Posterior Pole Retinal Thickness for Detection of Structural Damage in Anterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy
- PMID: 28167986
- PMCID: PMC5291057
- DOI: 10.3109/01658107.2013.809462
Posterior Pole Retinal Thickness for Detection of Structural Damage in Anterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy
Abstract
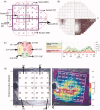
This objectives of this study were to compare posterior pole retinal thickness (PPRT) and peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer thickness (RNFLT) between the affected eyes of patients with previous nonarteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy (NAION) and their unaffected eyes and to assess the structure-function relationship. Eighteen eyes with NAION and 14 contralateral unaffected eyes were included in this cross-sectional study. Humphrey visual field (VF) sensitivities were obtained. RNFLT (six sectors) and PPRT (four quadrants) were measured with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (Spectralis; Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany). These parameters were compared between both eyes of patients with unilateral NAION. The correlation of RNFLT and PPRT with VF mean sensitivity (MS) values (linear units) was also analysed. The main outcome measure was the correlation of MS values with PPRT and RNFLT. A significant difference existed between the affected eyes and the unaffected fellow eyes in the MS values, all sectors of RNFLT, and all quadrants of PPRT. A significant linear correlation was observed between RNFLT and PPRT and corresponding MS values in global and regional measures. The strongest correlation was between inferior temporal VF and its corresponding superior nasal retinal quadrant thickness. The area under the receiver operator characteristic curves comparing superior nasal PPRT and RNFLT between the normal and affected eyes was 0.97 and 0.96, respectively. The results show that PPRT and RNFLT provide equivalent performance to detect structural damage in ischaemic optic neuropathy.
Keywords: ischaemic optic neuropathy; nerve fibre layer thickness; retinal thickness; spectral-domain optical coherence tomography.
Figures

References
-
- Arnold AC. Ischemic optic neuropathy. In: Miller NR, Newman NJ, Biousse V, editors. Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Vol. 1 Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:349–384
-
- Tesser RA, Niendorf ER, Levin LA. The morphology of an infarct in nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Ophthalmology 2003;110:2031–2035 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein SL, Guo Y, Kelman SE, Flower RW, Johnson MA. Functional and cellular responses in a novel rodent model of anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003;44:4153–4162 - PubMed
-
- Cho JW, Sung KR, Lee S, Yun SC, Kang SY, Choi J, Na JH, Lee Y, Kook MS. Relationship between visual field sensitivity and macular ganglion cell complex thickness as measured by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010;51:6401–6407 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
