Gene-environment interaction between lead and Apolipoprotein E4 causes cognitive behavior deficits in mice
- PMID: 28173832
- PMCID: PMC5297175
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-017-0155-2
Gene-environment interaction between lead and Apolipoprotein E4 causes cognitive behavior deficits in mice
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Gene-environment interaction between lead and Apolipoprotein E4 causes cognitive behavior deficits in mice.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Nov 3;12(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0223-7. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 29100536 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by progressive cognitive decline and memory loss. Environmental factors and gene-environment interactions (GXE) may increase AD risk, accelerate cognitive decline, and impair learning and memory. However, there is currently little direct evidence supporting this hypothesis.
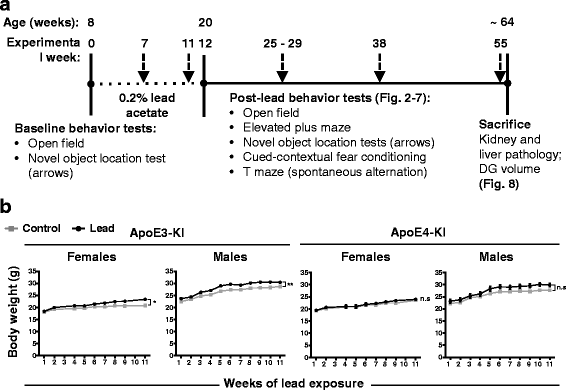
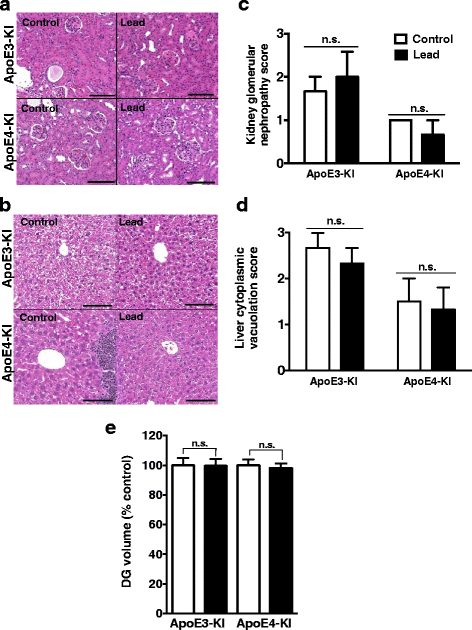
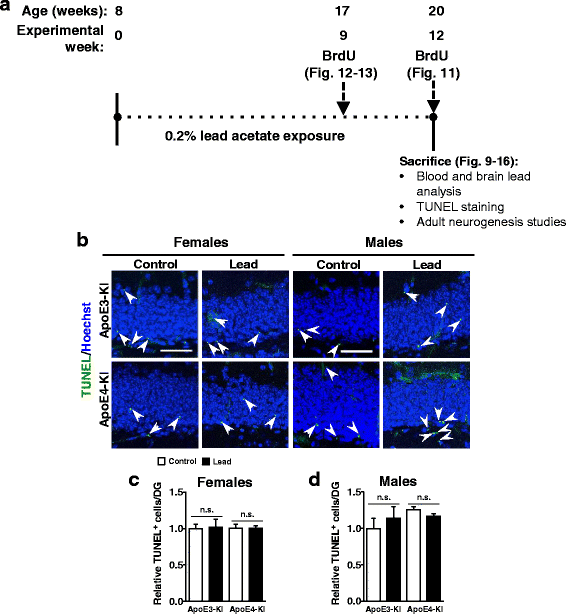
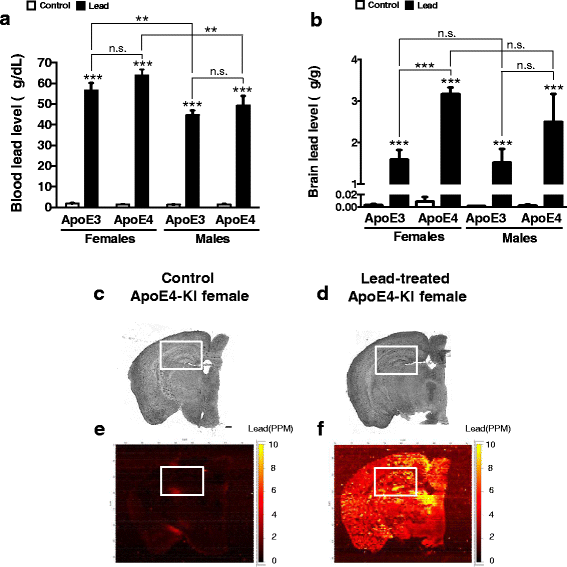
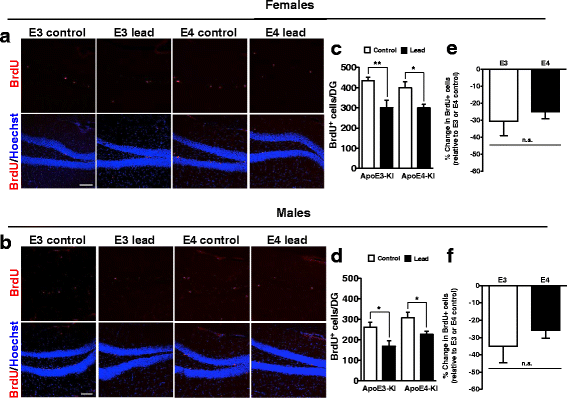
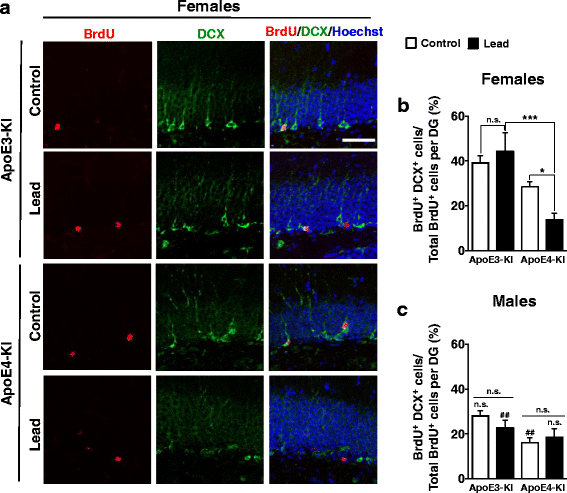
Methods: In this study, we assessed for a GXE between lead and ApoE4 on cognitive behavior using transgenic knock-in (KI) mice that express the human Apolipoprotein E4 allele (ApoE4-KI) or Apolipoprotein E3 allele (ApoE3-KI). We exposed 8-week-old male and female ApoE3-KI and ApoE4-KI mice to 0.2% lead acetate via drinking water for 12 weeks and assessed for cognitive behavior deficits during and after the lead exposure. In addition, we exposed a second (cellular) cohort of animals to lead and assessed for changes in adult hippocampal neurogenesis as a potential underlying mechanism for lead-induced learning and memory deficits.
