The development of mucosal vaccines for both mucosal and systemic immune induction and the roles played by adjuvants
- PMID: 28168169
- PMCID: PMC5292352
- DOI: 10.7774/cevr.2017.6.1.15
The development of mucosal vaccines for both mucosal and systemic immune induction and the roles played by adjuvants
Abstract
Vaccination is the most successful immunological practice that improves the quality of human life and health. Vaccine materials include antigens of pathogens and adjuvants potentiating the effectiveness of vaccination. Vaccines are categorized using various criteria, including the vaccination material used and the method of administration. Traditionally, vaccines have been injected via needles. However, given that most pathogens first infect mucosal surfaces, there is increasing interest in the establishment of protective mucosal immunity, achieved by vaccination via mucosal routes. This review summarizes recent developments in mucosal vaccines and their associated adjuvants.
Keywords: Adjuvants; Mucosal immunity; Vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

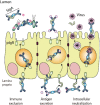
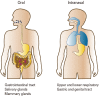
References
-
- Kwok R. Vaccines: the real issues in vaccine safety. Nature. 2011;473:436–438. - PubMed
-
- Gutjahr A, Tiraby G, Perouzel E, Verrier B, Paul S. Triggering intracellular receptors for vaccine adjuvantation. Trends Immunol. 2016;37:573–587. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann MF, Jennings GT. Vaccine delivery: a matter of size, geometry, kinetics and molecular patterns. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:787–796. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

