Osteoarthritis-associated basic calcium phosphate crystals activate membrane proximal kinases in human innate immune cells
- PMID: 28173838
- PMCID: PMC5296949
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1225-0
Osteoarthritis-associated basic calcium phosphate crystals activate membrane proximal kinases in human innate immune cells
Abstract
Background: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic debilitating joint disorder of particularly high prevalence in the elderly population. Intra-articular basic calcium phosphate (BCP) crystals are present in the majority of OA joints and are associated with severe degeneration. They are known to activate macrophages, synovial fibroblasts, and articular chondrocytes, resulting in increased cell proliferation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteases (MMPs). This suggests a pathogenic role in OA by causing extracellular matrix degradation and subchondral bone remodelling. There are currently no disease-modifying drugs available for crystal-associated OA; hence, the aim of this study was to explore the inflammatory pathways activated by BCP crystals in order to identify potential therapeutic targets to limit crystal-induced inflammation.
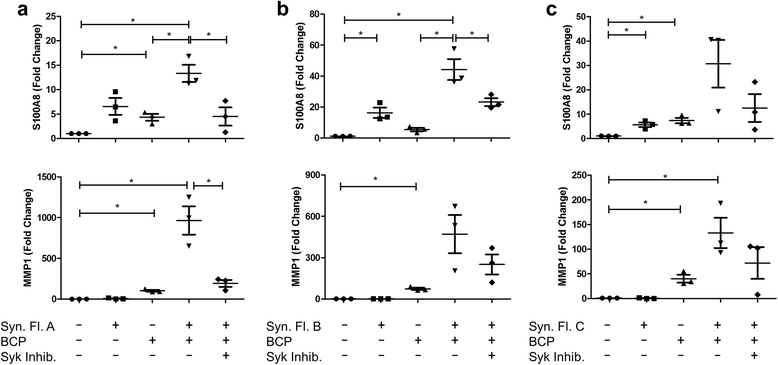
Methods: Primary human macrophages and dendritic cells were stimulated with BCP crystals, and activation of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K), and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) was detected by immunoblotting. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-primed macrophages were pre-treated with inhibitors of Syk, PI3K, and MAPKs prior to BCP stimulation, and cytokine production was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Aa an alternative, cells were treated with synovial fluid derived from osteoarthritic knees in the presence or absence of BCP crystals, and gene induction was assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
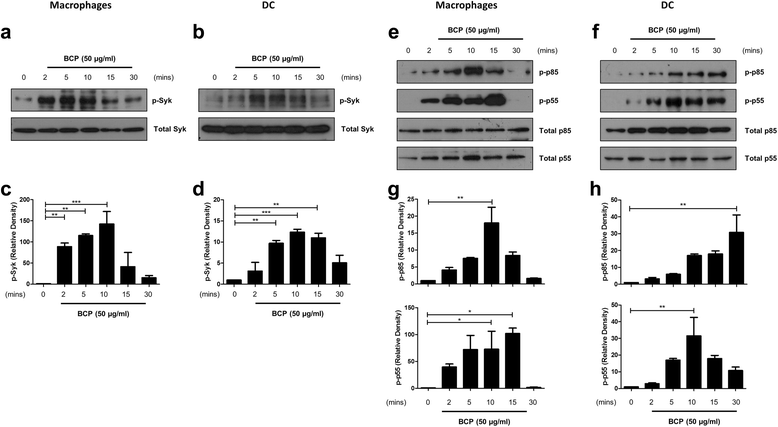
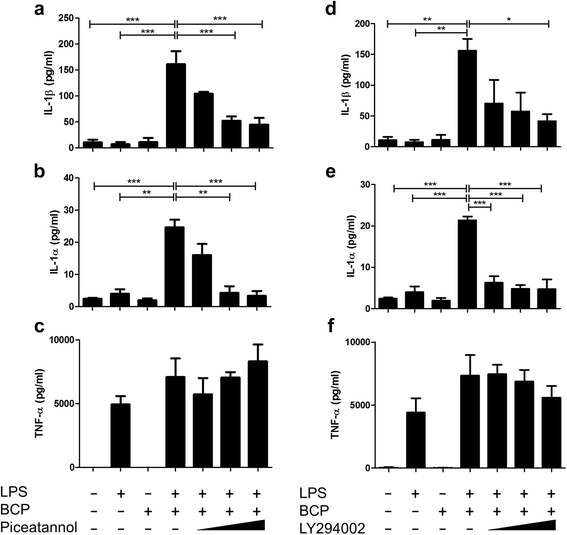
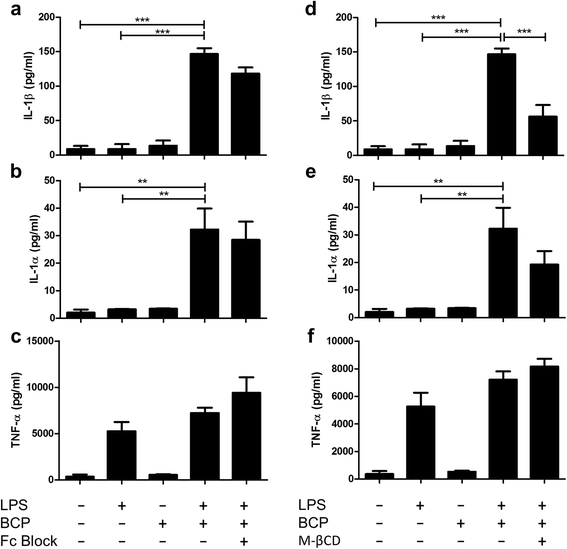
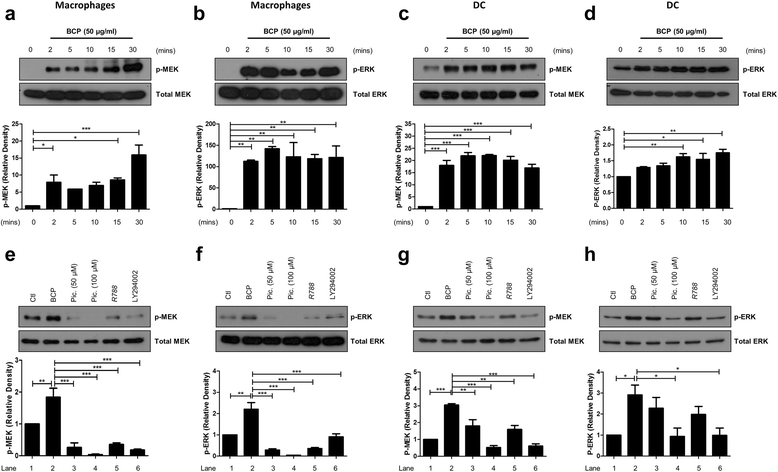
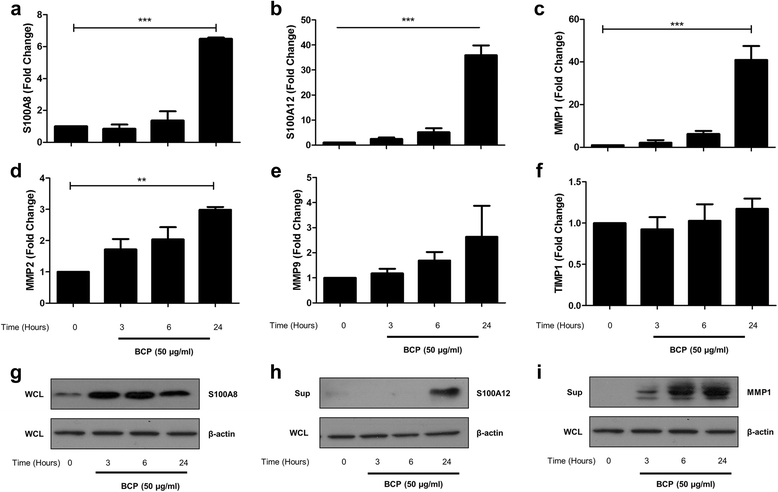
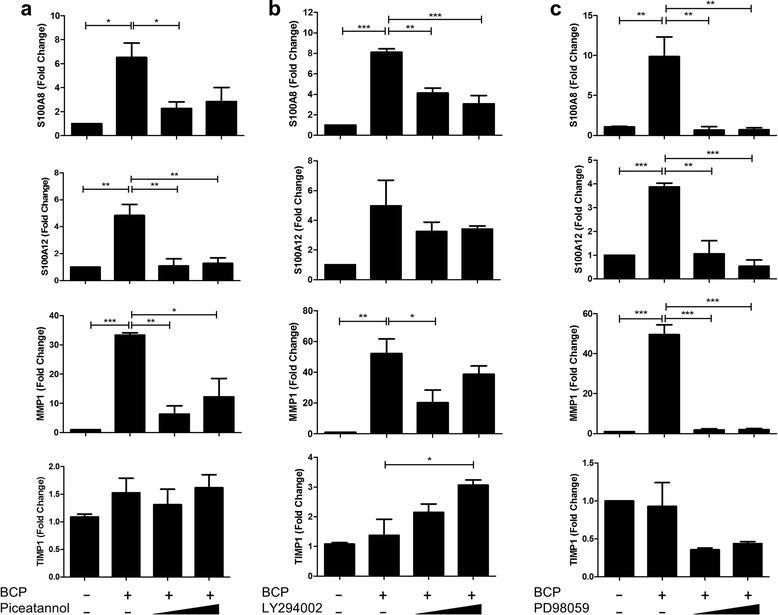
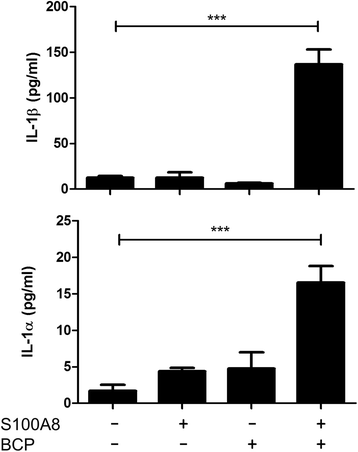
Results: We demonstrate that exposure of primary human macrophages and dendritic cells to BCP crystals leads to activation of the membrane-proximal tyrosine kinases Syk and PI3K. Furthermore, we show that production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1α and IL-1β and phosphorylation of downstream MEK and ERK MAPKs is suppressed following treatment with inhibitors of Syk or PI3K. Finally, we demonstrate that treatment of macrophages with BCP crystals induces the production of the damage-associated molecule S100A8 and MMP1 in a Syk-dependent manner and that synovial fluid from OA patients together with BCP crystals exacerbates these effects.
Conclusions: We identify Syk and PI3K as key signalling molecules activated by BCP crystals prior to inflammatory cytokine and DAMP expression and therefore propose that Syk and PI3K represent potential targets for the treatment of BCP-related pathologies.
Keywords: BCP crystals; Inflammation; PI3K; S100 proteins; Syk.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cholesterol crystals activate Syk and PI3 kinase in human macrophages and dendritic cells.Atherosclerosis. 2016 Aug;251:197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.06.035. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Atherosclerosis. 2016. PMID: 27356299
-
Osteoarthritis-associated basic calcium phosphate crystals induce pro-inflammatory cytokines and damage-associated molecules via activation of Syk and PI3 kinase.Clin Immunol. 2012 Sep;144(3):228-36. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2012.06.007. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22854286
-
Intra-articular basic calcium phosphate and monosodium urate crystals inhibit anti-osteoclastogenic cytokine signalling.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016 Dec;24(12):2141-2152. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016. PMID: 27426968
-
Basic calcium phosphate crystals and osteoarthritis pathogenesis: novel pathways and potential targets.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016 Mar;28(2):122-6. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000245. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26720903 Review.
