Use of Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) to predict the treatment response to eribulin chemotherapy in breast cancer
- PMID: 28166544
- PMCID: PMC5293550
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170634
Use of Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) to predict the treatment response to eribulin chemotherapy in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Eribulin mesylate (eribulin) is currently indicated for treatment of locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer (MBC). It is a cytotoxic agent with unique mechanisms that suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cancer cells. On the other hand, Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), which are considered indicators of immune response monitoring, have been reported as prognostic factors and predictors of therapeutic efficacy. We thought that eribulin, which has an EMT-inhibiting mechanism, may produce an antitumor effect by improving the immune microenvironment, and in this study investigated the effects of breast cancer eribulin chemotherapy on the immune microenvironment with TILs as a marker.
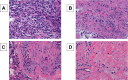
Methods: TILs was evaluated in 52 patients with MBC who underwent chemotherapy with eribulin. The correlation between TILs evaluated according to the standard method, and prognosis, including the efficacy of eribulin chemotherapy, was investigated retrospectively.
Results: Of the 52 MBC patients, 29 (55.8%) were in the high TILs group and 23 (44.2%) were in the low TILs group. The high TILs group included significantly more triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) (p = 0.008) than the low TILs group. In an analysis of outcomes, TNBC patients in the high TILs group had significantly longer disease-free survival than TNBC patients in the low TILs group (p = 0.033, log-rank), but no significant differences were seen in all breast cancer patients (p = 0.489, log-rank) or in non-TNBC patients (p = 0.878, log-rank). In a multivariate analysis of recurrence in TNBC patients, being in the high TILs group was again an independent factor for a good outcome (p = 0.031, HR = 0.063).
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that TILs may be useful as a predictive marker of the therapeutic effect of eribulin chemotherapy in TNBC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Hirata J, Katsuno M, Kaneko S, Umemura T, Nishimura J, Motomura S, et al. Clinical significance of human bone marrow stromal cell colonies in acute leukemias. Leuk Res. 1986;10(12):1441–5. Epub 1986/01/01. - PubMed
-
- Kuznetsov G, Towle MJ, Cheng H, Kawamura T, TenDyke K, Liu D, et al. Induction of morphological and biochemical apoptosis following prolonged mitotic blockage by halichondrin B macrocyclic ketone analog E7389. Cancer Res. 2004;64(16):5760–6. Epub 2004/08/18. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1169 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bai RL, Paull KD, Herald CL, Malspeis L, Pettit GR, Hamel E. Halichondrin B and homohalichondrin B, marine natural products binding in the vinca domain of tubulin. Discovery of tubulin-based mechanism of action by analysis of differential cytotoxicity data. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(24):15882–9. Epub 1991/08/25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

