Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyponatremia: Compilation of the Guidelines
- PMID: 28174217
- PMCID: PMC5407738
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2016101139
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyponatremia: Compilation of the Guidelines
Abstract
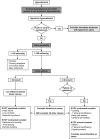
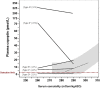
Hyponatremia is a common water balance disorder that often poses a diagnostic or therapeutic challenge. Therefore, guidelines were developed by professional organizations, one from within the United States (2013) and one from within Europe (2014). This review discusses the diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia, comparing the two guidelines and highlighting recent developments. Diagnostically, the initial step is to differentiate hypotonic from nonhypotonic hyponatremia. Hypotonic hyponatremia is further differentiated on the basis of urine osmolality, urine sodium level, and volume status. Recently identified parameters, including fractional uric acid excretion and plasma copeptin concentration, may further improve the diagnostic approach. The treatment for hyponatremia is chosen on the basis of duration and symptoms. For acute or severely symptomatic hyponatremia, both guidelines adopted the approach of giving a bolus of hypertonic saline. Although fluid restriction remains the first-line treatment for most forms of chronic hyponatremia, therapy to increase renal free water excretion is often necessary. Vasopressin receptor antagonists, urea, and loop diuretics serve this purpose, but received different recommendations in the two guidelines. Such discrepancies may relate to different interpretations of the limited evidence or differences in guideline methodology. Nevertheless, the development of guidelines has been important in advancing this evolving field.
Keywords: cerebral edema; copeptin; osmotic demyelination syndrome; urea; vasopressin; vasopressin receptor antagonist.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Adrogué HJ, Madias NE: The challenge of hyponatremia. J Am Soc Nephrol 23: 1140–1148, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Sterns RH: Disorders of plasma sodium--causes, consequences, and correction. N Engl J Med 372: 55–65, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Winzeler B, Jeanloz N, Nigro N, Suter-Widmer I, Schuetz P, Arici B, Bally M, Blum C, Bock A, Huber A, Mueller B, Christ-Crain M: Long-term outcome of profound hyponatremia: A prospective 12 months follow-up study. Eur J Endocrinol 175: 499–507, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

