Inhibition of dynamin-related protein 1 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic mice
- PMID: 28173848
- PMCID: PMC5297196
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-017-0501-2
Inhibition of dynamin-related protein 1 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic mice
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Inhibition of dynamin-related protein 1 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic mice.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 May 4;16(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0540-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28472959 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Many cardioprotective pharmacological agents failed to exert their protective effects in diabetic hearts subjected to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (MI/R). Identify the molecular basis linking diabetes with MI/R injury is scientifically important and may provide effective therapeutic approaches. Dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1)-mediated mitochondrial fission plays an important role in MI/R injury under non-diabetic conditions. Importantly, recent studies indicated that Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission is enhanced in the myocardium of diabetic mice. The above evidences suggested that Drp1 may be one critical molecule linking diabetes with MI/R injury. We hypothesized that inhibition of Drp1 may be effective to reduce MI/R injury in diabetic hearts.
Methods: High-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice were subjected to MI/R or sham operation. Mdivi-1 (1.2 mg/kg), a small molecule inhibitor of Drp1 or vehicle was administrated 15 min before the onset of reperfusion. Outcome measures included mitochondrial morphology, mitochondrial function, myocardial injury, cardiac function and oxidative stress.
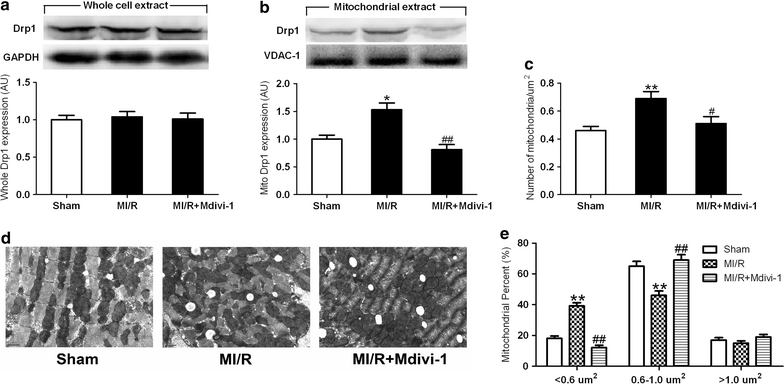
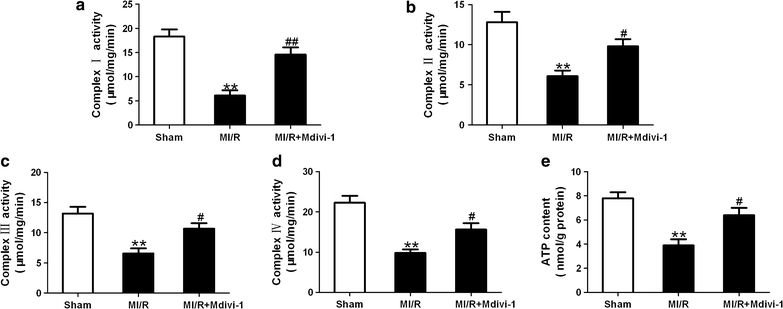
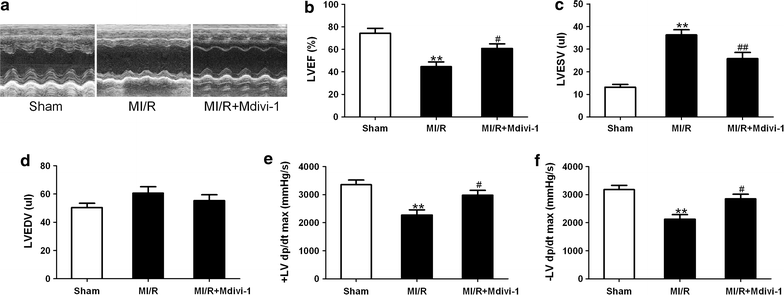
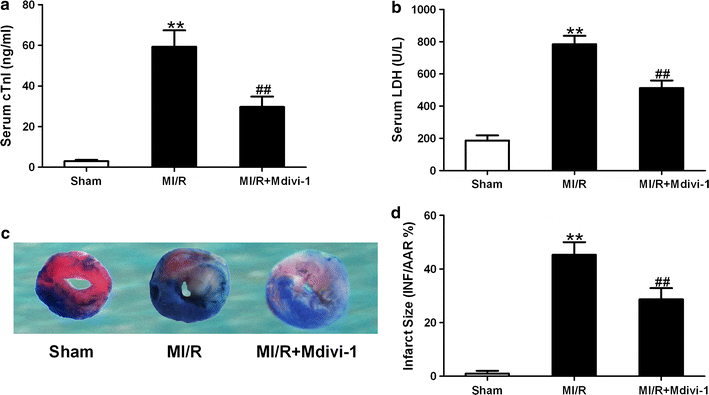
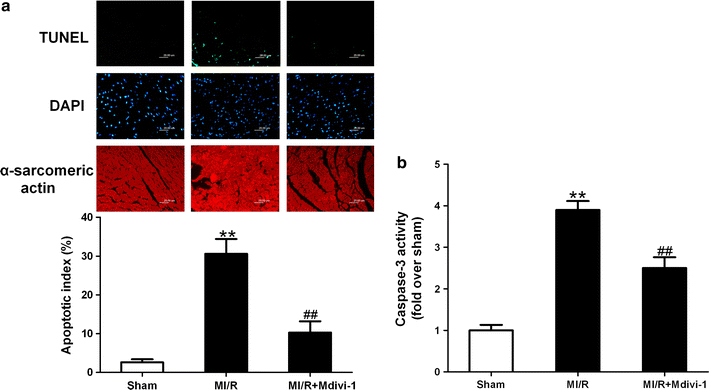
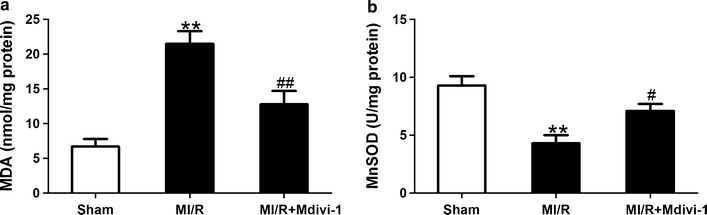
Results: Mitochondrial fission was significantly increased following MI/R as evidenced by enhanced translocation of Drp1 to mitochondria and decreased mitochondrial size. Delivery of Mdivi-1 into diabetic mice markedly inhibited Drp1 translocation to the mitochondria and reduced mitochondrial fission following MI/R. Inhibition of Drp1 in diabetic hearts improved mitochondrial function and cardiac function following MI/R. Moreover, inhibition of Drp1 reduced myocardial infarct size and serum cardiac troponin I and lactate dehydrogenase activities. These cardioprotective effects were associated with decreased cardiomyocyte apoptosis and malondialdehyde production and increased activities of antioxidant enzyme manganese superoxide dismutase.
Conclusions: Pharmacological inhibition of Drp1 prevents mitochondrial fission and reduces MI/R injury in diabetic mice. The findings suggest Drp1 may be a potential novel therapeutic target for diabetic cardiac complications.
Keywords: Diabetes; Drp1; Ischemia–reperfusion; Mitochondrial fission.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes impairs the protective effects of sevoflurane postconditioning in the myocardium subjected to ischemia/ reperfusion injury in rats: important role of Drp1.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Feb 16;21(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-01906-w. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 33593294 Free PMC article.
