Health-related Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Living in the United States and Canada
- PMID: 28169971
- PMCID: PMC5403561
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001525
Health-related Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Living in the United States and Canada
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of the study was to determine whether selected sociodemographic and hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific clinical factors are associated with health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among pediatric patients chronically infected with HBV.
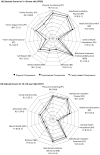
Methods: Children with chronic HBV enrolled in the Hepatitis B Research Network completed the Child Health Questionnaire at study entry. Caregivers of children 5 to <10 years completed the parent-reported form (CHQ-Parent Report Form); youth 10 to <18 years completed the child-reported CHQ-Child Report Form. We examined univariable associations of the Child Health Questionnaire scores with selected independent variables: sex, adoption status, maternal education, alanine aminotransferase (U/L), aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index, and HBV-specific symptom count.
Results: A total of 244 participants (83 young children 5-<10 years, 161 youth 10-<18 years) were included, all HBV treatment-naïve. Among young children, increased alanine aminotransferase level was negatively associated with CHQ-Parent Report Form psychosocial summary t score (r = -0.28, P = 0.01). No other subscale comparisons for young children were statistically significant. Among youth, adoption was associated with better physical functioning and general health (P < 0.01). Higher maternal education was associated with better role/functioning-physical and -emotional scores (P < 0.05). Maternal education and adoption status were linked with adoption associated with higher maternal education. Increased symptom count in youth was associated with worse HRQoL in subscales measuring bodily pain, behavior, mental health, and self-esteem (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: Although overall HRQoL is preserved in children with chronic HBV, some sociodemographic and HBV-related clinical factors were associated with impaired HRQoL in our pediatric patients at baseline. Measurement of HRQoL can focus resources on education and psychosocial support in children and families most in need.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Bortolotti F, Calzia R, Cadrobbi P, Giacchini R, Ciravegna B, Armigliato M, et al. Liver cirrhosis associated with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in childhood. J Pediatr. 1986;108(2):224–7. - PubMed
-
- Hsu HC, Wu MZ, Chang MH, Su IJ, Chen DS. Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma develops exclusively in hepatitis B surface antigen carriers in three decades in Taiwan. Report of 51 cases strongly associated with rapid development of liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1987;5(3):260–7. - PubMed
-
- Stadler LP, Mezoff AG, Staat MA. Hepatitis B virus screening for internationally adopted children. Pediatrics. 2008;122(6):1223–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources