ 2003;326(7403):1367. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Glazenburg E, Graham-Brown R, Hanifin J, Berth-Jones J, Meer J. Intermittent dosing with topical fluticasone propionate delays the time to relapse in adults and children with chronic atopic dermatitis - two randomised controlled studies. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2001;117(2):533.
Bissonnette 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bissonnette R, Maari C, Provost N, Bolduc C, Nigen S, Rougier A, et al. A double-blind study of tolerance and efficacy of a new urea-containing moisturizer in patients with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 2010;9(1):16-21. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Boguniewicz 2008 {published data only}
-
- Boguniewicz M, Eichenfield L, Hebert A, Jarratt M. A multicenter, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical study to examine the efficacy and safety of MAS063DP nonsteroidal cream in the management of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in infants and children. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2007;56(2):AB69.
-
- Boguniewicz M, Zeichner JA, Eichenfield LF, Hebert AA, Jarratt M, Lucky AW et al. MAS063DP is effective monotherapy for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in infants and children: a multicenter, randomized, vehicle-controlled study. The Journal of Pediatrics 2008;152(6):854-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bohnsack 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bohnsack K, Tausch I, Gassmuller J, Rippke F. Efficacy on the symptom "dry skin"and long-term dermal tolerance of Laceran Lotion 10% urea in patients with atopic dermatitis [Wirksamkeit auf das Symptom "trockene Haut" und Langzeitveträglichkeit von Laceran Lotion 10% Urea bei Patienten mit Atopischem Ekzem]. Zeitschrift fur Hautkrankheiten 1997;72(1):34-9.
Boralevi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Boralevi F, Saint Aroman M, Delarue A, Raudsepp H, Kaszuba A, Bylaite M, et al. Long-term emollient therapy improves xerosis in children with atopic dermatitis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2014;28(11):1456-62. [DOI: 10.1111/jdv.12314] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Breternitz 2008 {published data only}
-
- Breternitz M, Kowatzki D, Langenauer M, Elsner P, Fluhr JW. Placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized, prospective study of a glycerol-based emollient on eczematous skin in atopic dermatitis: biophysical and clinical evaluation. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology 2008;21(1):39-45. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Danby 2011 {published data only}
-
- Danby S, Al Enezi T, Chittock J, Kennedy K, Sultan A, Cork M. A randomized comparison of aqueous cream and Oilatum Junior bath additive on skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2011;165(Suppl 1):44-5. - PubMed
-
- Danby S, Al Enezi T, Chittock J, Kennedy K, Sultan A, Cork M. A randomized comparison of aqueous cream and Oliatum junior bath additive on skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2011;165(1):115. - PubMed
De Belilovsky 2011 {published data only}
-
- De Belilovsky C, Baudouin C, Bredif S, Chadoutaud B, Msika P. Sunflower oleodistillate: A topical PPAR-alpha (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors) agonist developed for atopic dermatitis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2011;131(S1):S141.
-
- De Belilovsky C, Chadoutaud B, Baudouin C, Msika P. Sunflower oleodistillate: A topical PPAR-alpha agonist developed for atopic dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;64(2 Suppl 1):AB58.
-
- De Belilovsky C, Msika P, Menu F, Baudouin C, Chadoutaud B. Natural PPAR-alpha agonist and atopic dermatitis: From research to clinical efficacy. European Journal of Pediatric Dermatology 2010;20(1):63.
-
- De Belilovsky C, Roo-Rodriguez E, Baudouin C, Menu F, Chadoutaud B, Msika P. Natural peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist cream demonstrates similar therapeutic response to topical steroids in atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2011;22(6):359-65. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Draelos 2008 {published data only}
-
- Draelos ZD. The effect of ceramide-containing skin care products on eczema resolution duration. Cutis 2008;81(1):87-91. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Draelos 2009 {published data only}
-
- Draelos ZD. An evaluation of prescription device moisturizers. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 2009;8(1):40-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Draelos 2011 {published data only}
-
- Draelos ZD. A clinical evaluation of the comparable efficacy of hyaluronic acid-based foam and ceramide-containing emulsion cream in the treatment of mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 2011;10(3):185-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Emer 2011 {published data only}
-
- Emer JJ, Frankel A, Sohn A, Lebwohl M. A bilateral comparison study of pimecrolimus cream 1% and a topical medical device cream in the treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2011;10(7):735-43. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Evangelista 2014 {published data only}
-
- Evangelista MT, Abad-Casintahan F, Lopez-Villafuerte L. The effect of topical virgin coconut oil on SCORAD index, transepidermal water loss, and skin capacitance in mild to moderate pediatric atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. International Journal of Dermatology 2014;53(1):100-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Evangelista MTP, Casintahan FA, Villafuerte LL. The effect of topical virgin coconut oil on SCORAD, transepidermal water loss and skin capacitance in mild to moderate pediatric atopic dermatitis: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial. In: Conference: 2013 Annual American Contact Dermatitis Society, ACDS Meeting Miami Beach, FL United States. 2013.
Faergemann 2009 {published data only}
-
- Faergemann J, Olsson P, Svensson A. A randomized, single-blind comparison of the efficacy, tolerability and cosmetic acceptance of Propyless or Fenuril treatment of patients with dry skin. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2009;89(3):305-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Faergemann J, Svensson A. A randomised investigator-blind study comparing the efficacy, tolerability and cosmetic acceptance of Propyless and Fenuril on dry skin. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2005;19(Suppl 2):196-7.
Ferreira 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ferreira MJ, Fiadeiro T, Silva M, Soares AP. Topical gamma-linolenic acid therapy in atopic dermatitis. A clinical and biometric evaluation. Allergo Journal 1998;7(4):213-6.
Frankel 2011 {published data only}
-
- Frankel A, Sohn A, Emer J, Lebwohl M. Bilateral comparison study of pimecrolimus cream 1% and a ceramide-hyaluronic acid based emollient foam in the treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;64(2 Suppl 1):AB59. - PubMed
-
- Frankel A, Sohn A, Patel RV, Lebwohl M. Bilateral comparison study of pimecrolimus cream 1% and a ceramide-hyaluronic acid emollient foam in the treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2011;10(6):666-72. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Fredriksson 1975 {published data only}
-
- Fredriksson T, Gip L. Urea creams in the treatment of dry skin and hand dermatitis. International Journal of Dermatology 1975;14(6):442-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gao 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gao Y. Effectiveness observation on moisturizer for infant eczema. China Journal of Leprosy and Skin Diseases [Zhong Guo Ma Feng Pi Fu Bing Za Zhi] 2008;24(4):294.
Gayraud 2015 {published data only}
-
- Gayraud F, Imko-Walczuk, Sayag M, Jourdan E. Comparative, randomized, double-blinded study assessing the efficacy of a new kind of dermocosmetic product containing skin barrier therapy on infants and children with moderate atopic dermatitis. Journal of the German Society of Dermatology 2014;12(Suppl 2):14.
-
- Gayraud F, Sayag M, Jourdan E. Efficacy and tolerance assessment of a new type of dermocosmetic in infants and children with moderate atopic dermatitis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 2015;14(2):107-12. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gehring 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gehring W, Gloor M. Treatment of the atopic dermatitis with a water-in-oil emulsion with or without the addition of hydrocortisone - Results of a controlled double-blind randomized study using clinical evaluation and bioengineering methods [Behandlung der neurodermitis atopica mit einer W/O-Emulsion mit und ohne Hydrocortison - Ergebnisse einder klinisch u. meßmethodische controllierten randomisierten Doppelblindstudie]. H+G Zeitschrift für Hautkrankheiten 1996;71(7):554-60.