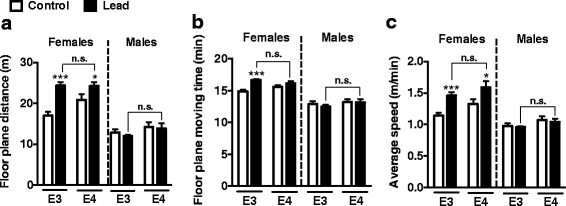
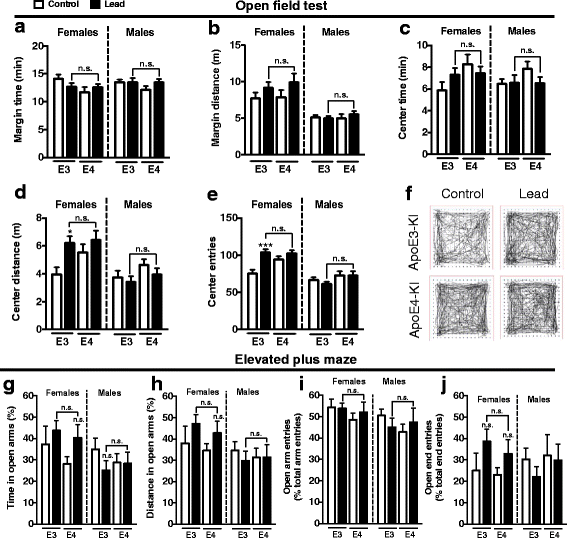
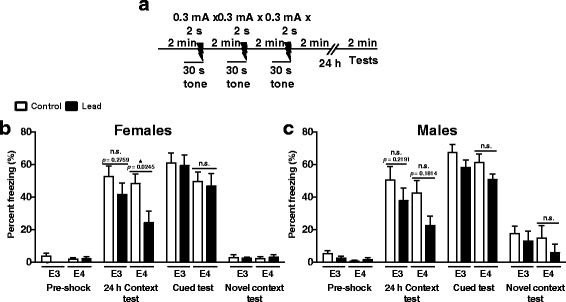
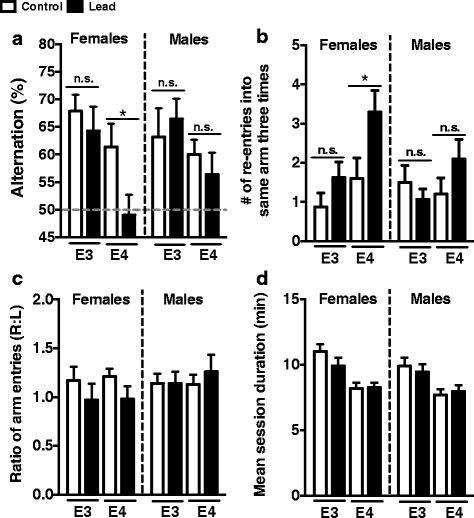
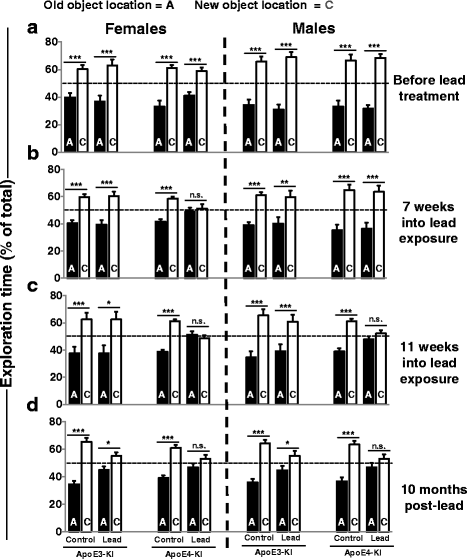
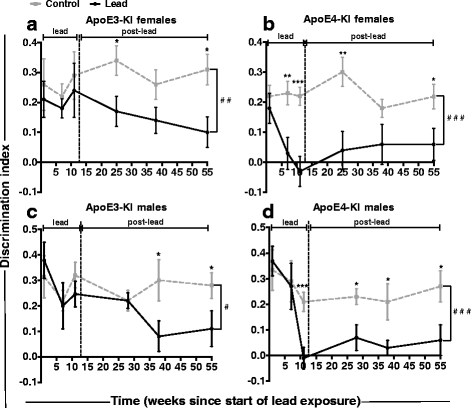
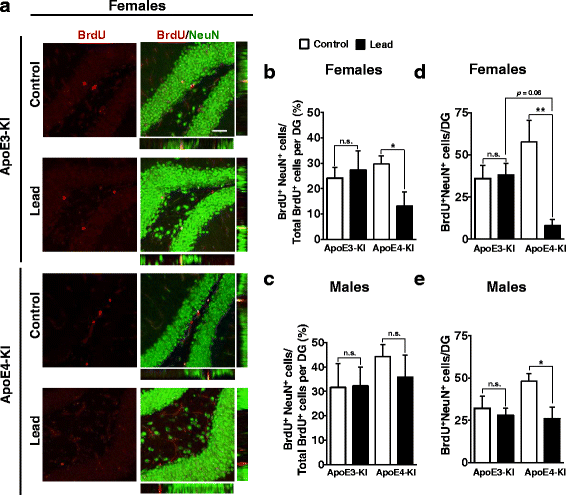
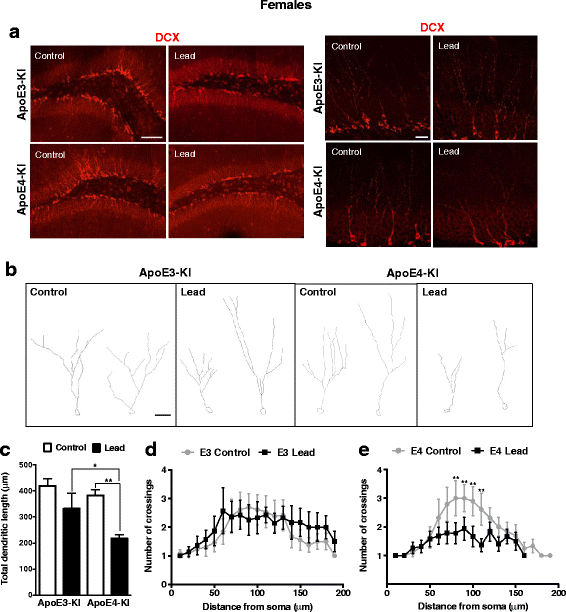
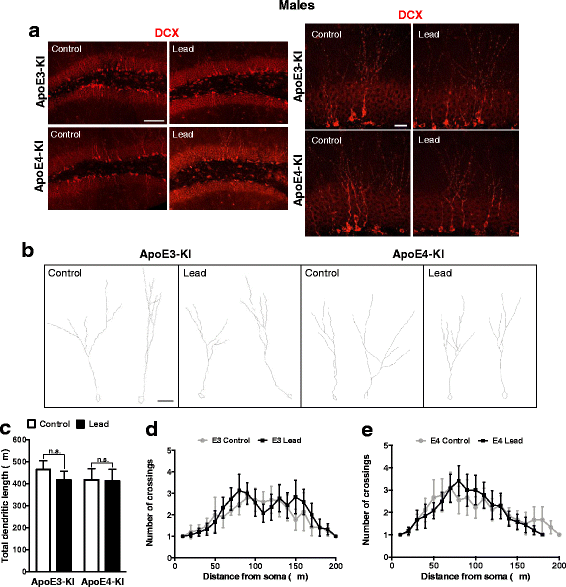
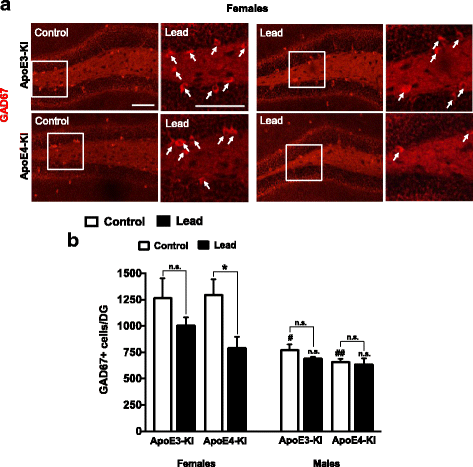
Results: In the behavior cohort, we found that lead reduced contextual fear memory in all animals; however, this decrease was greatest and statistically significant only in lead-treated ApoE4-KI females. Similarly, only lead-treated ApoE4-KI females exhibited a significant decrease in spontaneous alternation in the T-maze. Furthermore, all lead-treated animals developed persistent spatial working memory deficits in the novel object location test, and this deficit manifested earlier in ApoE4-KI mice, with female ApoE4-KI mice exhibiting the earliest deficit onset. In the cellular cohort, we observed that the maturation, differentiation, and dendritic development of adult-born neurons in the hippocampus was selectively impaired in lead-treated female ApoE4-KI mice.
Conclusions: These data suggest that GXE between ApoE4 and lead exposure may contribute to cognitive impairment and that impaired adult hippocampal neurogenesis may contribute to these deficits in cognitive behavior. Together, these data suggest a role for GXE and sex differences in AD risk.
