Genotoxic Effects of Culture Media on Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 28176872
- PMCID: PMC5297241
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42222
Genotoxic Effects of Culture Media on Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
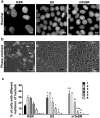
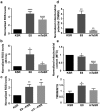
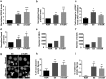
Culture conditions play an important role in regulating the genomic integrity of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells (HPSCs). We report that HPSCs cultured in Essential 8 (E8) and mTeSR, two widely used media for feeder-free culturing of HPSCs, had many fold higher levels of ROS and higher mitochondrial potential than cells cultured in Knockout Serum Replacement containing media (KSR). HPSCs also exhibited increased levels of 8-hydroxyguanosine, phospho-histone-H2a.X and p53, as well as increased sensitivity to γ-irradiation in these two media. HPSCs in E8 and mTeSR had increased incidence of changes in their DNA sequence, indicating genotoxic stress, in addition to changes in nucleolar morphology and number. Addition of antioxidants to E8 and mTeSR provided only partial rescue. Our results suggest that it is essential to determine cellular ROS levels in addition to currently used criteria i.e. pluripotency markers, differentiation into all three germ layers and normal karyotype through multiple passages, in designing culture media.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Cho Y. M. et al. Dynamic changes in mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant enzymes during the spontaneous differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 348, 1472–8 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Saretzki G. et al. Downregulation of multiple stress defense mechanisms during differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 26, 455–64 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Armstrong L. et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell lines show stress defense mechanisms and mitochondrial regulation similar to those of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 28, 661–73 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

