A Randomized controlled trial of the effect of yoga and peer support on glycaemic outcomes in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a feasibility study
- PMID: 28173786
- PMCID: PMC5297169
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1574-x
A Randomized controlled trial of the effect of yoga and peer support on glycaemic outcomes in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a feasibility study
Abstract
Background: Type two diabetes is a complex and demanding chronic disease and its impact in a state (Kerala) which leads India in terms of the number of people with Diabetes is profound. Though the male to female ratio among the people with diabetes is roughly equal, women are uniquely and more severely affected. Management of type two Diabetes requires considerable dexterity on the part of the patient to manage drugs, diet and exercise. Therefore, in a low middle-income country like India it is necessary to look at low cost interventions that can empower the patient and build on available resources to help manage diabetes. Hence, we studied the feasibility and effect of two low cost interventions; yoga and peer support on glycaemic and other outcomes among women with type two diabetes.
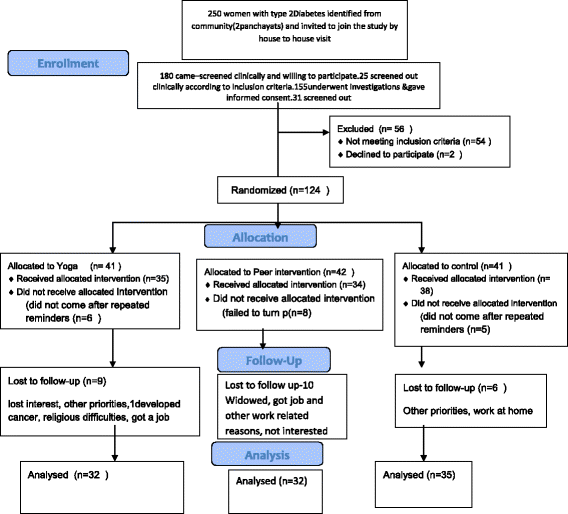
Methods: An open label parallel three armed randomized control trial was conducted among 124 recruited women with Diabetes for three months. Block randomization with a block length of six was carried out with each group having at least 41 women. In the Yoga arm, sessions by an instructor, consisting of a group of postures coordinated with breathing were conducted for an hour, two days a week. In the peer support arm each peer mentor after training visited 13-14 women with diabetes every week followed by a phone call. The meeting was about applying disease management or prevention plans in daily life.
Results: There was a trend in decline of fasting plasma glucose in the peer and yoga group and of glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) in the yoga group only, though not significant. A significant decrease was observed in diastolic blood pressure and hip circumference in the yoga group. The process indicated that most (80%) of the women in the yoga group attended classes regularly and 90% of the women in the peer group reported that peer mentoring was useful.
Conclusion: The effect of yoga and peer support on glycaemic outcomes was incremental. Longer term studies are necessary to ascertain the benefits shown by this feasibility study.
Trial registration: CTRI/2011/12/002227 dated 14/12/2011.
Keywords: Glycaemic outcomes; Peer support; RCT; Type 2 Diabetes; Women; Yoga.
Figures
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. 6th edition. 2014 update. Available at www.idf.org/sites/default/files/Atlas-poster-2014_EN.pdf. Accessed 17 Feb 2015.
-
- Mohan V, Sandeep S, Deepa R, Shah B, Varghese C. Epidemiology of type two diabetes: Indian scenario. Indian J Med Res. 2007;125:217–230. - PubMed
-
- Thankappan KR, Shah B, Mathur P, Sarma PS, Srinivas G, Mini GK, et al. Risk factor profile for chronic non-communicable diseases: results of a community-based study in Kerala, India. Indian J Med Res. 2010;131:53–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous