Genetic Association and Risk Scores in a Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Meta-analysis of 16,707 Subjects
- PMID: 28170284
- PMCID: PMC5516277
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0331OC
Genetic Association and Risk Scores in a Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Meta-analysis of 16,707 Subjects
Abstract
The heritability of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) cannot be fully explained by recognized genetic risk factors identified as achieving genome-wide significance. In addition, the combined contribution of genetic variation to COPD risk has not been fully explored. We sought to determine: (1) whether studies of variants from previous studies of COPD or lung function in a larger sample could identify additional associated variants, particularly for severe COPD; and (2) the impact of genetic risk scores on COPD. We genotyped 3,346 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 2,588 cases (1,803 severe COPD) and 1,782 control subjects from four cohorts, and performed association testing with COPD, combining these results with existing genotyping data from 6,633 cases (3,497 severe COPD) and 5,704 control subjects. In addition, we developed genetic risk scores from SNPs associated with lung function and COPD and tested their discriminatory power for COPD-related measures. We identified significant associations between SNPs near PPIC (P = 1.28 × 10-8) and PPP4R4/SERPINA1 (P = 1.01 × 10-8) and severe COPD; the latter association may be driven by recognized variants in SERPINA1. Genetic risk scores based on SNPs previously associated with COPD and lung function had a modest ability to discriminate COPD (area under the curve, ∼0.6), and accounted for a mean 0.9-1.9% lower forced expiratory volume in 1 second percent predicted for each additional risk allele. In a large genetic association analysis, we identified associations with severe COPD near PPIC and SERPINA1. A risk score based on combining genetic variants had modest, but significant, effects on risk of COPD and lung function.
Keywords: alpha-1 antitrypsin; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; genetic epidemiology; genetic risk factors; genetic risk score.
Figures
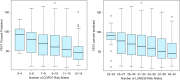

References
-
- Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Xu J. Deaths: final data for 2011. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2015;63:1–120. - PubMed
-
- Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agustí AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Nishimura M, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:347–365. - PubMed
-
- Ingebrigtsen T, Thomsen SF, Vestbo J, van der Sluis S, Kyvik KO, Silverman EK, Svartengren M, Backer V. Genetic influences on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease—a twin study. Respir Med. 2010;104:1890–1895. - PubMed
-
- McCloskey SC, Patel BD, Hinchliffe SJ, Reid ED, Wareham NJ, Lomas DA. Siblings of patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease have a significant risk of airflow obstruction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1419–1424. - PubMed
-
- Silverman EK, Chapman HA, Drazen JM, Weiss ST, Rosner B, Campbell EJ, O’Donnell WJ, Reilly JJ, Ginns L, Mentzer S, et al. Genetic epidemiology of severe, early-onset chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: risk to relatives for airflow obstruction and chronic bronchitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:1770–1778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL113264/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018526/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 ES011080/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139634/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076113/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL124233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076115/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007427/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076103/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N024842/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HR076114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076110/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076112/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL105339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076109/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126596/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076119/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076108/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK106116/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076106/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL114501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

