Myocardial Oxygen Consumption and Efficiency in Aortic Valve Stenosis Patients With and Without Heart Failure
- PMID: 28167498
- PMCID: PMC5523773
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004810
Myocardial Oxygen Consumption and Efficiency in Aortic Valve Stenosis Patients With and Without Heart Failure
Abstract
Background: Myocardial oxygen consumption (MVO2) and its coupling to contractile work are fundamentals of cardiac function and may be involved causally in the transition from compensated left ventricular hypertrophy to failure. Nevertheless, these processes have not been studied previously in patients with aortic valve stenosis (AS).
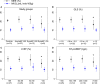
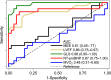
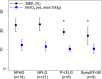
Methods and results: Participants underwent 11C-acetate positron emission tomography, cardiovascular magnetic resonance, and echocardiography to measure MVO2 and myocardial external efficiency (MEE) defined as the ratio of left ventricular stroke work and the energy equivalent of MVO2. We studied 10 healthy controls (group A), 37 asymptomatic AS patients with left ventricular ejection fraction ≥50% (group B), 12 symptomatic AS patients with left ventricular ejection fraction ≥50% (group C), and 9 symptomatic AS patients with left ventricular ejection fraction <50% (group D). MVO2 did not differ among groups A, B, C, and D (0.105±0.02, 0.117±0.024, 0.129±0.032, and 0.104±0.026 mL/min per gram, respectively; P=0.07), whereas MEE was reduced in group D (21.0±1.6%, 22.3±3.3%, 22.1±4.2%, and 17.3±4.7%, respectively; P<0.05). Similarly, patients with global longitudinal strain greater than -12% and paradoxical low-flow, low-gradient AS had impaired MEE (P<0.05 versus controls). The ability to discriminate between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients was superior for global longitudinal strain compared with MVO2 and MEE (area under the curve 0.98, 0.48, and 0.61, respectively; P<0.05).
Conclusions: AS patients display a persistent ability to maintain normal MVO2 and MEE (ie, the ability to convert energy into stroke work); however, patients with left ventricular ejection fraction <50%; global longitudinal strain greater than -12%; or paradoxical low-flow, low-gradient AS demonstrate reduced MEE. These findings suggest that mitochondrial uncoupling contributes to the dismal prognosis in patients with reduced contractile function or paradoxical low-flow, low-gradient AS.
Keywords: aortic valve stenosis; myocardial external efficiency; myocardial metabolism; myocardial oxygen consumption; positron emission tomography.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
References
-
- Rossebo AB, Pedersen TR, Boman K, Brudi P, Chambers JB, Egstrup K, Gerdts E, Gohlke‐Barwolf C, Holme I, Kesaniemi YA, Malbecq W, Nienaber CA, Ray S, Skjaerpe T, Wachtell K, Willenheimer R; SEAS Investigators . Intensive lipid lowering with simvastatin and ezetimibe in aortic stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1343–1356. - PubMed
-
- Cowell SJ, Newby DE, Prescott RJ, Bloomfield P, Reid J, Northridge DB, Boon NA; Scottish Aortic Stenosis and Lipid Lowering Trial, Impact on Regression (SALTIRE) Investigators . A randomized trial of intensive lipid‐lowering therapy in calcific aortic stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2389–2397. - PubMed
-
- Chan KL, Teo K, Dumesnil JG, Ni A, Tam J; ASTRONOMER Investigators . Effect of Lipid lowering with rosuvastatin on progression of aortic stenosis: results of the aortic stenosis progression observation: measuring effects of rosuvastatin (ASTRONOMER) trial. Circulation. 2010;121:306–314. - PubMed
-
- Bing R, Hammond M, Handelsman J, Powers S, Spencer F, Eckenhoff J, Goodale W, Hafkenschiel JH, Kety S. The measurement of coronary blood flow, oxygen consumption, and efficiency of the left ventricle in man. Am Heart J. 1949;38:1. - PubMed
-
- Neubauer S. The failing heart—an engine out of fuel. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1140–1151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