-
Basic calcium phosphate crystals as a unique therapeutic target in osteoarthritis.Front Biosci. 2005 Jan 1;10:530-41. doi: 10.2741/1549. Print 2005 Jan 1. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15574390 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential immune-modulatory effects of wheat phytase on the performance of a mouse macrophage cell line, Raw 264.7, exposed to long-chain inorganic polyphosphate.Anim Biosci. 2021 Mar;34(3):463-470. doi: 10.5713/ajas.20.0060. Epub 2020 May 12. Anim Biosci. 2021. PMID: 32777888 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative analysis of NLRP3-related inflammatory mediators in synovial fluid in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis and internal derangement.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Feb 26;22(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04092-0. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 33637064 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-Containing Crystals and Osteoarthritis: an Unhealthy Alliance.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018 Mar 8;20(3):13. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0721-9. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29516278 Review.
-
The interplay between autophagy and programmed cell death in osteoarthritis: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Aug;480(8):4627-4646. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05279-y. Epub 2025 Apr 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40216661 Review.
-
Pyroptosis Plays a Role in Osteoarthritis.Aging Dis. 2020 Oct 1;11(5):1146-1157. doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.1127. eCollection 2020 Oct. Aging Dis. 2020. PMID: 33014529 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rachow JW, Ryan LM, McCarty DJ, Halverson PC. Synovial fluid inorganic pyrophosphate concentration and nucleotide pyrophosphohydrolase activity in basic calcium phosphate deposition arthropathy and Milwaukee shoulder syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:408–13. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310313. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

