A clinical score to predict mortality in septic acute kidney injury patients requiring continuous renal replacement therapy: the HELENICC score
- PMID: 28173756
- PMCID: PMC5297177
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-017-0312-8
A clinical score to predict mortality in septic acute kidney injury patients requiring continuous renal replacement therapy: the HELENICC score
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to identify predictors of early (7-day) mortality in patients with septic acute kidney injury (AKI) who required continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT).
Methods: Prospective cohort of 186 septic AKI patients undergoing CRRT at a tertiary hospital, from October 2005 to November 2010.
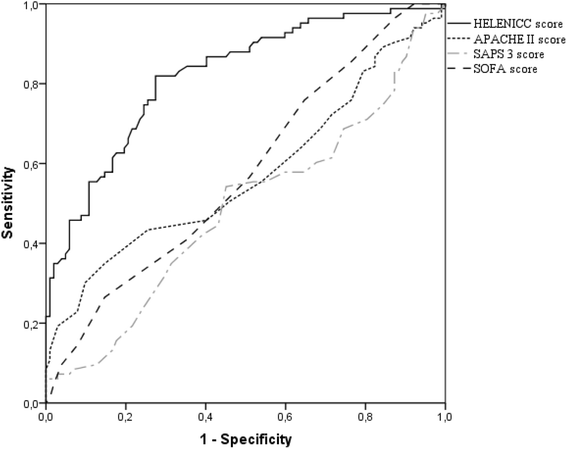
Results: After multivariate adjustment, five variables were associated to early mortality: norepinephrine utilization, liver failure, medical condition, lactate level, and pre-dialysis creatinine level. These variables were combined in a score, which demonstrated good discrimination, with a C-statistic of 0.82 (95% CI = 0.76-0.88), and good calibration (χ 2 = 4.3; p = 0.83). SAPS 3, APACHE II and SOFA scores demonstrated poor performance in this population.
Conclusions: The HEpatic failure, LactatE, NorepInephrine, medical Condition, and Creatinine (HELENICC) score outperformed tested generic models. Future studies should further validate this score in different cohorts.
Keywords: 7-day mortality; Hemodiafiltration; Risk score; Septic acute kidney injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[An analysis of clinical characteristics of septic acute kidney injury by using criteria of Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Apr;52(4):299-304. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23925356 Chinese.
-
Severe acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery: short-term outcomes in patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT).J Nephrol. 2016 Apr;29(2):229-239. doi: 10.1007/s40620-015-0213-1. Epub 2015 May 29. J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26022723
-
Mortality and associated risk factors in patients with blood culture positive sepsis and acute kidney injury requiring continuous renal replacement therapy-A retrospective study.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 5;16(4):e0249561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249561. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33819306 Free PMC article.
-
The use of antimicrobials in septic patients with acute kidney injury.J Bras Nefrol. 2017 Jul-Sep;39(3):323-328. doi: 10.5935/0101-2800.20170055. J Bras Nefrol. 2017. PMID: 29044341 Review. English, Portuguese.
-
Acute renal failure in multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome.Kidney Blood Press Res. 1997;20(3):164-6. doi: 10.1159/000174133. Kidney Blood Press Res. 1997. PMID: 9293432 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Optimal timing of initiating continuous renal replacement therapy in septic shock patients with acute kidney injury.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 19;9(1):11981. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48418-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31427640 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of platelets in the early warning of new-onset AKI in the ICU by using supervise learning: a retrospective analysis.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2194433. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2194433. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37013397 Free PMC article.
-
Use of vasopressors in patients with acute kidney injury on continuous kidney replacement therapy.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 19;19(12):e0315643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315643. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39700078 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury: Clinical Predictors and Beyond.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 11;10(6):1175. doi: 10.3390/jcm10061175. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33799741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Validation of Machine Learning Models for Real-Time Mortality Prediction in Critically Ill Patients With Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 15;9:853102. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.853102. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35783603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(2):580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, et al. External validation of severity scoring systems for acute renal failure using a multinational database. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(9):1961–1967. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000172279.66229.07. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