Keywords: Adult hippocampal neurogenesis; Apolipoprotein E; Cognitive behavior; Lead; Learning and memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inducible and Conditional Activation of Adult Neurogenesis Rescues Cadmium-Induced Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Deficits in ApoE4-KI Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 23;24(11):9118. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119118. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298071 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Gene-Environment Interactions Between Cadmium Exposure and Apolipoprotein E4 on Memory in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Jan 1;173(1):189-201. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz218. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31626305 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4 Causes Age-Dependent Disruption of Slow Gamma Oscillations during Hippocampal Sharp-Wave Ripples.Neuron. 2016 May 18;90(4):740-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.04.009. Epub 2016 May 5. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27161522 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive deficits in human ApoE4 knock-in mice: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Behav Brain Res. 2024 Aug 5;471:115123. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115123. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Behav Brain Res. 2024. PMID: 38972485
-
Apolipoprotein E4, inhibitory network dysfunction, and Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2019 Jun 11;14(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13024-019-0324-6. Mol Neurodegener. 2019. PMID: 31186040 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic polymorphisms of GRIN2A and GRIN2B modify the neurobehavioral effects of low-level lead exposure in children.Environ Res. 2018 Aug;165:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Environ Res. 2018. PMID: 29655037 Free PMC article.
-
Human Hair as a Possible Surrogate Marker of Retained Tissue Gadolinium: A Pilot Autopsy Study Correlating Gadolinium Concentrations in Hair With Brain and Other Tissues Among Decedents Who Received Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents.Invest Radiol. 2020 Oct;55(10):636-642. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000681. Invest Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32433314 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible and Conditional Activation of Adult Neurogenesis Rescues Cadmium-Induced Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Deficits in ApoE4-KI Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 23;24(11):9118. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119118. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298071 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Gene-Environment Interactions Between Cadmium Exposure and Apolipoprotein E4 on Memory in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Jan 1;173(1):189-201. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz218. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31626305 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Metal Levels, Cognitive Test Performance, and Dementia in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Dec 2;7(12):e2448286. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.48286. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 39621345 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

