Activation of the DLPFC Reveals an Asymmetric Effect in Risky Decision Making: Evidence from a tDCS Study
- PMID: 28174549
- PMCID: PMC5258744
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00038
Activation of the DLPFC Reveals an Asymmetric Effect in Risky Decision Making: Evidence from a tDCS Study
Abstract
The phenomenon of loss aversion (the tendency for losses to have a greater impact than comparable gains) has long been observed in daily life. Neurocognitive studies and brain imaging studies have shed light on the correlation between the phenomenon of loss aversion and the brain region of the prefrontal cortex. Recent brain stimulation studies using bilateral transcranial magnetic stimulation or transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) have obtained various results showing the causal relationship between brain regions and decision making. With the goal of studying whether unilateral stimulation can change participants' risky decision making in the frames of gains and losses, we applied different polarities of tDCS over the regions of the right or left prefrontal cortex. We also designed a risk measurement table (Multiple Price List) to reflect the participants' attitudes toward risky decision making via the crossover point including the frames of gains and losses. The results of our experiment indicated that the participants tended to be more risk averse in the gain frame after receiving left anodal tDCS and more risk seeking in the loss frame after receiving right cathodal tDCS, which was consistent with the hypothesis that the process of risky decision making was correlated with the interaction of multiple systems in the brain. Our conclusion revealed an asymmetric effect of right/left DLPFC when the participants faced gains and losses, which partially provided the neural evidence and a feasible paradigm to help better understand risky decision making and loss aversion. The current study can not only expand the traditional understanding of the behavioral preferences of humans in economics but also accommodate empirical observations of behavioral economists on the preferences of humans.
Keywords: asymmetric effect; dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; loss aversion; risk preference; transcranial direct current stimulation.
Figures
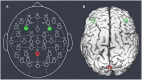
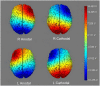

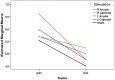
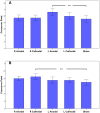
Similar articles
-
Modulating activity in the prefrontal cortex changes decision-making for risky gains and losses: a transcranial direct current stimulation study.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Jun 1;286:17-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.02.037. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25721740
-
Activation of prefrontal cortex by transcranial direct current stimulation reduces appetite for risk during ambiguous decision making.J Neurosci. 2007 Jun 6;27(23):6212-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0314-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17553993 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Modulating the activity of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex by tDCS alters distributive decisions behind the veil of ignorance via risk preference.Behav Brain Res. 2017 Jun 15;328:70-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.03.045. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Behav Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28389339
-
Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS).Clin Neurophysiol. 2017 Jan;128(1):56-92. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2016.10.087. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 27866120 Review.
-
Neural Activation in Risky Decision-Making Tasks in Healthy Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis of fMRI Data.Brain Sci. 2021 Aug 6;11(8):1043. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11081043. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34439662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
When brain stimulation backfires: the effects of prefrontal cortex stimulation on impulsivity.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2022 Feb 3;17(1):101-108. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa049. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 32342101 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Neurobase of ambiguity loss aversion about decision making.Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 26;14:1055640. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1055640. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36777223 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Transcranial Electrical Stimulation on Gambling and Gaming: A Systematic Review of Studies on Healthy Controls, Participants with Gambling/Gaming Disorder, and Substance Use Disorder.J Clin Med. 2023 May 11;12(10):3407. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103407. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37240512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex plays causal role in probability weighting during risky choice.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 27;12(1):16115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18529-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36167703 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of Cerebral Hemodynamics and Network Properties Induced by Newsvendor Problem in the Human Prefrontal Cortex.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Jan 15;14:598502. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.598502. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33519401 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