Gehring 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gehring W, Bopp R, Rippke F, Gloor M. Effect of topically applied evening primrose oil on epidermal barrier function in atopic dermatitis as a function of vehicle. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1999;49(7):635-42. - PubMed
Giordano‐Labadie 2006 {published data only}
-
- Giordano Labadie F, Cambazard F, Guillet C, Combemale P, Mengeaud V. Interest of a moisturizer milk containing oat rhealba extracts in atopic dermatitis. In: 20th World Congress of Dermatology Paris 1st- 5th of July. P0203 edition. 2002.
-
- Giordano-Labadie F, Cambazard F, Guillet G, Combemale P, Mengeaud V. Evaluation of a new moisturizer (Exomega milk) in children with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2006;17(2):78-81. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Glazenburg 2009 {published data only}
-
- Glazenburg EJ, Wolkerstorfer A, Gerretsen AL, Mulder PG, Oranje AP. Efficacy and safety of fluticasone propionate 0.005% ointment in the long-term maintenance treatment of children with atopic dermatitis: differences between boys and girls? Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2009;20(1):59-66. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Glazenburg EJ, Wolkerstorfer A, Gerretsen AL, Oranje AP. Twice weekly topical fluticasone propionate delays the time to relapse in children with chronic atopic dermatitis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2003;17(Suppl 3):184.
Grimalt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Grimalt R, Cambazard F. Evaluation of the corticosteroid-sparing effect of a new emollient in 162 atopic infants. In: 4th European Association of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Spring Symposium Saariselka, Lapland, Finland. February 9-12th. 2006:P-009.
-
- Grimalt R, Mengeaud V, Cambazard F, Study IG . The steroid-sparing effect of an emollient therapy in infants with atopic dermatitis: a randomized controlled study. Dermatology 2007;214(1):61-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Josse M, Mengeaud V, Durosier V, Sibaud V, Grimalt R, Cambazard F. Evaluation of the Corticosteroid-Sparing Effect of an Emollient Milk in a Large Population of Infants Affected by Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2005;125(3):612.
Hagströmer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hagströmer L, Nyrén M, Emstesam L. Urea and sodium chloride in moisturisers for dry atopic skin: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 1999;12(Suppl 2):S160.
-
- Hagströmer L, Nyrén M, Emtestam L. Do urea and sodium chloride together increase the efficacy of moisturisers for atopic dermatitis skin? A comparative, double-blind and randomised study. Skin Pharmacology and Applied Skin Physiology 2001;14(1):27-33. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Hagströmer L, Nyrén M, Emtestam L. Moisturisers for dry atopic skin: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Contact Dermatitis 2000;42(Suppl):52.
Hagströmer 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hagströmer L, Kuzmina N, Lapins J, Talme T, Emtestam L. Biophysical assessment of atopic dermatitis skin and effects of a moisturizer. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 2006;31(2):272-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hamada 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hamada M, Gyoutoku T, Sato S, Matsuda T, Kinukawa N, Furue M. The usefulness of camellia oil spray for treatment of atopic dermatitis. Nishinihon Journal of Dermatology 2008;70(2):213-8.
Hanifin 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hanifin JM, Hebert AA, Mayes S, Paller A, Sheretz EF, Wagner Aetal. Bilateral regimen comparison of desonide lotion, 0.05% vs desonide lotion, 0.05% plus a moisturizing cream in patients with atopic dermatitis. In: Australasian Journal of Dermatology. Vol. 38. 1997:233.
-
- Hanifin JM, Hebert AA, Mays SR, Paller A, Sherertz EF, Wagner AM, et al. Effects of a low-potency corticosteroid lotion plus a moisturizing regimen in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1998;59(4):227-33.
Hanifin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Glazenburg EJ, Meer JB. Safety of fluticasone propionate. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2002;16(Suppl 1):P2-34.
-
- Hanifin J, Berth-Jones J. Consensus from 4 studies—use of twice weekly fluticasone propionate can maintain remission in moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2003;121(1):199.
-
- Hanifin J, Gupta AK, Rajagopalan R. Intermittent dosing of fluticasone propionate cream for reducing the risk of relapse in atopic dermatitis patients. British Journal of Dermatology 2002;147(3):528-37. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Harper 1995 {published data only}
-
- Harper J. Double-blind comparison of an antiseptic oil-based bath additive (Oilatum Plus) with regular Oilatum (Oilatum emollient) for the treatment of atopic eczema. In: Lever R, Levy J, editors(s). The Bacteriology of Eczema. Round Table Series 37 edition. Vol. 37. London: The Royal Society of Medicine Press Ltd, 1995:42-7.
Hlela 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hlela C, Lunjani N, Gumedze F, Kakande B, Khumalo NP. Affordable moisturisers are effective in atopic eczema: A randomised controlled trial. South African Medical Journal 2015;105(9):780-4. - PubMed
Janmohamed 2014 {published data only}
-
- Janmohamed SR, Gutermuth J, Oranje AP. The wet-wrap method with diluted corticosteroids versus emollients in children with atopic dermatitis-a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2015;135(S2):S38. - PubMed
-
- Janmohamed SR, Oranje AP, Devillers AC, Rizopoulos D, Praag MC, Van Gysel, et al. The proactive wet-wrap method with diluted corticosteroids versus emollients in children with atopic dermatitis: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;70(6):1076-82. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Jirabundansuk 2014 {published data only}
-
- Jirabundansuk P, Ophaswongse S, Udompataikul M. Comparative trial of moisturizer containing spent grain wax, Butyrospermum parkii extract, Argania spinosa kernel oil vs. 1% hydrocortisone cream in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2014;97(8):820-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kircik 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kircik L. Skin barrier function and hydration effects of hydrolipid cream alone and in combination in the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis: Investigator-blinded, split-body, pilot study results. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;62(3 Suppl 1):AB67.
Kircik 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kircik LH. Effect of skin barrier emulsion cream vs a conventional moisturizer on transepidermal water loss and corneometry in atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2014;13(12):1482-4. [PMID: 25607793] - PubMed
Korting 2010 {published data only}
-
- Korting HC, Schöllmann C, Cholcha W, Wolff L, Collaborative SG . Efficacy and tolerability of pale sulfonated shale oil cream 4% in the treatment of mild to moderate atopic eczema in children: a multicentre randomized vehicle-controlled trial. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2010;24(10):1176-82. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Larregue 1996 {published data only}
-
- Larregue M, Devaux J, Audebert C, Gelmetti DR. A double-blind controlled study on the efficacy and tolerability of 6% ammonium lactate cream in children with atopic dermatitis. Nouvelles Dermatologiques 1996;15(10):720-1.
Laumann 2006 {published data only}
-
- Laumann A, Lai S, Lucky AW, Schlessinger J, Jarratt M Jones TM, et al. The efficacy and safety of MimyX Cream in reducing the risk of relapse in atopic dermatitis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2006;126(Suppl 1s):45.
Lodén 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lodén M, Andersson AC, Andersson C, Frödin T, Oman H, Lindberg M. Instrumental and dermatologist evaluation of the effect of glycerine and urea on dry skin in atopic dermatitis. Skin Research and Technology 2001;7(4):209-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lodén 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lodén M, Andersson AC, Anderson C, Bergbrant IM, Frödin T, Ohman H, et al. A double-blind study comparing the effect of glycerin and urea on dry, eczematous skin in atopic patients. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2002;82(1):45-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Marseglia 2014 {published data only}
Miller 2011 {published data only}
-
- Miller DW, Clark AR, Fleischer AB, Yentzer BA, Koch SB. An over the counter moisturizer is as clinically effective as, and more cost-effective than, prescription barrier creams in the treatment of children with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;64(2 Suppl 1):AB57. - PubMed
-
- Miller DW, Koch SB, Yentzer BA, Clark AR, O'Neill JR, Fountain J, et al. An over-the-counter moisturizer is as clinically effective as, and more cost-effective than, prescription barrier creams in the treatment of children with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis: a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2011;10(5):531-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Msika 2008 {published data only}
-
- Msika C, De Belilovsky C, Menu F, Baudouin C, Chadoutaud B. Natural PPAR-alpha agonist and atopic dermatitis: From research to clinical efficacy. Contact Dermatitis 2010;63(Suppl 1):68.
-
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Chadoutaud IB, Nicolas JF. New Natural PPAR-a agonist for childhood atopic dermatitis: Dermocorticoid-sparing and quality of life improvement. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2006;126(Suppl 3):S102.
-
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Chadoutaud IB, Nicolas JF. New natural PPAR-a agonist for childhood atopic dermatitis: Dermocorticoid- sparing and quality of life improvement. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2007;56(2):AB67.
-
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Menu F, Baudouin C, Chadoutaud B. Natural PPAR-alpha agonist and Atopic dermatitis: From research to clinical efficacy. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2010;130(10):2524.
-
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Menu F, Baudouin C, Chadoutaud B. Natural PPAR-alpha agonist and atopic dermatitis: From research to clinical efficacy. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2010;130(Suppl 1):S54.
Namazova‐Baranova 2012 {published data only}
-
- Namazova-Baranova L, Vishneva E, Levina J, Torshkhoeva R, Alekseeva A, Efendieva K, et al. Combined therapy of atopic dermatitis in children. Allergy 2012;67(Suppl 96):181-2.
-
- Namazova-Baranova LS, Vishneva EA, Torshhoeva RM, Dzagoeva ZN, Alexeeva AA, Levina JG, et al. Non-steroidal topical medications in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children. Pediatric Pharmacology [Pediatricheskaya farmakologiya] 2012;9(1):66-70.
Nebus 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nebus J, Nystrand G, Fowler J, Wallo W. A daily oat-based skin care regimen for atopic skin. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;62(3 Suppl 1):AB67.
Nho 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kim YS, Jung YL, Youm JK, Park JH, Bae YI, Lee SH. The effects of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α (PPARα) activator on patients with facial erythema. Korean Journal of Dermatology 2014;52(8):608-14.
-
- Nho Y, Kim H, Jung Y, Kim S, Kim Y, Lee Setal. A combination of PPARα activator and ceramide improves red face originated from variable skin diseases. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2014;134(S1):S95.
Noh 2011 {published data only}
-
- Noh S, Jung JY, Park WS, Koh HJ, Lee KH. The Steroid-sparing Effect of an Emollient APDDR-0801 in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Korean Journal of Dermatology 2011;49(3):227-33.
Nuñez 2013 {published data only}
-
- Nuñez C, Hogan D, Humphrey M, Zhang P, Lisante T, Doshi U. A colloidal oatmeal OTC cream is as clinically effective as a prescription barrier repair cream for the management of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in African American children. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2013;68(4 Suppl 1):AB73.
Park 2014 {published data only}
Patrizi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Patrizi A, Capitanio B, Neri I, Giacomini F, Sinagra JL, Raone B, et al. A double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of MAS063DP (ATOPICLAIR[trademark]) in the management of atopic dermatitis in paediatric patients. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2008;19(7):619-25. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Patrizi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bianchi P, Villeneuve C, Theunis J, Casas C, Patrizi A, Bacquey A, et al. Evaluation of a novel emollient balm containing Aquaphilus dolomiae extract in atopic dermatitis children: Effect on clinical parameters, skin barrier and microflora. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2014;134(Suppl 1):S96.
-
- Patrizi A, Bacquey A, Schmitt AM, Decoster CJ, Phulpin C, Theunis J, et al. Clinical and biometrologic evaluation of a novel emollient balm containing an Aquaphilus dolomiae extract in 1-to 4-year-old children suffering from atopic dermatitis: International,multicenter, randomized versus control group study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;70(5 Suppl 1):AB62.
Peltonen 2014 {published data only}
-
- Peltonen JM, Pylkkänen L, Jansén CT, Volanen I, Lehtinen T, Laihia JK, et al. Three randomised phase I/IIa trials of 5% cis-urocanic acid emulsion cream in healthy adult subjects and in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2014;94(4):415-20. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Peserico 2008 {published data only}
-
- Peserico A, Städtler G, Sebastian M, Fernandez RS, Vick K, Bieber T. Reduction of relapses of atopic dermatitis with methylprednisolone aceponate cream twice weekly in addition to maintenance treatment with emollient: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, controlled study. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;158(4):801-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Pigatto 1996 {published data only}
-
- Pigatto PD, Bigardi AS, Cannistraci C, Picardo M. 10% urea cream (Laceran) for atopic dermatitis: A clinical and laboratory evaluation. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 1996;7(3):171-5.
Puschmann 2003 {published data only}
-
- Puschmann M, Melzer A, Welzel J. Extensive treatment of itching, dry dermatoses with a polidocanol-urea-combination. Aktuelle Dermatologie 2003;29(3):77-81.
Shi 2015 {published data only}
-
- Shi VY, Foolad N, Ornelas JN, Hassoun L, Monico G, Takeda N, et al. Comparing the effect of bleach and water baths on skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis: a split-body randomized controlled trial. British Journal of Dermatology 2016;175(1):212-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Shi VY, Foolad N, Takeda N, Hassoun L, Johal R, Saric S, et al. The effect of dilute bleach bath and moisturizers on skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(Suppl 1):AB76.
Shiratori 1977 {published data only}
-
- Shiratori A, Ikazi M, Tamada T, Sato Y, Igarashi R, Ishikawa H, et al. A double-blind study on clinical efficacy of urea ointment. Rinsho Hyoka (Clinical Evaluation) 1977;5(1):103-25.
Simpson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Dutronc Y, Guennoun M. Hydration potential of a new body moisturizer. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;64(2 Suppl 1):AB58.
-
- Simpson E, Dutronc Y. A new body moisturiser increases skin hydration and improves atopic dermatitis symptoms among children and adults. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2011;10(7):744-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Simpson E Dutronc Y Caveney S. A new body moisturizer increases skin hydration among children and adults with atopic dermatitis symptoms. Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery 2012;31(1):A5.
Simpson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Simpson E, Böhling A, Bielfeldt S, Bosc C, Kerrouche N. Improvement of skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis patients with a new moisturizer containing a ceramide precursor. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2013;24(2):122-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Simpson E. Improvement of skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis patients with a new moisturizer containing a ceramide precursor. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2013;68(4 Suppl 1):AB77. - PubMed
Sugarman 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sugarman IL, Parish LJ. A topical physiologic lipid-based, barrier repair formulation (Epiceram™ cream) is highly effective monotherapy for moderate-to-severe pediatric atopic dermatitis: a multicenter, investigator-blinded trial comparing a barrier repair formulation, Epiceram™, to fluticasone proprionate (Cutivate®) cream. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2008;128(Suppl 1):S54.
-
- Sugarman JL, Parish LC. Efficacy of a lipid-based barrier repair formulation in moderate-to-severe pediatric atopic dermatitis. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2009;8(12):1106-11. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Takeuchi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Takeuchi S, Saeki H, Tokunaga S, Torii H, Nakamura K, Soma Y, et al. A randomized,multicenter trial of topical tacrolimus for treatment of pruritus in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2009;89:704.
-
- Takeuchi S Furue M. Itch control in atopic dermatitis. In: New Trends in Allergy VII and 6th Georg Rajka Symposium on Atopic Dermatitis, Munich, Germany. 2010.
