Painting a new picture of personalised medicine for diabetes
- PMID: 28175964
- PMCID: PMC6518376
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4210-x
Painting a new picture of personalised medicine for diabetes
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Painting a new picture of personalised medicine for diabetes.Diabetologia. 2017 May;60(5):940. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4234-2. Diabetologia. 2017. PMID: 28243793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
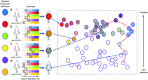
The current focus on delivery of personalised (or precision) medicine reflects the expectation that developments in genomics, imaging and other domains will extend our diagnostic and prognostic capabilities, and enable more effective targeting of current and future preventative and therapeutic options. The clinical benefits of this approach are already being realised in rare diseases and cancer but the impact on management of complex diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, remains limited. This may reflect reliance on inappropriate models of disease architecture, based around rare, high-impact genetic and environmental exposures that are poorly suited to our emerging understanding of type 2 diabetes. This review proposes an alternative 'palette' model, centred on a molecular taxonomy that focuses on positioning an individual with respect to the major pathophysiological processes that contribute to diabetes risk and progression. This model anticipates that many individuals with diabetes will have multiple parallel defects that affect several of these processes. One corollary of this model is that research efforts should, at least initially, be targeted towards identifying and characterising individuals whose adverse metabolic trajectory is dominated by perturbation in a restricted set of processes.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Complex disease; Diabetes; Environment; Genetics; Pathogenesis; Review; Risk; Taxonomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Duality of interests
MMcC serves on advisory panels for Pfizer and NovoNordisk; has received honoraria from Pfizer, NovoNordisk and Eli Lilly; and has received research funding from Pfizer, Eli Lilly, NovoNordisk, Sanofi-Aventis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Astra Zeneca, Janssen, Takeda, Roche, Merck, Abbvie and Servier as part of precompetitive research initiatives supported by the Innovative Medicines Initiative and the Accelerating Medicines Partnership.
Contribution statement
MMcC was the sole contributor to this paper.
Figures
References
-
- International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (2010) http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en. Accessed 10 Nov 2016
-
- Frank LL. Diabetes mellitus in the texts of old Hindu medicine (Charaka, Susruta, Vagbhata) Am J Gastroenterol. 1957;27:76–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

