Cloning, expression and molecular characterization of a Cystoisospora suis specific uncharacterized merozoite protein
- PMID: 28173829
- PMCID: PMC5297187
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-2003-1
Cloning, expression and molecular characterization of a Cystoisospora suis specific uncharacterized merozoite protein
Abstract
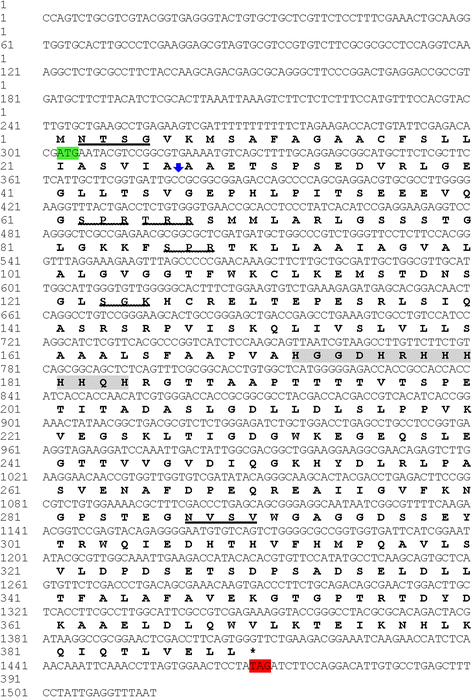
Background: The genome of the apicomplexan parasite Cystoisospora suis (syn. Isospora suis) has recently been sequenced and annotated, opening the possibility for the identification of novel therapeutic targets against cystoisosporosis. It was previously proposed that a 42 kDa uncharacterized merozoite protein, encoded by gene CSUI_005805, might be a relevant vaccine candidate due to its high immunogenic score, high expression level and species-specificity as determined in silico.
Methods: The 1170 bp coding sequence of the CSUI_005805 gene was PCR amplified and cloned into the bacterial expression vector pQE-31. The specificity of the expressed recombinant protein was evaluated in an immunoblot, and relative levels of expression in different developmental stages and subcellular localization were determined by quantitative real-time PCR and indirect immunofluorescence assay, respectively.
Results: The CSUI_005805 gene encoded for a 389 amino acid protein containing a histidine-rich region. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that CSUI_005805 was differentially expressed during the early development of C. suis in vitro, with higher transcript levels in merozoites compared to sporozoites. The recombinant protein was specifically recognized by sera from chicken immunized with recombinant CSUI_005805 protein and sera from piglets experimentally infected with C. suis, all of which suggested that despite prokaryotic expression, the recombinant CSUI_005805 protein maintained antigenic determinants and could elicit an immune response in the host. Immunofluorescence labelling and confocal microscopy revealed localization primarily at the surface of the parasite.
Conclusions: The results suggest that CSUI_005805 is highly expressed in merozoites and might thus be critical for their survival and establishment inside host cells. Owing to its specificity, localization and expression pattern, CSUI_005805 could be exploited as an attractive candidate for alternative control strategies against C. suis such as vaccines.
Keywords: Apicomplexa; Cystoisosporosis; Invasion inhibition; Protozoa; Recombinant antigen; Swine.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization and analysis of a novel calcium-dependent protein kinase from Eimeria tenella.Parasitology. 2013 May;140(6):746-55. doi: 10.1017/S0031182012002107. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Parasitology. 2013. PMID: 23369433
-
Molecular Characterization and Immune Protection of a New Conserved Hypothetical Protein of Eimeria tenella.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 16;11(6):e0157678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157678. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27309852 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular characterization and immune protection of microneme 2 of Eimeria acervulina.Vet Parasitol. 2016 Jan 15;215:96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.10.028. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Vet Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 26790744
-
Identification and molecular characterization of microneme 5 of Eimeria acervulina.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 22;9(12):e115411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115411. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25531898 Free PMC article.
-
Cystoisospora suis - A Model of Mammalian Cystoisosporosis.Front Vet Sci. 2015 Nov 30;2:68. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2015.00068. eCollection 2015. Front Vet Sci. 2015. PMID: 26664994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anticoccidial drugs of the livestock industry.Parasitol Res. 2019 Jul;118(7):2009-2026. doi: 10.1007/s00436-019-06343-5. Epub 2019 May 31. Parasitol Res. 2019. PMID: 31152233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Cystoisospora suis sexual stages in vitro.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Mar 18;13(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04014-4. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32188507 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody and cytokine response to Cystoisospora suis infections in immune-competent young pigs.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Jul 4;11(1):390. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2974-6. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 29973271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindsay DS, Current W, Power T. Enteric coccidial infections and coccidiosis in swine. Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet. 1992;14:698–02.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

