Cardiovascular benefits associated with higher dietary K+ vs. lower dietary Na+: evidence from population and mechanistic studies
- PMID: 28174181
- PMCID: PMC5406991
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00453.2016
Cardiovascular benefits associated with higher dietary K+ vs. lower dietary Na+: evidence from population and mechanistic studies
Abstract
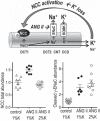
The World Health Organization ranks hypertension the leading global risk factor for disease, specifically, cardiovascular disease. Blood pressure (BP) is higher in Westernized populations consuming Na+-rich processed foods than in isolated societies consuming K+-rich natural foods. Evidence suggests that lowering dietary Na+ is particularly beneficial in hypertensive individuals who consume a high-Na+ diet. Nonetheless, numerous population studies demonstrate a relationship between higher dietary K+, estimated from urinary excretion or dietary recall, and lower BP, regardless of Na+ intake. Interventional studies with K+ supplementation suggest that it provides a direct benefit; K+ may also be a marker for other beneficial components of a "natural" diet. Recent studies in rodent models indicate mechanisms for the K+ benefit: the distal tubule Na+-Cl- cotransporter (NCC) controls Na+ delivery downstream to the collecting duct, where Na+ reabsorbed by epithelial Na+ channels drives K+ secretion and excretion through K+ channels in the same region. High dietary K+ provokes a decrease in NCC activity to drive more K+ secretion (and Na+ excretion, analogous to the actions of a thiazide diuretic) whether Na+ intake is high or low; low dietary K+ provokes an increase in NCC activity and Na+ retention, also independent of dietary Na+ Together, the findings suggest that public health efforts directed toward increasing consumption of K+-rich natural foods would reduce BP and, thus, cardiovascular and kidney disease.
Keywords: ENaC; NCC; dietary potassium; dietary sodium; hypertension.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