-
Hydralazine protects the heart against acute ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Jan 7;118(1):282-294. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa343. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33386841 Free PMC article.
-
HACE1 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of mitochondrial fission in mice.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Feb 3;25(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04445-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 39901081 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial bioenergetics and cardiolipin alterations in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: implications for pharmacological cardioprotection.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):H1341-H1352. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00028.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30095969 Review.
-
Roles of mitochondrial dynamics modulators in cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Nov;21(11):2643-2653. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13330. Epub 2017 Sep 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28941171 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of lncRNA AK139328 alleviates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic mice via modulating miR-204-3p and inhibiting autophagy.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Oct;22(10):4886-4898. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13754. Epub 2018 Jul 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30047214 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructural Evidence of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Osteomyelitis Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 16;24(6):5709. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065709. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982790 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-3: therapeutic target for diabetic myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Mol Med. 2025 Feb 26;31(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01117-5. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40012041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PCSK9 inhibitor and atorvastatin reduce cardiac impairment in ovariectomized prediabetic rats via improved mitochondrial function and Ca2+ regulation.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Aug;24(16):9189-9203. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15556. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32628813 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotection by isosteviol derivate JC105: A unique drug property to activate ERK1/2 only when cells are exposed to hypoxia-reoxygenation.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(18):10924-10934. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15721. Epub 2020 Aug 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32794652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghaboura N, Tamareille S, Ducluzeau PH, Grimaud L, Loufrani L, Croue A, et al. Diabetes mellitus abrogates erythropoietin-induced cardioprotection against ischemic-reperfusion injury by alteration of the RISK/GSK-3beta signaling. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(1):147–162. doi: 10.1007/s00395-010-0130-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