Tan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tan WP, Goon A, Suresh S, Tey HL, Chiam LY. A randomized double-blind controlled trial to compare a triclosan-containing emollient with vehicle for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2010;60(3 Suppl 1):AB70. - PubMed
-
- Tan WP, Suresh S, Tey HL, Chiam LY, Goon AT. A randomized double-blind controlled trial to compare a triclosan-containing emollient with vehicle for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 2010;35(4):e109-12. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Thumm 2000 {published data only}
-
- Thumm EJ, Stoss M, Bayerl C, Schürholz T. Randomized trial to study efficacy of a 20% and 10% Hippophae rhamnoides containing creme used by patients with mild to intermediate atopic dermatitis [Überprüfung der Wirksamkeit einer 20%igen und 10%igen Sanddornkernölcreme bei Patienten mit leichter bis mittelgradiger atopischer Dermatitis]. Aktuelle Dermatologie 2000;26(8-9):285-90.
Tripodi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tripodi S, Di Rienzo Businco A, Panetta V, Pingitore G, Volterrani A, Frediani T, et al. Lack of efficacy of topical furfuryl palmitate in pediatric atopic dermatitis: a randomized double-blind study. Journal of Investigational Allergology & Clinical Immunology 2009;19(3):204-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Udompataikul 2011 {published data only}
-
- Udompataikul M, Srisatwaja W. Comparative trial of moisturizer containing licochalcone A vs. hydrocortisone lotion in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology: JEADV 2011;25(6):660-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Verallo‐Rowell 2008 {published data only}
-
- Verallo-Rowell VM, Dillague KM, Syah-Tjundawan BS. Novel antibacterial and emollient effects of coconut and virgin olive oils in adult topic dermatitis. Dermatitis 2008;19(6):308-15. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Wanakul 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wananukul S, Chatproedprai S, Chunharas A, Limpongsanuruk W, Singalavanija S, Chantorn R. Comparison study of moisturiser containing licochalcone A and 1%hydrocortisone in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2012;67(Suppl 96):634. - PubMed
-
- Wananukul S, Chatproedprai S, Chunharas A, Limpongsanuruk W, Singalavanija S, Nitiyarom R, et al. Randomized, double-blind, split-side, comparison study of moisturizer containing licochalcone A and 1% hydrocortisone in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2013;96(9):1135-42. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Weber 2015 {published data only}
-
- Weber TM, Samarin F, Babcock MJ, Filbry A, Arrowitz CE, Rippke E. A novel daily moisturizing cream for effective management of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in infants and children. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(5 Suppl 1):AB73.
-
- Weber TM, Samarin F, Babcock MJ, Filbry A, Rippke F. Steroid-Free Over-the-Counter Eczema Skin Care Formulations Reduce Risk of Flare, Prolong Time to Flare, and Reduce Eczema Symptoms in Pediatric Subjects With Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2015;14(5):478-85. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Wilhelm 1998 {published data only}
-
- Wilhelm KP, Schölermann A, Bohnsack K, Wilhelm D, Rippke F. Efficacy and tolerability of a topical preparation containing 10% urea in patients with atopic dermatitis [Wirksamkeit und Verträglichkeit einer topischer Zubereitung mit 10% Urea (Laceran® Salbe 10% Urea bei Neurodermitis]. Aktuelle Dermatologie 1998;24(1-2):26-30.
Wirén 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hjalte F, Asseburg C, Tennvall GR. Cost-effectiveness of a barrier-strengthening moisturizing cream as maintenance therapy vs. no treatment after an initial steroid course in patients with atopic dermatitis in Sweden--with model applications for Denmark, Norway and Finland. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2010;24(4):474-80. [PMID: PMID: 19793150] - PubMed
-
- Wirén K, Nohlgård C, Nyberg F, Holm L, Svensson M, Johannesson A, et al. Treatment with a barrier-strengthening moisturizing cream delays relapse of atopic dermatitis: a prospective and randomized controlled clinical trial. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology: JEADV 2009;23(11):1267-72. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Wu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Wu Y-Q, Pan J-S, Zhao W-Q. Clinical observation of moisture and softening cream (MSC) combined with compound flumetasone ointment for chronic eczema. Journal of Clinical Dermatology 2014;43(7):434-6.
References to studies excluded from this review
Duggan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Duggan C. Eczema on trial. Journal of Family Health 2015;25(3):10, 12. - PubMed
Dutronc 2011B {published data only}
-
- Dutronc Y. Irritation potential and cosmetic acceptability of a new body moisturizer. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;64(2 Suppl 1):AB58.
Schoelermann 2003 {published data only}
-
- Schölermann A. 10% urea: an effective moisturizer in various dry skin conditions. In: 20th World Congress of Dermatology Paris 1st to 5th July. 2002- P0259.
-
- Schoelermann A, Fibry A, Rippke F. 10% urea: an effective moisturizer in various dry skin conditions. British Journal of Dermatology 2003;149(Suppl 64):79.
Szczepanowska 2008 {published data only}
-
- Szczepanowska J, Reich A, Szepietowski JC. Emollients improve treatment results with topical corticosteroids in childhood atopic dermatitis: a randomized comparative study. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2008;19(7):614-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yang XY, Xu LM, Zhou AM, Wen H, Wu Y, Hao F, et al. The adjuvant treatment of atopic dermatitis with medical skin preparation containing extracts from Portulaca oleracea and avocado. Journal of Clinical Dermatology 2010;39(7):460-2.
References to ongoing studies
ACTRN12615000782538 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12615000782538. A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled comparative trial of Ceramide Cream and Ceramide Cleanser in the management of moderate eczema in adults. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ACTRN12615000782538 Date first received: 28 July 2015.
ACTRN12615000920594 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12615000920594. A randomised double blinded placebo controlled study investigating Atopis for the improvement of skin health in subjects with eczema. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ACTRN12615000920594 Date first received: 2 September 2015.
ACTRN12615001343594 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12615001343594. Epaderm ointment in children with eczema [Pilot study comparing two emollients, Emulsifying ointment B.P. and Epaderm topical ointment in children with eczema]. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ACTRN12615001343594 Date first received: 9 December 2015.
ChiCTR‐IOR‐15007139 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR-IOR-15007139. Effect andEfficacy of a Linoleic Acid-Ceramide Containing Moisturizer in atopic dermatitis [Effect and Efficacy of a Linoleic Acid-Ceramide Containing Moisturizer as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of atopic dermatitis:A Randomized Controlled Trial]. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ChiCTR-IOR-15007139 Date first received: 31 August 2015.
EudraCT2004‐002926‐23 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT 2004-002926-23. Evaluation of the impact of the moisturizing milk RV2478B on the use of corticoids and on quality of life, in a population of children with atopic dermatitis. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2004-002926-23/IT Date first received: 15 January 2007.
EudraCT2005‐003396‐21 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2005-003396-21. Long-term management of atopic dermatitis with the emollient V0034 CR. A randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-groups, double-blind study in infants and children. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2005-003396-21.
EudraCT2006‐000877‐30 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2006-000877-30. A 6 week, multi centre study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of E45 complete emollient therapy and E45 itch relief cream in the treatment of mild to moderate atopic eczema compared to a patients normal emollient regime defined as the frequent use of emollient/s (not containing lauromacrogols) listed in the BNF. - Harbour Study. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2006-000877-30.
EudraCT2007‐002133‐36 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2007-002133-36. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical study to examine the efficacy and safety of Zarzenda® in comparison to Elidel® in the management of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2007-002133-36.
