Metabolic syndrome and the hepatorenal reflex
- PMID: 28168086
- PMCID: PMC5264275
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.194147
Metabolic syndrome and the hepatorenal reflex
Abstract
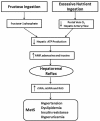
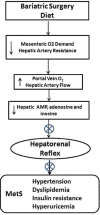
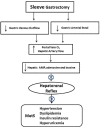
Insufficient hepatic O2 in animal and human studies has been shown to elicit a hepatorenal reflex in response to increased hepatic adenosine, resulting in the stimulation of renal as well as muscle sympathetic nerve activity and activating the renin angiotensin system. Low hepatic ATP, hyperuricemia, and hepatic lipid accumulation reported in metabolic syndrome (MetS) patients may reflect insufficient hepatic O2 delivery, potentially accounting for the sympathetic overdrive associated with MetS. This theoretical concept is supported by experimental results in animals fed a high fructose diet to induce MetS. Hepatic fructose metabolism rapidly consumes ATP resulting in increased adenosine production and hyperuricemia as well as elevated renin release and sympathetic activity. This review makes the case for the hepatorenal reflex causing sympathetic overdrive and metabolic syndrome in response to exaggerated splanchnic oxygen consumption from excessive eating. This is strongly reinforced by the fact that MetS is cured in a matter of days in a significant percentage of patients by diet, bariatric surgery, or endoluminal sleeve, all of which would decrease splanchnic oxygen demand by limiting nutrient contact with the mucosa and reducing the nutrient load due to loss of appetite or dietary restriction.
Keywords: Bariatric; cholesterol; diabetes; hepatorenal; metabolic syndrome; obesity; sympathetic.
Conflict of interest statement
The author and his institution did not receive any funding or other monetary support for any aspect of the submitted work. The author has received no payment for services and has no financial relationships or intellectual property relevant to the work. The author has no other relationships that would influence or give the appearance of potentially influencing the work.
Figures
Corrected and republished from
-
Metabolic syndrome and the hepatorenal reflex.Surg Neurol Int. 2016 Sep 13;7:83. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.190438. eCollection 2016. Surg Neurol Int. 2016. PMID: 27656314 Free PMC article. Review.
Similar articles
-
Metabolic syndrome and the hepatorenal reflex.Surg Neurol Int. 2016 Sep 13;7:83. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.190438. eCollection 2016. Surg Neurol Int. 2016. PMID: 27656314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High fructose consumption combined with low dietary magnesium intake may increase the incidence of the metabolic syndrome by inducing inflammation.Magnes Res. 2006 Dec;19(4):237-43. Magnes Res. 2006. PMID: 17402291 Review.
-
Exercise training modulates the hepatic renin-angiotensin system in fructose-fed rats.Exp Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;102(9):1208-1220. doi: 10.1113/EP085924. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Exp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28626963
-
Decreases in portal flow trigger a hepatorenal reflex to inhibit renal sodium and water excretion in rats: role of adenosine.Hepatology. 2002 Jan;35(1):167-75. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.30425. Hepatology. 2002. PMID: 11786973
-
Reflex effects of hepatic baroreceptors on renal and cardiac sympathetic nerve activity.Am J Physiol. 1980 May;238(5):R390-4. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1980.238.5.R390. Am J Physiol. 1980. PMID: 7377377
Cited by
-
Common Denominator of MASLD and Some Non-Communicable Diseases.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 29;46(7):6690-6709. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070399. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)-A Condition Associated with Heightened Sympathetic Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 19;22(8):4241. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084241. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic Innervations and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Semin Liver Dis. 2023 May;43(2):149-162. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-57237. Epub 2023 May 8. Semin Liver Dis. 2023. PMID: 37156523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and correlations of hepatorenal functions in diabetes and cardiovascular disease among stratified adults.Acta Biomed. 2019 Jan 22;90(1):97-103. doi: 10.23750/abm.v90i1.6576. Acta Biomed. 2019. PMID: 30889161 Free PMC article.
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Clinical and Research Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 1;23(21):13320. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113320. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362108 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbatini F, Rizzello M, Casella G, Alessandri G, Capoccia D, Leonetti F, et al. Long term effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, and adjustable gastric banding on type 2 diabetes. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:1005–10. - PubMed
-
- Abdelmalek MF, Lazo M, Horska A, Bonekamp S, Lipkin EW, Balasubramanyam A, et al. Fatty Liver Subgroup of Look AHEAD Research Group. Higher dietary fructose is associated with impaired hepatic adenosine triphosphate homeostasis in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Hepatology. 2012;56:952–60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aguilar M, Bhuket T, Torres S, Liu B, Wong RJ. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the United States 2003-2012. JAMA. 2015;313:1973–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
