A Case of Neonatal Marfan Syndrome: A Management Conundrum and the Role of a Multidisciplinary Team
- PMID: 28168077
- PMCID: PMC5266800
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8952428
A Case of Neonatal Marfan Syndrome: A Management Conundrum and the Role of a Multidisciplinary Team
Abstract
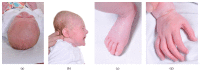
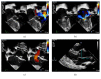
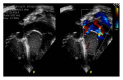
Neonatal Marfan syndrome (nMFS) is a rare condition with a poor prognosis. It is genotypically and phenotypically distinct from the typical Marfan syndrome and carries a poorer prognosis. This case report describes the progression of a 14-month-old girl diagnosed with nMFS at 5 months of age. Her diagnosis followed the identification of a fibrillin-1 mutation (FBN1 gene, exon 26, chromosome 15), which is a common locus of nMFS. This patient developed severe cardiac complications resulting in congestive cardiac failure in early life and required major cardiac surgery. Since surgical intervention, our patient is still reliant on a degree of ventilator support, but the patient has gained weight and echocardiography has demonstrated improved left ventricular function and improved tricuspid and mitral valve regurgitation. Therefore, we argue the importance of a cautious multidisciplinary approach to early surgical intervention in cases of nMFS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Morse R. P., Rockenmacher S., Pyeritz R. E., et al. Diagnosis and management of infantile Marfan syndrome. Pediatrics. 1990;86(6):888–895. - PubMed
-
- Revencu N., Quenum G., Detaille T., Verellen G., De Paepe A., Verellen-Dumoulin C. Congenital diaphragmatic eventration and bilateral uretero-hydronephrosis in a patient with neonatal Marfan syndrome caused by a mutation in exon 25 of the FBN1 gene and review of the literature. European Journal of Pediatrics. 2004;163(1):33–37. doi: 10.1007/s00431-003-1330-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