EudraCT2008‐003485‐25 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2008-003485-25. Impact of the V0034CR 01B emollient on atopic dermatitis symptoms in children. A randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-groups, double-blind study. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2008-003485-25/DE Date first received: 12 September 2008.
EudraCT2008‐006844‐21 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2008-006844-21. Evaluation of a developmental ‘long lasting’ emollient in subjects with dry skin. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2008-006844-21/GB.
EudraCT2009‐010609‐35 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2009-010609-35. Is treatment with emollients always beneficial? Comparative biophysical and molecular biological studies of the skin barrier function in patients with atopic dermatitis, ichthyosis vulgaris and x-linked ichthyosis. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2009-010609-35/SE.
EudraCT2009‐016572‐78 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2009-016572-78. Arm immersion test to compare the skin effects of routine bathing with and without the use of an emollient bath additive. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=eudract_number:2009-01... Date first received: 17 March 2010.
EudraCT2012‐004621‐24 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2012-004621-24. Emollients in the management of atopic dermatitis in children: prevention of flares. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2012-004621-24.
EudraCT2014‐001026‐16 {published data only}
-
- EudraCT2014-001026-16. Randomised, double-blind, bilateral comparison of two emollients in patients with dry skin. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2014-001026-16.
ISRCTN97515110 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN97515110. Investigating whether topical application of a non toxic molecule improves epidermal pH and barrier function in atopic dermatitis. isrctn.com/ISRCTN97515110 Date first received: 21 October 2010.
JPRN‐UMIN000005158 {published data only}
-
- JPRN-UMIN000005158. Randomized controlled trial to evaluate clinical efficacy of once- or twice-daily skin care with emollient for prevention of atopic dermatitis exacerbation. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=JPRN-UMIN000005158 Date first received: 7 March 2011.
JPRN‐UMIN000010009 {published data only}
-
- JPRN-UMIN000010009. Study to evaluate the efficacy of conventional topical therapy for atopic dermatitis based on Filaggrin-gene mutations. http://apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=JPRN-UMIN000010009.
JPRN‐UMIN000017957 {published data only}
-
- JPRN-UMIN000017957. The effect of moisturizer on both sweating function and sensitive skin in patients with atopic dermatitis, a randomized comparative study. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=JPRN-UMIN000017957 Date first received: 18 June 2015.
NCT00180141 {published data only}
-
- NCT00180141. Elidel-study: Elidel in patients with atopic dermatitis [Control of therapy with Elidel vs placebo in patients with atopic dermatitis using bioengineering methods]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00180141 Date first received: 12 September 2005.
NCT00576238 {published data only}
-
- NCT00576238. Skin tolerance study of betamethasone creams in atopic eczema and the preventative properties of a moisturiser [A multi centre, parallel, randomised study of the skin tolerance of betamethasone creams on atopic eczema and the influence of moisturiser treatment on the recurrence of eczema]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00576238?term=NCT00576238&rank=1 Date first received: 18 December 2007.
NCT00828412 {published data only}
-
- NCT00828412. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of two topical creams for pediatric atopic dermatitis [A randomized, investigator-blind, six-week, parallel group, multicenter pilot study to compare the safety and efficacy of EpiCeram skin barrier emulsion and desonide cream 0.05% in the twice daily treatment of pediatric subjects with moderate atopic dermatitis]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00828412 Date first received: 21 January 2009.
NCT01779258 {published data only}
-
- NCT01779258. Emollients in the management of atopic dermatitis [Emollients in the management of atopic dermatitis in children: Prevention of flares]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01779258 Date first received: 28 January 2013.
NCT01781663 {published data only}
-
- NCT01781663. Efficacy of KAM2904 face cream and KAM3008 body lotion treatment in children with atopic dermatitis (AD). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01781663 Date first received: 29 January 2013.
NCT01915914 {published data only}
-
- NCT01915914. A randomized, open-label, comparative study to evaluate an intermittent dosing regimen of fluticasone propionate 0.05% cream (twice per week) in reducing the risk of relapse when added to regular daily moisturization using PHYSIOGEL lotion in paediatric subjects with stabilized atopic dermatitis. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01915914 Date first received: 27 June 2013.
NCT02028546 {published data only}
-
- NCT02028546. The effect of bathing and moisturizers on skin hydration in atopic dermatitis: an in vivo study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02028546 Date first received: 19 December 2013.
NCT02286700 {published data only}
-
- NCT02286700. Skin effects of a topical amino acid moisturizing cream and desonide in atopic dermatitis [A randomized, double-blind, active control, 5 week study to evaluate the safety and skin effects of a new, twice-daily, topically applied amino acid moisturizing cream vs. desonide cream in adult atopic dermatitis]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT02286700 Date first received: 4 November 2014.
NCT02376049 {published data only}
-
- NCT02376049. A clinical trial to compare topical agents in adults with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis (AD) [An explorative clinical trial to evaluate an intra patient comparison design of topical agents in adults with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02376049 Date first received: 25 February 2015.
NCT02589392 {published data only}
-
- NCT02589392. Cetaphil Restoraderm effect on young children with atopic dermatitis [Effect of Cetaphil® Restoraderm® moisturizer on very dry skin in children with a controlled atopic dermatitis: a randomised, parallel group study]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02589392 Date first received: 23 October 2015.
NTR4541 {published data only}
-
- NTR4541. Efficacy of Dermalex Eczema in atopic dermatitis patients [Efficacy of a skin barrier repair cream (Dermalex Eczema) in atopic dermatitis patients - EDA]. www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=4541 Date first received: 28 April 2014.
Ridd 2015 {published data only}
Additional references
Andersen 2015
-
- Andersen RM, Thyssen JP, Maibach HI. Qualitative vs. quantitative atopic dermatitis criteria - in historical and present perspectives. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2016;30(4):604-18. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Apfelbacher 2013
Arkwright 2013
-
- Arkwright PD, Motala C, Subramanian H, Spergel J, Schneider LC, Wollenberg A, et al. Management of difficult-to-treat atopic dermatitis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice 2013;1(2):142-51. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ashcroft 2007
Bamford 2013
Basra 2015
-
- Basra MK, Salek MS, Camilleri L, Sturkey R, Finlay AY. Determining the minimal clinically important difference and responsiveness of the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): further data. Dermatology 2015;230(1):27-33. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bath‐Hextall 2008
Bath‐Hextall 2010
-
- Bath-Hextall FJ, Birnie AJ, Ravenscroft JC, Williams HC. Interventions to reduce Staphylococcus aureus in the management of atopic eczema: an updated Cochrane review. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;163(1):12-26. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bath‐Hextall 2012
Bieber 2008
-
- Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358(14):1483-94. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Birnie 2002
Bliddal 2009
-
- Bliddal H, Christensen R. The treatment and prevention of knee osteoarthritis: a tool for clinical decision-making. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2009;10(11):1793-804. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Boguniewicz 2011
Borenstein 2009
-
- Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higging JPT, Rothstein HR. Introduction to Meta-Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2009.
Bos 2010
-
- Bos JD, Brenninkmeijer EE, Schram ME, Middelkamp-Hup MA, Spuls PI, Smitt JH. Atopic eczema or atopiform dermatitis. Experimental Dermatology 2010;19(4):325-31. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Boyle 2006
Bradburn 2007
-
- Bradburn MJ, Deeks JJ, Berlin JA, Russell Localio A. Much ado about nothing: a comparison of the performance of meta-analytical methods with rare events. Statistics in Medicine 2007;26(1):53-77. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Calderon 2010
Caussin 2008
-
- Caussin J, Gooris GS, Bouwstra JA. FTIR studies show lipophilic moisturizers to interact with stratum corneum lipids, rendering the more densely packed. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2008;1778(6):1517-24. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Caussin 2009a
-
- Caussin J. Skin, dry skin and moisturization. In: Doctoral thesis: Stratum corneum hydration : mode of action of moisturizers on a molecular level. Leiden: Division of Drug Delivery Technology (LACDR), Faculty of Science, Leiden University, 2009:7-21.
