ARPP-16 Is a Striatal-Enriched Inhibitor of Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulated by Microtubule-Associated Serine/Threonine Kinase 3 (Mast 3 Kinase)
- PMID: 28167675
- PMCID: PMC5354324
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4559-15.2017
ARPP-16 Is a Striatal-Enriched Inhibitor of Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulated by Microtubule-Associated Serine/Threonine Kinase 3 (Mast 3 Kinase)
Abstract
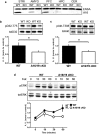
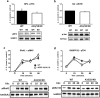
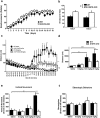
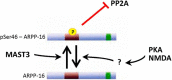
ARPP-16 (cAMP-regulated phospho-protein of molecular weight 16 kDa) is one of several small acid-soluble proteins highly expressed in medium spiny neurons of striatum that are phosphorylated in response to dopamine acting via D1 receptor/protein kinase A (PKA) signaling. We show here that ARPP-16 is also phosphorylated in vitro and in vivo by microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase 3 (MAST3 kinase), an enzyme of previously unknown function that is enriched in striatum. We find that ARPP-16 interacts directly with the scaffolding A subunit of the serine/threonine protein phosphatase, PP2A, and that phosphorylation of ARPP-16 at Ser46 by MAST3 kinase converts the protein into a selective inhibitor of B55α- and B56δ-containing heterotrimeric forms of PP2A. Ser46 of ARPP-16 is phosphorylated to a high basal stoichiometry in striatum, suggestive of basal inhibition of PP2A in striatal neurons. In support of this hypothesis, conditional knock-out of ARPP-16 in CaMKIIα::cre/floxed ARPP-16/19 mice results in dephosphorylation of a subset of PP2A substrates including phospho-Thr75-DARPP-32, phospho-T308-Akt, and phospho-T202/Y204-ERK. Conditional knock-out of ARPP-16/19 is associated with increased motivation measured on a progressive ratio schedule of food reinforcement, yet an attenuated locomotor response to acute cocaine. Our previous studies have shown that ARPP-16 is phosphorylated at Ser88 by PKA. Activation of PKA in striatal slices leads to phosphorylation of Ser88, and this is accompanied by marked dephosphorylation of Ser46. Together, these studies suggest that phospho-Ser46-ARPP-16 acts to basally control PP2A in striatal medium spiny neurons but that dopamine acting via PKA inactivates ARPP-16 leading to selective potentiation of PP2A signaling.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT We describe a novel mechanism of signal transduction enriched in medium spiny neurons of striatum that likely mediates effects of the neurotransmitter dopamine acting on these cells. We find that the protein ARPP-16, which is highly expressed in striatal medium spiny neurons, acts as a selective inhibitor of certain forms of the serine/threonine protein phosphatase, PP2A, when phosphorylated by the kinase, MAST3. Under basal conditions, ARPP-16 is phosphorylated by MAST3 to a very high stoichiometry. However, the actions of MAST3 are antagonized by dopamine and cAMP-regulated signaling leading to disinhibition of ARPP-16 and increased PP2A action.
Keywords: cocaine; dopamine; medium spiny neuron; motivation; protein kinase A.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/372709-14$15.00/0.
Figures
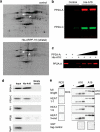
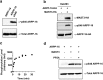
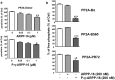
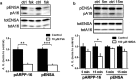
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
