Ultrasound-Mediated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transfection as a Targeted Cancer Therapy Platform
- PMID: 28169315
- PMCID: PMC5294424
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42046
Ultrasound-Mediated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transfection as a Targeted Cancer Therapy Platform
Abstract
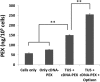
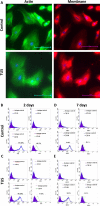
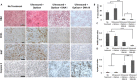
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) hold tremendous potential as a targeted cell-based delivery platform for inflammatory and cancer therapy. Genetic manipulation of MSCs, however, is challenging, and therefore, most studies using MSCs as therapeutic cell carriers have utilized viral vectors to transduce the cells. Here, we demonstrate, for the first time, an alternative approach for the efficient transfection of MSCs; therapeutic ultrasound (TUS). Using TUS with low intensities and moderate frequencies, MSCs were transfected with a pDNA encoding for PEX, a protein that inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and studied as a cell vehicle for in vivo tumor therapy. TUS application did not alter the MSCs' stemness or their homing capabilities, and the transfected MSCs transcribed biologically active PEX. Additionally, in a mouse model, 70% inhibition of prostate tumor growth was achieved following a single I.V. administration of MSCs that were TUS-transfected with pPEX. Further, the repeated I.V. administration of TUS-pPEX transfected-MSCs enhanced tumor inhibition up to 84%. Altogether, these results provide a proof of concept that TUS-transfected MSCs can be effectively used as a cell-based delivery approach for the prospective treatment of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Therapeutic ultrasound facilitates antiangiogenic gene delivery and inhibits prostate tumor growth.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Aug;6(8):2371-82. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0019. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17699732
-
Apoptin-modified human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit growth of lung carcinoma in nude mice.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):1023-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3501. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25816208 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced by inflammatory cytokines produce angiogenetic factors and promote prostate cancer growth.BMC Cancer. 2017 Dec 21;17(1):878. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3879-z. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29268703 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress of gene recombinant mesenchymal stem cells as tumor targeting delivery vehicles].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013 Aug;48(8):1209-20. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 24187826 Review. Chinese.
-
Targeted antitumor therapy mediated by prodrug-activating mesenchymal stromal cells.Cancer Lett. 2017 Nov 1;408:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.016. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28838843 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetically modified macrophages accomplish targeted gene delivery to the inflamed brain in transgenic Parkin Q311X(A) mice: importance of administration routes.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 16;10(1):11818. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68874-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32678262 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical basis, state and challenges of living cell-based drug delivery systems.Theranostics. 2024 Aug 19;14(13):5152-5183. doi: 10.7150/thno.99257. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39267776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Biology to Deliver Therapeutic and Imaging Entities via Cell-Based Methods.Chemistry. 2018 Jun 21;24(35):8717-8726. doi: 10.1002/chem.201706180. Epub 2018 May 14. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29543990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: A New Era in the Cell-Based Targeted Gene Therapy of Cancer.Front Immunol. 2017 Dec 18;8:1770. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01770. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29326689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate type II diabetic mellitus in Goto-Kakizaki rats.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019 Feb 28;11:22. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0417-y. eCollection 2019. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 30858895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu Y.-L., Fu Y.-H., Tabata Y. & Gao J.-Q. Mesenchymal stem cells: a promising targeted-delivery vehicle in cancer gene therapy. Journal of Controlled Release 147, 154–162 (2010). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