Caussin 2009b
-
- Caussin J, Rozema E, Gooris GS, Wiechers JW, Pavel S, Bouwstra JA. Hydrophilic and lipophilic moisturizers have similar penetration profiles but different effects on SC water distribution in vivo. Experimental Dermatology 2009;18(11):954-61. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Chamlin 2002
-
- Chamlin SL, Kao J, Frieden IJ, Sheu MY, Fowler AJ, Fluhr JW. Ceramide-dominant barrier repair lipids alleviate childhood atopic dermatitis: changes in barrier function provide a sensitive indicator of disease activity. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2002;47(2):198-208. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Charman 2000
-
- Charman CR, Morris AD, Williams HC. Topical corticosteroid phobia in patients with atopic eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;142(5):931-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Charman 2004
-
- Charman CR, Venn AJ, Williams HC. The patient-oriented eczema measure: development and initial validation of a new tool for measuring atopic eczema severity from the patients' perspective. Archives of Dermatology 2004;140(12):1513-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Chung 2008
Cooke 2016
-
- Cooke A, Cork MJ, Victor S, Campbell M, Danby S, Chittock J, et al. Olive oil, sunflower oil or no oil for baby dry skin or massage: A pilot, assessor-blinded, randomized controlled trial (the Oil in Baby SkincaRE [OBSeRvE] Study). Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2016;96(3):323-30. [PMID: 26551528] - PubMed
Cork 2003a
-
- Cork MJ, Britton J, Butler L, Young S, Murphy R, Keohane SG. Comparison of parent knowledge, therapy utilization and severity of atopic eczema before and after explanation and demonstration of topical therapies by a specialist dermatology nurse. British Journal of Dermatology 2003;149(3):582-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cork 2003b
-
- Cork MJ, Timmins J, Holden C, Carr J, Berry V, Tazi-Ahnini R, et al. An audit of adverse drug reactions to aqueous cream in children with atopic eczema. Pharmaceutical Journal 2003;271:747-8.
Cork 2006
-
- Cork MJ, Robinson DA, Vasilopoulos Y, Ferguson A, Moustafa M, MacGowan A et al. New perspectives on epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis: gene-environment interactions. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2006;118(1):3-21. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cork 2009
-
- Cork MJ, Danby SG, Vasilopoulos Y, Hadgraft J, Lane ME, Moustafa M. Epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2009;129(8):1892-908. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Costa 1989
-
- Costa C, Rilliet A, Nicolet M, Saurat JH. Scoring atopic dermatitis: the simpler the better? Acta Dermato-Venereologica 1989;69(1):41-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cury Martins 2015
Danby 2011b
-
- Danby SG, Al-Enezi T, Sultan A, Chittock J, Kennedy K, Cork MJ. The effect of aqueous cream BP on the skin barrier in volunteers with a previous history of atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2011;165(2):329-34. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Danby 2013
-
- Danby SG, AlEnezi T, Sultan A, Lavender T, Chittock J, Brown K, et al. Effect of olive and sunflower seed oil on the adult skin barrier: implications for neonatal skin care. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2013;30(1):42-50. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Danby 2016
-
- Danby SG, Chalmers J, Brown K, Williams HC, Cork MJ. A functional mechanistic study of the effect of emollients on the structure and function of the skin barrier. British Journal of Dermatology 2016;175(5):1011-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Deckers 2012
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177-88. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Dharmage 2014
-
- Dharmage SC, Lowe AJ, Matheson MC, Burgess JA, Allen KJ, Abramson MJ. Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march revisited. Allergy 2014;69(1):17-27. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Diepgen 1989
-
- Diepgen TL, Fartasch M, Hornstein OP. Evaluation and relevance of atopic basic and minor features in patients with atopic dermatitis and in the general population. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. Supplementum 1989;144:50-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Diepgen 1996
-
- Diepgen TL, Sauerbrei W, Fartasch M. Development and validation of diagnostic scores for atopic dermatitis incorporating criteria of data quality and practical usefulness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1996;49(9):1031-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Eichenfield 2014a
Eichenfield 2014b
-
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, Krol A, Paller AS, Schwarzenberger K. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2. Management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;71(1):116-32. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Elias 2011
Elias 2014
Emerson 2000
-
- Emerson RM, Charman CR, Williams HC. The Nottingham Eczema Severity Score: preliminary refinement of the Rajka and Langeland grading. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;142(2):288-97. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ersser 2014
European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis 1993
-
- No authors listed. Severity scoring of atopic dermatitis: the SCORAD index. Consensus Report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology 1993;186(1):23-31. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Finlay 1994
-
- Finlay AY, Khan GK. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)-a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 1994;19(3):210-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Flohr 2004
-
- Flohr C, Johansson SG, Wahlgren CF, Williams H. How atopic is atopic dermatitis? Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2004;114(1):150-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Flohr 2008
-
- Flohr C, Weiland SK, Weinmayr G, Björkstén B, Bråbäck L, Brunekreef B, et al. The role of atopic sensitization in flexural eczema: findings from the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood Phase Two. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2008;121(1):141-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Flohr 2009
-
- Flohr C, Weinmayr G, Weiland SK, Addo-Yobo E, Annesi-Maesano I, Björkstén B, et al. How well do questionnaires perform compared with physical examination in detecting flexural eczema? Findings from the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Phase Two. British Journal of Dermatology 2009;161(4):846-53. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Flohr 2014
-
- Flohr C, Mann J. New insights into the epidemiology of childhood atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2014;69(1):3-16. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Futamura 2014
Gaunt 2016
Ghadially 1992
-
- Ghadially R, Halkier-Sorensen L, Elias PM. Effects of petrolatum on stratum corneum structure and function. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1992;26(3 Pt 2):387-96. [PMID: ] - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed September 2016. Hamilton (ON): GRADE Working Group, McMaster University, 2015.
Gu 2013
Guyatt 2013a
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Santesso N, Helfand M, Vist G, Kunz R. GRADE guidelines: 12. Preparing summary of findings tables-binary outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(2):158-72. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2013b
-
- Guyatt GH, Thorlund K, Oxman AD, Walter SD, Patrick D, Furukawa TA. GRADE guidelines: 13. Preparing summary of findings tables and evidence profiles-continuous outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(2):173-83. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Haeck 2011
-
- Haeck IM, Knol MJ, Ten Berge O, Velsen SG, Bruin-Weller MS, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium versus cyclosporin A as long-term treatment in adult patients with severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;64(6):1074-84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Haileamlak 2005
-
- Haileamlak A, Dagoye D, Williams H, Venn AJ, Hubbard R, Britton J, et al. Early life risk factors for atopic dermatitis in Ethiopian children. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2005;115(2):370-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Halling‐Overgaard 2016
Hanifin 1980
-
- Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 1980;92(Suppl):44-7.
