Postretrieval Extinction Attenuates Alcohol Cue Reactivity in Rats
- PMID: 28169439
- PMCID: PMC5332343
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.13323
Postretrieval Extinction Attenuates Alcohol Cue Reactivity in Rats
Abstract
Background: Conditioned responses to alcohol-associated cues can hinder recovery from alcohol use disorder (AUD). Cue exposure (extinction) therapy (CET) can reduce reactivity to alcohol cues, but its efficacy is limited by phenomena such as spontaneous recovery and reinstatement that can cause a return of conditioned responding after extinction. Using a preclinical model of alcohol cue reactivity in rats, we evaluated whether the efficacy of alcohol CET could be improved by conducting CET during the memory reconsolidation window after retrieval of cue-alcohol associations.
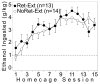
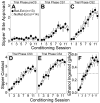
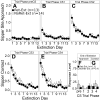
Methods: Rats were provided with intermittent access to unsweetened alcohol. Rats were then trained to predict alcohol access based on a visual cue. Next, rats were treated with either standard extinction (n = 14) or postretrieval extinction (n = 13). Rats were then tested for long-term memory of extinction and susceptibility to spontaneous recovery and reinstatement.
Results: Despite equivalent extinction, rats treated with postretrieval extinction exhibited reduced spontaneous recovery and reinstatement relative to rats treated with standard extinction.
Conclusions: Postretrieval CET shows promise for persistently attenuating the risk to relapse posed by alcohol cues in individuals with AUD.
Keywords: Alcohol Cue; Exposure Therapy; Reconsolidation; Relapse; Retrieval.
Copyright © 2017 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures
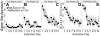


Similar articles
-
Effect of naltrexone during extinction of alcohol-reinforced responding and during repeated cue-conditioned reinstatement sessions in a cue exposure style treatment.Alcohol. 2008 Nov;42(7):553-63. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.06.003. Epub 2008 Sep 6. Alcohol. 2008. PMID: 18774673 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol seeking in C57BL/6 mice induced by conditioned cues and contexts in the extinction-reinstatement model.Alcohol. 2006 Feb;38(2):81-8. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2006.05.004. Alcohol. 2006. PMID: 16839854
-
Effects of D-cycloserine on extinction of mesolimbic cue reactivity in alcoholism: a randomized placebo-controlled trial.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Jul;232(13):2353-62. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3882-5. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25697860 Clinical Trial.
-
From lab to clinic: Extinction of cued cravings to reduce overeating.Physiol Behav. 2016 Aug 1;162:174-80. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.03.018. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 26994737 Review.
-
Targeting extinction and reconsolidation mechanisms to combat the impact of drug cues on addiction.Neuropharmacology. 2009;56 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):186-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.07.027. Epub 2008 Jul 30. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 18708077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder and Substance Use Disorder as Two Pathologies Affecting Memory Reactivation: Implications for New Therapeutic Approaches.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Feb 13;13:26. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00026. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30814940 Free PMC article.
-
Friend recollections, and a collection of collaborations with Nadia.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jul 29;16:954906. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.954906. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35967900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cue-alcohol associative learning in female rats.Alcohol. 2019 Dec;81:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 31002878 Free PMC article.
-
Memory editing from science fiction to clinical practice.Nature. 2019 Aug;572(7767):43-50. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1433-7. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31367027 Review.
-
Exploring Post-Retrieval Strategies to Reduce Drug Craving in Methamphetamine Use Disorders.Addict Biol. 2025 Jun;30(6):e70049. doi: 10.1111/adb.70049. Addict Biol. 2025. PMID: 40536786 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bouton M. Context and behavioral processes in extinction. Learn Mem. 2004;11:485–494. - PubMed
-
- Cofresí RU, Lewis SM, Chaudhri N, Lee HJ, Monfils M-H, Gonzales RA. Modeling Pavlovian alcohol seeking in rats using a retractable sipper to study both appetitive and consummatory behavior. 45th Annual Meeting of the Society for Neuroscience; Chicago, IL. Oct 17-21.2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

