Effect of a low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field on expression and secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells
- PMID: 28173722
- PMCID: PMC5536647
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060516683077
Effect of a low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field on expression and secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells
Abstract
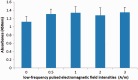
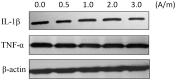
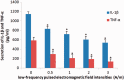
Objective To investigate changes in nucleus pulposus cell expression and secretion of interleukin (IL)-1β and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α following stimulation with a low-frequency (LF) pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF). Methods Primary rat nucleus pulposus cells were isolated and cultured in vitro, followed by stimulation with LF-PEMFs at a frequency of 2 Hz and different intensities, ranging from 0.5-3.0 A/m. Cells were observed for morphological changes, and proliferation rates were measured by cell viability counts. Expression of IL-1β and TNF-α within the nucleus pulposus cells was measured using western blotting, and levels of IL-1β and TNF-α secreted in the culture media were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results Stimulation of nucleus pulposus cells with LF-PEMFs did not appear to affect cell morphology or nucleus pulposus cell IL-1β and TNF-α expression levels. LF-PEMFs did not significantly affect cell proliferation, however, levels of IL-1β and TNF-α secreted into the culture media were found to be significantly reduced in an intensity-dependent manner. Conclusion Low-frequency PEMF stimulation may inhibit secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α in cultured nucleus pulposus cells.
Keywords: Low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field; interleukin-1β (IL-1β); nucleus pulposus cells; tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α).
Figures

References
-
- Kim JH, Studer RK, Sowa GA, et al. Activated macrophage-like THP-1 cells modulate anulus fibrosus cell production of inflammatory mediators in response to cytokines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008; 33: 2253–2259. - PubMed
-
- Lencel P, Delplace S, Pilet P, et al. Cell-specific effects of TNF-α and IL-1β on alkaline phosphatase: implication for syndesmophyte formation and vascular calcification. Lab Invest 2011; 91: 1434–1442. - PubMed
-
- Gaspari S, Marcovecchio ML, Breda L, et al. Growth in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: the role of inflammation. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2011; 29: 104–110. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