Hanifin 2001
-
- Hanifin JM, Thurston M, Omoto M, Cherill R, Tofte SJ, Graeber M. The eczema area and severity index (EASI): assessment of reliability in atopic dermatitis. EASI Evaluator Group. Experimental Dermatology 2001;10(1):11-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Harcharik 2014
-
- Harcharik S, Emer J. Steroid-sparing properties of emollients in dermatology. Skin Therapy Letter 2014;19(1):5-10. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Hoare 2000
Hogewoning 2010
-
- Hogewoning AA, Larbi IA, Addo HA, Amoah AS, Boakye D, Hartgers F, et al. Allergic characteristics of urban schoolchildren with atopic eczema in Ghana. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2010;24(12):1406-12. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hogewoning 2012
-
- Hogewoning AA, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Amoah AS, Boakye DA, Yazdanbakhsh M, Kremsner PG, et al. Point and period prevalences of eczema in rural and urban schoolchildren in Ghana, Gabon and Rwanda. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2012;26(4):488-94. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Holm 2007
-
- Holm EA, Wulf HC, Thomassen L, Jemec GB. Assessment of atopic eczema: clinical scoring and noninvasive measurements. British Journal of Dermatology 2007;157(4):674-80. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hon 2016
-
- Hon KL, Tsang YC, Lee VW, Pong NH, Ha G, Lee ST, et al. Efficacy of sodium hypochlorite (bleach) baths to reduce Staphylococcus aureus colonization in childhood onset moderate-to-severe eczema: A randomized, placebo-controlled cross-over trial. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2016;27(2):156-62. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Jadotte 2014
-
- Jadotte YT, Santer M, Vakirlis E, Schwartz RA, Bauer A, Gundersen DA, et al. Complementary and alternative medicine treatments for atopic eczema. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 1. Art. No: CD010938. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010938] - DOI
Janssens 2012
Jenner 2004
-
- Jenner N, Campbell J, Marks R. Morbidity and cost of atopic eczema in Australia. Australian Journal of Dermatology 2004;45(1):16-22. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Johansson 2004
-
- Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, et al. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2004;113(5):832-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kanti 2014
-
- Kanti V, Grande C, Stroux A, Bührer C, Blume-Peytavi U, Garcia Bartels N. Influence of sunflower seed oil on the skin barrier function of preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Dermatology 2014;229(3):230-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Katayama 2014
-
- Katayama I, Kohno Y, Akiyama K, Aihara M, Kondo N, Saeki H, et al. Japanese Guideline for Atopic Dermatitis 2014. Allergology International 2014;63(3):377-98. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kezic 2008
-
- Kezic S, Kemperman PM, Koster ES, Jongh CM, Thio HB, Campbell LE, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene lead to reduced level of natural moisturizing factor in the stratum corneum. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2008;128(8):2117-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kunz 1997
-
- Kunz B, Oranje AP, Labrèze L, Stalder JF, Ring J, Taïeb A. Clinical validation and guidelines for the SCORAD index: consensus report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology 1997;195(1):10-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kvenshagen 2014
-
- Kvenshagen BK, Carlsen KH, Mowinckel P, Berents TL, Carlsen KC. Can early skin care normalise dry skin and possibly prevent atopic eczema? A pilot study in young infants. Allergologia et Immunopathologia 2014;42(6):539-43. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Küster 2015
-
- Küster D, Spuls PI, Flohr C, Smith C, Hooft L, Deckert S et al. Effects of systemic immunosuppressive therapies for moderate-to-severe eczema in children and adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 11. Art. No: CD011939. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011939] - DOI
Langan 2006
-
- Langan SM, Thomas KS, Williams HC. What is meant by a 'flare' in atopic dermatitis? A systematic review and proposal. Archives of Dermatology 2006;142(9):1190-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lawson 1998
-
- Lawson V, Lewis-Jones MS, Finlay AY, Reid P, Owens RG. The family impact of childhood atopic dermatitis: the Dermatitis Family Impact Questionnaire. British Journal of Dermatology 1998;138(1):107-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lee 2007
-
- Lee YL, Li CW, Sung FC, Yu HS, Sheu HM, Guo YL. Environmental factors, parental atopy and atopic eczema in primary-school children: a cross-sectional study in Taiwan. British Journal of Dermatology 2007;157(6):1217-24. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Leung 2000
-
- Leung DY. Atopic dermatitis: new insights and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2000;105(5):860-76. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lewis‐Jones 1995
-
- Lewis-Jones MS, Finlay AY. The Children's Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI): initial validation and practical use. British Journal of Dermatology 1995;132(6):942-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lewis‐Jones 2001
-
- Lewis-Jones MS, Finlay AY, Dykes PJ. The Infants' Dermatitis Quality of Life Index. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;144(1):104-10. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lewis‐Jones 2006
-
- Lewis-Jones S. Quality of life and childhood atopic dermatitis: the misery of living with childhood eczema. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2006;60(8):984-92. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Liberati 2009
Lindh 2015
-
- Lindh JD, Bradley M. Clinical effectiveness of moisturizers in atopic dermatitis and related disorders: A systematic review. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 2015;16(5):341-59. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lodén 2003
-
- Lodén M. Role of topical emollients and moisturizers in the treatment of dry skin barrier disorders. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 2003;4(11):771-88. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lodén 2012
-
- Lodén M. Effect of moisturizers on epidermal barrier function. Clinics in Dermatology 2012;30(3):286-96. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lucky 1997
-
- Lucky AW, Leach AD, Laskarzewski P, Wenck H. Use of an emollient as a steroid-sparing agent in the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children. Pediatric Dermatology 1997;14(4):321-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lynde 2005
-
- Lynde C, Barber K, Claveau J, Gratton D, Ho V, Krafchik B, et al. Canadian practical guide for the treatment and management of atopic dermatitis. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery 2005;8(Suppl 5):1-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Mack Correa 2012
Margolis 2014
Mason 2013
Moed 2012
-
- Moed H, Yang Q, Oranje AP, Panda S, Wouden JC. Different strategies for using topical corticosteroids for established eczema. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 10. Art. No: CD010080. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010080] - DOI
Moncrieff 2013
-
- Moncrieff G, Cork M, Lawton S, Kokiet S, Daly C, Clark C. Use of emollients in dry-skin conditions: consensus statement. Clinical & Experimental Dermatology 2013;38(3):231-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Murray 2012
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2197-223. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Möhrenschlager 2006
-
- Möhrenschlager M, Darsow U, Schnopp C, Ring J. Atopic eczema: what's new? Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2006;20(5):503-11. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Nankervis 2015
Nankervis 2016
-
- Nankervis H, Thomas KS, Delamere FM, Barbarot S, Rogers NK, Williams HC. Scoping systematic review of treatments for eczema. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library. Programme Grants for Applied Research 2016;4(7):1-480. [27280278] - PubMed
Nelson 2015
-
- Nelson EC, Eftimovska E, Lind C, Hager A, Wasson JH, Lindblad S. Patient reported outcome measures in practice. British Medical Journal 2015;350:g7818. [PMID: ] - PubMed
NICE 2007
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management (CG57) 2007. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57 (accessed prior to 5 October 2016).
Nutten 2015
-
- Nutten S. Atopic dermatitis: global epidemiology and risk factors. Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism 2015;66(Suppl 1):8-16. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Oakley 2016
-
- Oakley R, Lawton S. Views on unwanted effects of leave-on emollients and experiences surrounding their incidence. Dermatological Nursing 2016;15(4):38-43.
Odhiambo 2009
-
- Odhiambo JA, Williams HC, Clayton TO, Robertson CF, Asher MI, ISAAC Phase Three Study Group. Global variations in prevalence of eczema symptoms in children from ISAAC Phase Three. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2009;124(6):1251-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Palmer 2006
-
- Palmer CN, Irvine AD, Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Zhao Y, Liao H, Lee SP, et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nature Genetics 2006;38(4):441-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Penzer 2012
-
- Penzer R. Best practice in emollient therapy: a statement for health care professionals. Dermatological Nursing 2012;11(4):4-19.
