Tanshinone IIA Protects Endothelial Cells from H₂O₂-Induced Injuries via PXR Activation
- PMID: 28173640
- PMCID: PMC5685429
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.179
Tanshinone IIA Protects Endothelial Cells from H₂O₂-Induced Injuries via PXR Activation
Abstract
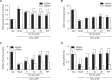
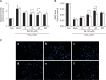
Tanshinone IIA (Tan IIA) is a pharmacologically active substance extracted from the rhizome of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (also known as the Chinese herb Danshen), and is widely used to treat atherosclerosis. The pregnane X receptor (PXR) is a nuclear receptor that is a key regulator of xenobiotic and endobiotic detoxification. Tan IIA is an efficacious PXR agonist that has a potential protective effect on endothelial injuries induced by xenobiotics and endobiotics via PXR activation. Previously numerous studies have demonstrated the possible effects of Tan IIA on human umbilical vein endothelial cells, but the further mechanism for its exerts the protective effect is not well established. To study the protective effects of Tan IIA against hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), we pretreated cells with or without different concentrations of Tan IIA for 24 h, then exposed the cells to 400 μM H₂O₂ for another 3 h. Therefore, our data strongly suggests that Tan IIA may lead to increased regeneration of glutathione (GSH) from the glutathione disulfide (GSSG) produced during the GSH peroxidase-catalyzed decomposition of H₂O₂ in HUVECs, and the PXR plays a significant role in this process. Tan IIA may also exert protective effects against H₂O₂-induced apoptosis through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway associated with the participation of PXR. Tan IIA protected HUVECs from inflammatory mediators triggered by H₂O₂ via PXR activation. In conclusion, Tan IIA protected HUVECs against H₂O₂-induced cell injury through PXR-dependent mechanisms.
Keywords: Apoptosis; HUVECs; Inflammation; Oxidative stress; PXR; Tanshinone IIA.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Tanshinone IIA ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammatory bowel disease via the pregnane X receptor.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Dec 7;9:6343-62. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S79388. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26674743 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA Attenuates H₂O₂ -induced injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Am J Chin Med. 2012;40(6):1307-19. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X12500966. Am J Chin Med. 2012. PMID: 23227799
-
Tanshinone IIA exerts protective effects in a LCA-induced cholestatic liver model associated with participation of pregnane X receptor.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Apr 22;164:357-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.047. Epub 2015 Feb 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25660334
-
Pharmacological Activity and Mechanism of Tanshinone IIA in Related Diseases.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Nov 5;14:4735-4748. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S266911. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33192051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tanshinone IIA: A Review of its Anticancer Effects.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 14;11:611087. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.611087. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33597880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Cell Pyroptosis via the AMPK Signaling Pathway in Atherosclerosis.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Nov 14;15:6293-6306. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S386470. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36408328 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine as an add-on therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with carotid atherosclerosis: An updated meta-analysis of 27 randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 23;14:1091718. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1091718. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37033624 Free PMC article.
-
The pregnane X receptor and its microbiota-derived ligand indole 3-propionic acid regulate endothelium-dependent vasodilation.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):E350-E361. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00572.2018. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31211619 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA: a Chinese herbal ingredient for the treatment of atherosclerosis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 1;14:1321880. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1321880. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38108067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medicinal Herbs Effective Against Atherosclerosis: Classification According to Mechanism of Action.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019 May 1;27(3):254-264. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2018.231. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019. PMID: 30917628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Epsztejn S, Glickstein H, Picard V, Slotki IN, Breuer W, Beaumont C, Cabantchik ZI. H-ferritin subunit overexpression in erythroid cells reduces the oxidative stress response and induces multidrug resistance properties. Blood. 1999;94:3593–3603. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

