CRISPR-Cas9-targeted fragmentation and selective sequencing enable massively parallel microsatellite analysis
- PMID: 28169275
- PMCID: PMC5309709
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14291
CRISPR-Cas9-targeted fragmentation and selective sequencing enable massively parallel microsatellite analysis
Abstract
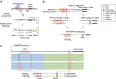
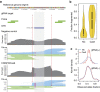
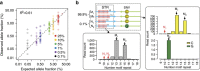
Microsatellites are multi-allelic and composed of short tandem repeats (STRs) with individual motifs composed of mononucleotides, dinucleotides or higher including hexamers. Next-generation sequencing approaches and other STR assays rely on a limited number of PCR amplicons, typically in the tens. Here, we demonstrate STR-Seq, a next-generation sequencing technology that analyses over 2,000 STRs in parallel, and provides the accurate genotyping of microsatellites. STR-Seq employs in vitro CRISPR-Cas9-targeted fragmentation to produce specific DNA molecules covering the complete microsatellite sequence. Amplification-free library preparation provides single molecule sequences without unique molecular barcodes. STR-selective primers enable massively parallel, targeted sequencing of large STR sets. Overall, STR-Seq has higher throughput, improved accuracy and provides a greater number of informative haplotypes compared with other microsatellite analysis approaches. With these new features, STR-Seq can identify a 0.1% minor genome fraction in a DNA mixture composed of different, unrelated samples.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

