The value of delta neutrophil index in young infants with febrile urinary tract infection
- PMID: 28169298
- PMCID: PMC5294644
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41265
The value of delta neutrophil index in young infants with febrile urinary tract infection
Abstract
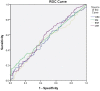
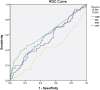
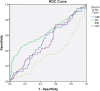
Delta neutrophil index (DNI) is the fraction of circulating immature granulocytes, which reflects severe bacterial infections and septic condition but has not been studied in urinary tract infection (UTI). Here, we evaluated the value of DNI in predicting acute pyelonephritis (APN) or vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) using the data of 288 patients. Conventional inflammatory markers (white blood cell [WBC] count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR], C-reactive protein [CRP]), and DNI were measured. WBC, CRP, ESR and DNI were higher in APN than in lower UTI (p < 0.01). Multiple logistic-regression analyses showed that DNI was a predictive factor for areas of lack of uptake on dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scans (P < 0.01). The area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUC) was also high for DNI (0.622, 95% CI 0.558-0.687, P < 0.01) as well as for CRP (0.731, 95% CI 0.673-0.789, P < 0.01) for the prediction of DMSA defects. DNI demonstrated the highest area under the ROC curve for diagnosis of VUR (0.620, 95% CI 0.542-0.698, P < 0.01). To the best of our knowledge, this is a first study demonstrating that DNI can be used as a diagnostic marker to distinguish APN from lower UTI and function as a diagnostic marker indicative of VUR compared to other conventional markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- National Collaborating Centre for, W. s. & Children’s, H. In Urinary Tract Infection in Children: Diagnosis, Treatment and Long-term Management (RCOG Press National Collaborating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health., 2007). - PubMed
-
- Okazaki Y. & Matsukawa A. Pathophysiology of sepsis and recent patents on the diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis for sepsis. Recent PatIinflamm Allergy Drug Discov 3, 26–32 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Lowsby R. et al.. Neutrophil to lymphocyte count ratio as an early indicator of blood stream infection in the emergency department. Emerg Med J 32, 531–534 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Nahm C. H., Choi J. W. & Lee J. Delta neutrophil index in automated immature granulocyte counts for assessing disease severity of patients with sepsis. Ann Clin Lab Sci 38, 241–246 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

