Evaluating a Medical School's Climate for Women's Success: Outcomes for Faculty Recruitment, Retention, and Promotion
- PMID: 28170291
- PMCID: PMC5446601
- DOI: 10.1089/jwh.2016.6018
Evaluating a Medical School's Climate for Women's Success: Outcomes for Faculty Recruitment, Retention, and Promotion
Abstract
Objective: Women are under-represented in academia. Causative factors include challenges of career-family integration. We evaluated factors reflecting institutional culture (promotion, retention, hiring, and biasing language in promotion letters) as part of an intervention to help shift culture and raise awareness of flexibility policies at the University of California, Davis (UCD).
Materials and methods: Data on faculty use of family-friendly policies were obtained at baseline, and surveys for policy awareness were conducted pre(2010)/post(2013) an NIH-funded study educational intervention. Data on hires, separations, and promotions were obtained pre(2007-2009, 2234 person-year data points)/post(2010-2012, 2384 person-year data points) intervention and compared by logistic regression and for gender differences. Department promotion letters (53) were also analyzed for biasing language.
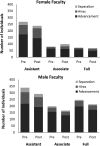
Results: Policy use was overall low, highest for female assistant professors, and for maternity leave. Awareness significantly increased for all policies postintervention. Promotions decreased, likely because of increases in advancement deferrals or tenure clock extensions. Pre/postintervention, female and male hires were near parity for assistant professors, but female hires were substantially lower than males for associate (54% less likely, p = 0.03) and full professors (70% less likely, p = 0.002). Once hired, women were no more likely to separate than men. Fewer associate/full professors separated than assistant professors (p = 0.002, p < 0.001, respectively), regardless of gender. Language in promotion letters was not gender biased.
Conclusions: We demonstrate a shift at UCD toward a culture of work-life flexibility, an environment in which letters of recommendation show very few biased descriptions, and in which assistant professor hiring is gender equitable. At the same time, a decrease in number of faculty members applying for promotion and an imbalance of men over women at senior hires independent of policy awareness may challenge the assumption that family-friendly policies, while promoting flexibility, also have a positive impact on professional advancement.
Keywords: biomedical science careers; career flexibility; women in medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander H, Lang J. The long-term retention and attrition of U.S. Medical school faculty Association of American Medical Colleges: Analysis in Brief 2014;14
-
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Distribution of full time faculty by department, rank and gender. Women in academic medicine: Benchmarking and statistics (2013–2014). Available at: www.aamc.org/members/gwims/statistics Accessed July24, 2015
-
- Hamel MB, Ingelfinger JR, Phimister E, Solomon CG. Women in academic medicine—Progress and challenges. N Engl J Med 2006;355:310–312 - PubMed
-
- Kaplan SH, Sullivan LM, Dukes KA, Phillips CF, Kelch RP, Schaller JG. Sex differences in academic advancement. Results of a national study of pediatricians. N Engl J Med 1996;335:1282–1289 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources