MicroRNAs Are Intensively Regulated during Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 28167951
- PMCID: PMC5253390
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00018
MicroRNAs Are Intensively Regulated during Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis
Abstract
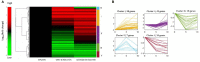
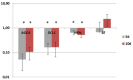
Several genes encoding transcription factors (TFs) were indicated to have a key role in the induction of somatic embryogenesis (SE), which is triggered in the somatic cells of plants. In order to further explore the genetic regulatory network that is involved in the embryogenic transition induced in plant somatic cells, micro-RNA (miRNAs) molecules, the products of MIRNA (MIR) genes and the common regulators of TF transcripts, were analyzed in an embryogenic culture of Arabidopsis thaliana. In total, the expression of 190 genes of the 114 MIRNA families was monitored during SE induction and the levels of the primary (pri-miRNAs) transcripts vs. the mature miRNAs were investigated. The results revealed that the majority (98%) of the MIR genes were active and that most of them (64%) were differentially expressed during SE. A distinct attribute of the MIR expression in SE was the strong repression of MIR transcripts at the early stage of SE followed by their significant up-regulation in the advanced stage of SE. Comparison of the mature miRNAs vs. pri-miRNAs suggested that the extensive post-transcriptional regulation of miRNA is associated with SE induction. Candidate miRNA molecules of the assumed function in the embryogenic response were identified among the mature miRNAs that had a differential expression in SE, including miR156, miR157, miR159, miR160, miR164, miR166, miR169, miR319, miR390, miR393, miR396, and miR398. Consistent with the central role of phytohormones and stress factors in SE induction, the functions of the candidate miRNAs were annotated to phytohormone and stress responses. To confirm the functions of the candidate miRNAs in SE, the expression patterns of the mature miRNAs and their presumed targets were compared and regulatory relation during SE was indicated for most of the analyzed miRNA-target pairs. The results of the study contribute to the refinement of the miRNA-controlled regulatory pathways that operate during embryogenic induction in plants and provide a valuable platform for the identification of the genes that are targeted by the candidate miRNAs in SE induction.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; MIRNA genes; gene expression; mature miRNA; pri-miRNA; somatic embryogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR156-SPL and miR169-NF-YA Modules Regulate the Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis via LEC- and Auxin-Related Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 25;25(17):9217. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179217. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273166 Free PMC article.
-
AGL15 Controls the Embryogenic Reprogramming of Somatic Cells in Arabidopsis through the Histone Acetylation-Mediated Repression of the miRNA Biogenesis Genes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 14;21(18):6733. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186733. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32937992 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of microRNAs involved in the somatic embryogenesis of Eucalyptus.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Apr 15;11(4):jkab070. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab070. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33693674 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs as key regulators via targeting the phytohormone signaling pathways during somatic embryogenesis of plants.3 Biotech. 2020 Nov;10(11):495. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02487-9. Epub 2020 Oct 29. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 33150121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of miRNA in somatic embryogenesis.Genomics. 2019 Sep;111(5):1026-1033. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.11.022. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30476555 Review.
Cited by
-
Alkaloid production and response to natural adverse conditions in Peganum harmala: in silico transcriptome analyses.BioTechnologia (Pozn). 2022 Dec 24;103(4):355-384. doi: 10.5114/bta.2022.120706. eCollection 2022. BioTechnologia (Pozn). 2022. PMID: 36685700 Free PMC article.
-
AGL15 Promotion of Somatic Embryogenesis: Role and Molecular Mechanism.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 28;13:861556. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.861556. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35419012 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Plant MicroRNA Expression: Its Potential Usability in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Improvement.Curr Genomics. 2023 Dec 12;24(4):197-206. doi: 10.2174/0113892029264886231016050547. Curr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 38169773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypermethylation of Auxin-Responsive Motifs in the Promoters of the Transcription Factor Genes Accompanies the Somatic Embryogenesis Induction in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 18;21(18):6849. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186849. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32961931 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA biogenesis and activity in plant cell dedifferentiation stimulated by cell wall removal.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jan 3;22(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03323-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 34979922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aida M., Ishida T., Tasaka M. (1999). Shoot apical meristem and cotyledon formation during Arabidopsis embryogenesis: interaction among the CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON and SHOOT MERISTEMLESS genes. Development 126, 1563–1570. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

