Fundamental limits in high-Q droplet microresonators
- PMID: 28169317
- PMCID: PMC5294640
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41997
Fundamental limits in high-Q droplet microresonators
Abstract
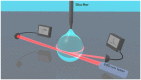
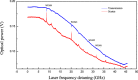
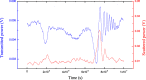
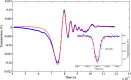
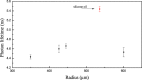
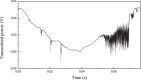
Liquid droplet whispering-gallery-mode microresonators open a new research frontier for sensing, optomechanics and photonic devices. At visible wavelengths, where most liquids are transparent, a major contribution to a droplet optical quality factor is expected theoretically from thermal surface distortions and capillary waves. Here, we investigate experimentally these predictions using transient cavity ring-down spectroscopy. With our scheme, the optical out-coupling and intrinsic loss are measured independently while any perturbation induced by thermal, acoustic and laser-frequency noise is avoided thanks to the ultra-short light-cavity interaction time. The measurements reveal a photon lifetime at least ten times longer than the thermal limit and indicate that capillary fluctuations activate surface scattering effects responsible for light coupling. This suggests that droplet microresonators are an ideal optical platform for ultra-sensitive spectroscopy of highly transparent liquid compounds in nano-liter volumes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquid Droplet Microresonators.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jan 24;19(3):473. doi: 10.3390/s19030473. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30682798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brillouin cavity optomechanics with microfluidic devices.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1994. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2994. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23744103
-
Optothermal dynamics in whispering-gallery microresonators.Light Sci Appl. 2020 Feb 24;9:24. doi: 10.1038/s41377-019-0239-6. eCollection 2020. Light Sci Appl. 2020. PMID: 32133127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Q-factor reconfigurable microresonators induced in side-coupled optical fibres.Light Sci Appl. 2023 Aug 18;12(1):197. doi: 10.1038/s41377-023-01247-7. Light Sci Appl. 2023. PMID: 37596274 Free PMC article.
-
Chasing the thermodynamical noise limit in whispering-gallery-mode resonators for ultrastable laser frequency stabilization.Nat Commun. 2017 Mar 31;8(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00021-9. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28364116 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
High-Sensitivity Whispering Gallery Mode Humidity Sensor Based on Glycerol Microdroplet Volumetric Expansion.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 3;21(5):1746. doi: 10.3390/s21051746. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802462 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Droplet Microresonators.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jan 24;19(3):473. doi: 10.3390/s19030473. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30682798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Practical lineshape of a laser operating near an exceptional point.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 17;11(1):6164. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85665-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33731783 Free PMC article.
-
Advances of Optofluidic Microcavities for Microlasers and Biosensors.Micromachines (Basel). 2018 Mar 9;9(3):122. doi: 10.3390/mi9030122. Micromachines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30424056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kippenberg T. J., Holzwarth R. & Diddams S. A. Microresonator-Based Optical Frequency Combs. Science 332, 555 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Aspelmeyer M., Kippenberg T. J. & Marquardt F. Cavity Optomechanics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 86, 1391 (2014).
-
- Hossein-Zadeh M. & Vahala K. J. Fiber-taper coupling to Whispering-Gallery modes of fluidic resonators embedded in a liquid medium, Opt. Express 14, 10800 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Jonáš A. et al.. In vitro and in vivo biolasing of fluorescent proteins suspended in liquid microdroplet cavities. Lab Chip 14, 3093 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

