Ligand fitting with CCP4
- PMID: 28177312
- PMCID: PMC5297919
- DOI: 10.1107/S2059798316020143
Ligand fitting with CCP4
Abstract
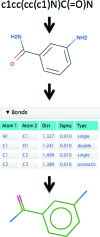
Crystal structures of protein-ligand complexes are often used to infer biology and inform structure-based drug discovery. Hence, it is important to build accurate, reliable models of ligands that give confidence in the interpretation of the respective protein-ligand complex. This paper discusses key stages in the ligand-fitting process, including ligand binding-site identification, ligand description and conformer generation, ligand fitting, refinement and subsequent validation. The CCP4 suite contains a number of software tools that facilitate this task: AceDRG for the creation of ligand descriptions and conformers, Lidia and JLigand for two-dimensional and three-dimensional ligand editing and visual analysis, Coot for density interpretation, ligand fitting, analysis and validation, and REFMAC5 for macromolecular refinement. In addition to recent advancements in automatic carbohydrate building in Coot (LO/Carb) and ligand-validation tools (FLEV), the release of the CCP4i2 GUI provides an integrated solution that streamlines the ligand-fitting workflow, seamlessly passing results from one program to the next. The ligand-fitting process is illustrated using instructive practical examples, including problematic cases such as post-translational modifications, highlighting the need for careful analysis and rigorous validation.
Keywords: CCP4; Coot; ligand fitting; model building.
Figures
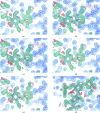
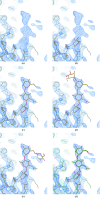
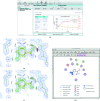
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