Petry 2013
-
- Petry V, Lipnharski C, Bessa GR, Silveira VB, Weber MB. Prevalence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and antibiotic resistance in patients with atopic dermatitis in Porto Alegre, Brazil. International Journal of Dermatology 2013;53(6):731-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Rajka 1989
-
- Rajka G, Langeland T. Grading of the severity of atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermato-venereologica. Supplementum 1989;144:13-14. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Rawlings 2004
-
- Rawlings AV, Canestrari DA, Dobkowski B. Moisturizer technology versus clinical performance. Dermatologic Therapy 2004;17(Suppl 1):49-56. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Rawlings 2005
-
- Rawlings AV, Matts PJ. Stratum corneum moisturization at the molecular level: an update in relation to the dry skin cycle. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2005;124(6):1099-110. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Rawlings 2014
-
- Rawlings AV. Molecular basis for stratum corneum maturation and moisturization. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(Suppl 3):19-28. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Reich 2016
-
- Reich A, Riepe C, Anastasiadou Z, Mędrek K, Augustin M, Szepietowski JC. Itch assessment with visual analogue scale and numerical rating scale: determination of minimal clinically important difference in chronic itch. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2016;96(7):978-80. [DOI: 10.2340/00015555-2433] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Riley 2011
-
- Riley RD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ. Interpretation of random effects meta-analyses. BMJ 2011;342:d549. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ring 2012a
-
- Ring J, Alomar A, Bieber T, Deleuran M, Fink-Wagner A, Gelmetti C. Guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) part I. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2012;26(8):1045-60. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ring 2012b
-
- Ring J, Alomar A, Bieber T, Deleuran M, Fink-Wagner A, Gelmetti C. Guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) Part II. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2012;26(9):1176-93. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Saeki 2009
-
- Saeki H, Furue M, Furukawa F, Hide M, Ohtsuki M, Katayama I, et al. Guidelines for management of atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatology 2009;36(10):563-77. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sagiv 2003
-
- Sagiv AE, Marcus Y. The connection between in vitro water uptake and in vivo skin moisturization. Skin Research & Technology 2003;9(4):306-11. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Santer 2013
-
- Santer M, Burgess H, Yardley L, Ersser SJ, Lewis-Jones S, Muller I, et al. Managing childhood eczema: qualitative study exploring carers' experiences of barriers and facilitators to treatment adherence. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2013;69(11):2493-501. [PMID: 23528163] - PubMed
Santer 2016
Schmitt 2007
-
- Schmitt J, Langan S, Williams HC. What are the best outcome measurements for atopic eczema? A systematic review. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2007;120(6):1389-98. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Schmitt 2014
-
- Schmitt J, Spuls PI, Thomas KS, Simpson E, Furue M, Deckert S, et al. The Harmonising Outcome Measures for Eczema (HOME) statement to assess clinical signs of atopic eczema in trials. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2014;134(4):800-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Schram 2012
-
- Schram ME, Spuls PI, Leeflang MM, Lindeboom R, Bos JD, Schmitt J. EASI, (objective) SCORAD and POEM for atopic eczema: responsiveness and minimal clinically important difference. Allergy 2012;67(1):99-106. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editors The GRADE Working Group. GRADE handbook for grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. www.guidelinedevelopment.org/handbook (accessed before 5 October 2016);(2013).
Serup 1995
-
- Serup J. EEMCO guidance for the assessment of dry skin(xerosis) and ichthyosis: clinical scoring systems. Skin Research and Technology 1995;1(3):109-114. - PubMed
Sidbury 2014a
-
- Sidbury R, Tom WL, Bergman JN, Cooper KD, Silverman RA, Berger TG. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: Section 4. Prevention of disease flares and use of adjunctive therapies and approaches. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;71(6):1218-33. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Sidbury 2014b
SIGN 2011
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Management of atopic eczema in primary care. SIGN publication no.125, 2011. www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/125/index.html (accessed 6 January 2016).
Silverberg 2013
-
- Silverberg JI, Hanifin JM. Adult eczema prevalence and associations with asthma and other health and demographic factors: a US population-based study. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2013;132(5):1132-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Silverberg 2014
-
- Silverberg JL. Atopic dermatitis: an evidence-based treatment update. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 2014;15(3):149-64. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Simpson 2010
Simpson 2014
Sirikudta 2013
-
- Sirikudta W, Kulthanan K, Varothai S, Nuchkull P. Moisturizers for patients with atopic dermatitis: an overview. Journal of Allergy and Therapy 2013;4(4):1-7. [DOI: 10.4172/2155-6121.1000143] - DOI
Stalder 2011
-
- Stalder JF, Barbarot S, Wollenberg A, Holm EA, De Raeve L, Seidenari S, et al. Patient-Oriented SCORAD (PO-SCORAD): a new self-assessment scale in atopic dermatitis validated in Europe. Allergy 2011;66(8):1114-21. [PMID: ] - PubMed
The EuroQol Group 1990
-
- The EuroQol Group. EuroQol-a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16(3):199-208. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Thomas 2015
Tierney 2007
van Smeden 2014a
-
- Smeden J, Janssens M, Kaye EC, Caspers PJ, Lavrijsen AP, Vreeken RJ, et al. The importance of free fatty acid chain length for the skin barrier function in atopic eczema patients. Experimental Dermatology 2014;23(1):45-52. [PMID: ] - PubMed
van Smeden 2014b
-
- Smeden J, Janssens M, Gooris GS, Bouwstra JA. The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2014;1841(3):295-313. [PMID: ] - PubMed
van Zuuren 2014
Wald 1943
-
- Wald A. Tests of statistical hypotheses concerning several parameters when the number of observations is large. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 1943;54:426-82.
Weidinger 2016
-
- Weidinger S, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2016;387(10023):1109-22. - PubMed
Whalley 2004
-
- Whalley D, McKenna SP, Dewar AL, Erdman RA, Kohlmann T, Niero M, et al. A new instrument for assessing quality of life in atopic dermatitis: international development of the Quality of Life Index for Atopic Dermatitis (QoLIAD. British Journal of Dermatology 2004;150(2):274-83. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Williams 1994
-
- Williams HC, Burney PG, Hay RJ, Archer CB, Shipley MJ, Hunter JJ, et al. The U.K. Working Party's Diagnostic Criteria for Atopic Dermatitis. I. Derivation of a minimum set of discriminators for atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 1994;131(3):383-96. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Williams 1996
-
- Williams HC, Burney PG, Pembroke AC, Hay RJ. Validation of the U.K. diagnostic criteria for atopic dermatitis in a population setting. U.K. Diagnostic Criteria for Atopic Dermatitis Working Party. British Journal of Dermatology 1996;135(1):12-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Williams 2005
-
- Williams HC. Clinical practice. Atopic dermatitis. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;352(22):2314-24. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Williams 2006
-
- Williams H, Flohr C. How epidemiology has challenged 3 prevailing concepts about atopic dermatitis. Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2006;118(1):209-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Williams 2008
-
- Williams H, Stewart A, Mutius E, Cookson W, Ross Anderson H, and the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Phase one and Three Study Groups. Is eczema really on the increase worldwide? Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology 2008;121(4):947-54. [EMBASE: 2008158035] - PubMed
Wolkerstorfer 1999
-
- Wolkerstorfer A, Waard van der Spek FB, Glazenburg EJ, Mulder PG, Oranje AP. Scoring the severity of atopic dermatitis: three item severity score as a rough system for daily practice and as a pre-screening tool for studies. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 1999;79(5):356-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Wollenberg 2016
-
- Wollenberg A, Oranje A, Deleuran M, Simon D, Szalai Z, Kunz B, et al. ETFAD/EADV Eczema task force 2015 position paper on diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in adult and paediatric patients. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2016;30(5):729-47. [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

